CRC Calculation Circuit
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 263 of 360
2.8 CRC Calculation Circuit
2.8.1 Overview
The Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) calculation circuit is used to detect errors in data blocks. The
calculation method compares CRC code formed from transmission data by use of a polynomial
generator with CRC check data to detect errors in transmission data. Using the CRC calculation circuit
allows generation of CRC code. A polynomial counter is used for the polynomial generation of
CRC_CCITT (X
16
+ X
12
+ X
5
+ 1).
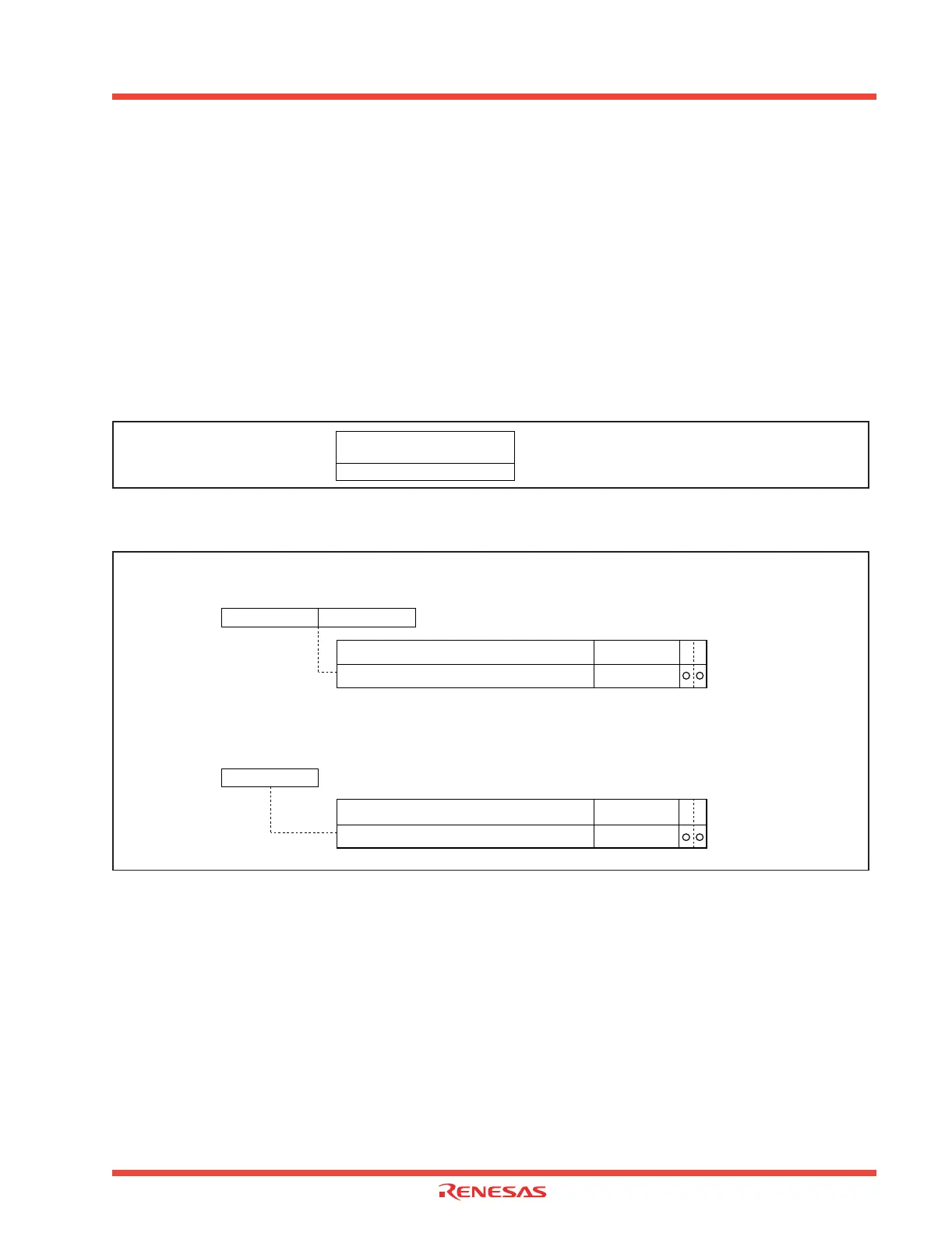
2.8.1.1 CRC calculation circuit-related registers
Figure 2.107 shows the memory map of CRC-related registers, and Figure 2.108 shows CRC-related
registers.
Figure 2.107: Memory map of CRC-related registers
Figure 2.108: CRC-related registers
2.8.2 Operation
The following describes the operation of CRC calculation. Figure 2.109 shows an example of the CRC
calculation circuit using data 0123
16
.
(1) The CRC calculation circuit sets an initial value in the CRC data register.
(2) Writing 1 byte of data to the CRC input register generates CRC code based on the data register.
CRC code generation for 1 byte of data finishes in two machine cycles.
(3) The CRC calculation circuit detects an error by means of comparing the CRC-checking data with
the content of the CRC data register, after the next byte of data is written to the CRC input register.
(4) The content of the CRC data register becomes the CRC code after all data is written.
03BC16
03BD16
03BE16
CRC data register (CRCD)
CRC input register (CRCIN)
Symbol
Address
When reset
CRCD
03BD
16
, 03BC
16
Indeterminate
b7 b0 b7 b0
(b15) (b8)
CRC data register
WR
CRC calculation result output register
Function
Values that
can be set
0000
16
to FFFF
16
Symbo
Address
When reset
CRCIN
03BE16
Indeterminate
b7 b0
CRC input register
WR
Data input register
Function
Values that
can be set
00
16
to FF
16

 Loading...
Loading...











