Basics of program processing
13.1 Events and OBs
S7-1500 Automation System
148 System Manual, 01/2013, A5E03461182-01
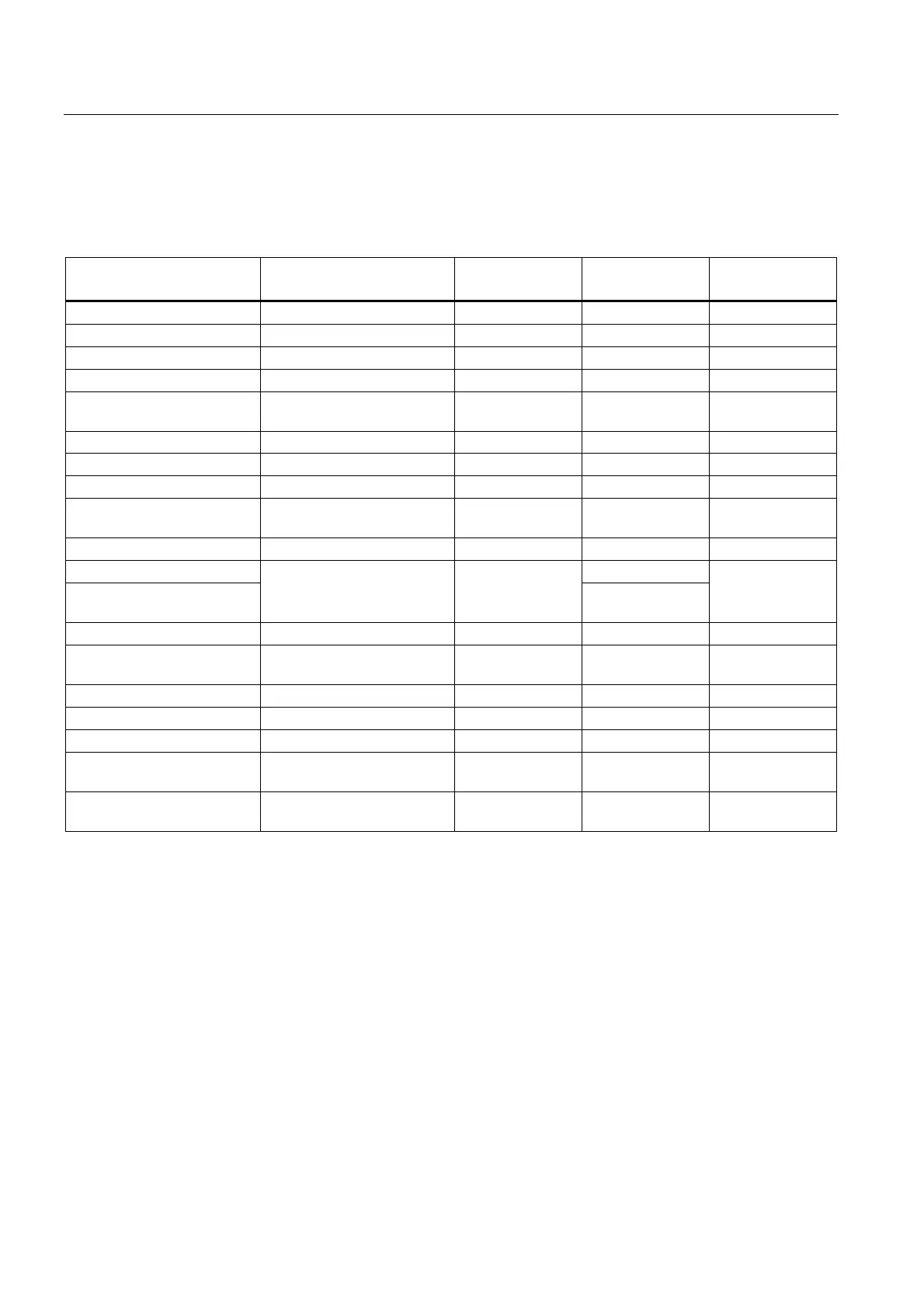
The following table provides an overview of the OB start events, including the possible
values for OB priority, possible OB numbers, default system reaction and number of OBs.
The table is sorted in ascending order by OB numbers.
Types of event sources Possible priorities
(default priority)
Possible OB
numbers
Default system
reaction
Number of OBs
Startup* 1 100, ≥ 123 Ignore 0 to 100
Cyclic program* 1 1, ≥ 123 Ignore 0 to 100
Time-of-day interrupt* 2 to 24 (2) 10 to 17, ≥ 123 not applicable 0 to 20
time-delay interrupt* 2 to 24 (3) 20 to 23, ≥ 123 not applicable 0 to 20
Cyclic interrupt* 2 to 24 (8 to 17, frequency
dependent)
30 to 38, ≥ 123 not applicable 0 to 20
Hardware interrupt* 2 to 26 (18) 40 to 47, ≥ 123 Ignore 0 to 50
Status interrupt 2 to 24 (4) 55 Ignore 0 or 1
Update interrupt 2 to 24 (4) 56 Ignore 0 or 1
Manufacturer-specific or
profile-specific interrupt
2 to 24 (4) 57 Ignore 0 or 1
Isochronous mode interrupt 16 to 26 (21) 61 to 64, ≥ 123 Ignore 0 to 2
Time error Ignore
Maximum cycle time
exceeded once
22 80
STOP
0 or 1
Diagnostic error interrupt 2 to 26 (5) 82 Ignore 0 or 1
Removal/insertion of
modules
2 to 26 (6) 83 Ignore 0 or 1
Rack error 2 to 26 (6) 86 Ignore 0 or 1
MC servo interrupt 17 to 26 (25) 91 not applicable 0 or 1
MC interpolator interrupt 16 to 26 (24) 92 not applicable 0 or 1
Programming error (only for
global error handling)
2 to 26 (7) 121 STOP 0 or 1
I/O access error (only for
global error handling)
2 to 26 (7) 122 Ignore 0 or 1
* To these event sources, besides the permanently assigned OB numbers (see column: possible OB numbers), you can
also assign OB numbers from the range ≥ 123 via the TIA Portal.

 Loading...
Loading...











