© 2008 Siemens Energy & Automation, Inc. All Rights Reserved
PMCM-9340D-0208 ACCESS 9340 and 9360 Meters
2/2008 Appendix B—Using the Command Interface
EN–205
Issuing Commands
To issue commands using the command interface, follow these
general steps:
1. Write the related parameter(s) to the command parameter
registers 8001–15.
2. Write the command code to command interface register 8000.
If no parameters are associated with the command, then you need
only to write the command code to register 8000. Table B–2 lists the
command codes that can be written to the command interface into
register 8000. Some commands have an associated registers where
you write parameters for that command. For example, when you write
the parameter 9999 to register 8001 and issue command code 3351,
all relays will be energized if they are set up for external control.
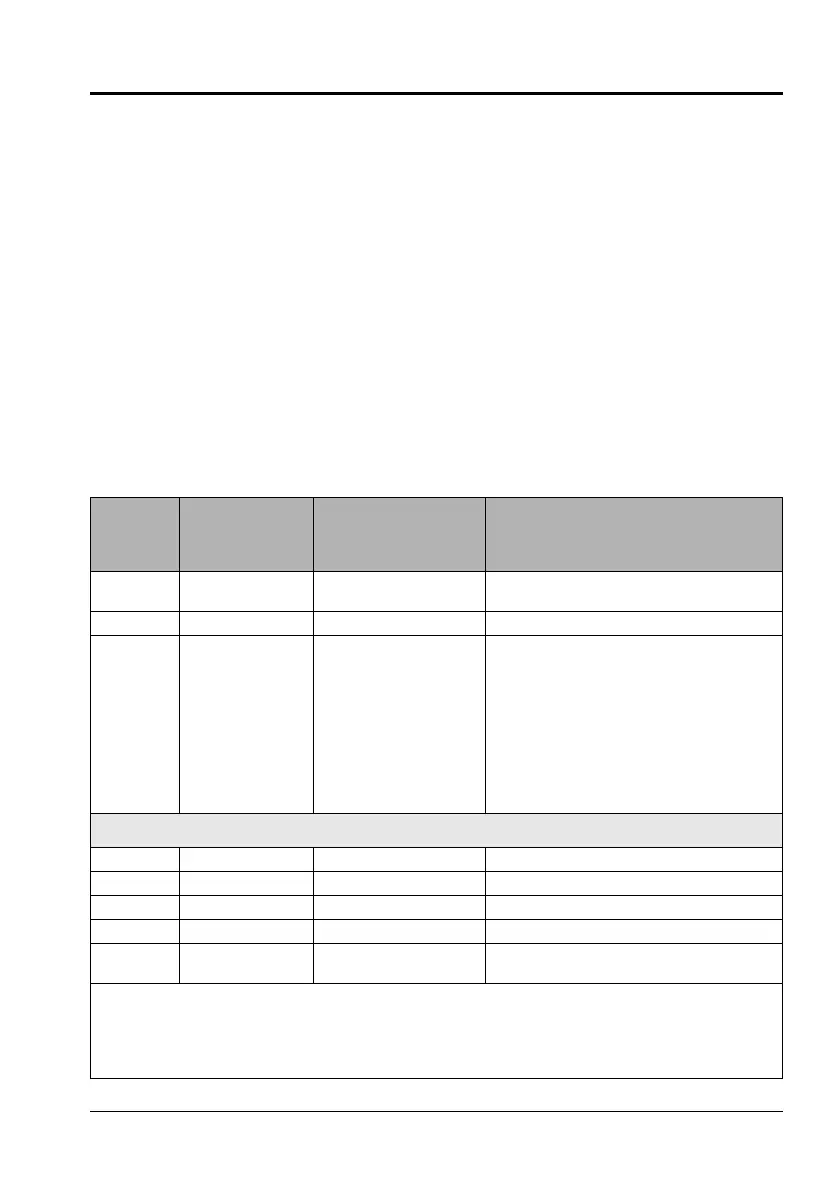
Table B–2: Command Codes
Command
Code
Command
Parameter
Register
Parameters Description
1110 None None
Causes soft reset of the unit (re-initializes the
meter).
1210 None None Clears the communications counters.
1310
8001
8002
8003
8004
8005
8006
Month
Day
Year
Hour
Minute
Second
Sets the system date and time. Values for the
registers are:
Month (1–12)
Day (1–31)
Year (4-digit, for example 2000)
Hour (Military time, for example 14 = 2:00pm)
Minute (1–59)
Second (1–59)
Relay Outputs
3310 8001 Relay Output Number ➀ Configures relay for external control.
3311 8001 Relay Output Number
➀ Configures relay for internal control.
3320 8001 Relay Output Number
➀ De-energizes designated relay.
3321 8001 Relay Output Number
➀ Energizes designated relay.
3330 8001 Relay Output Number
➀
Releases specified relay from latched
condition.
➀You must write to register 8001 the number that identifies which output you would like to use.
To determine the identifying number, refer to“I/O Point Numbers” on page 209 for instructions.
➁Data buffer location (register 8019) is the pointer to the first register where data will be stored. By default,
return data begins at register 8020, although you can use any of the registers from 8020–8149. Take care when
assigning pointers. Values may be corrupted if two commands are using the same register.

 Loading...
Loading...











