114
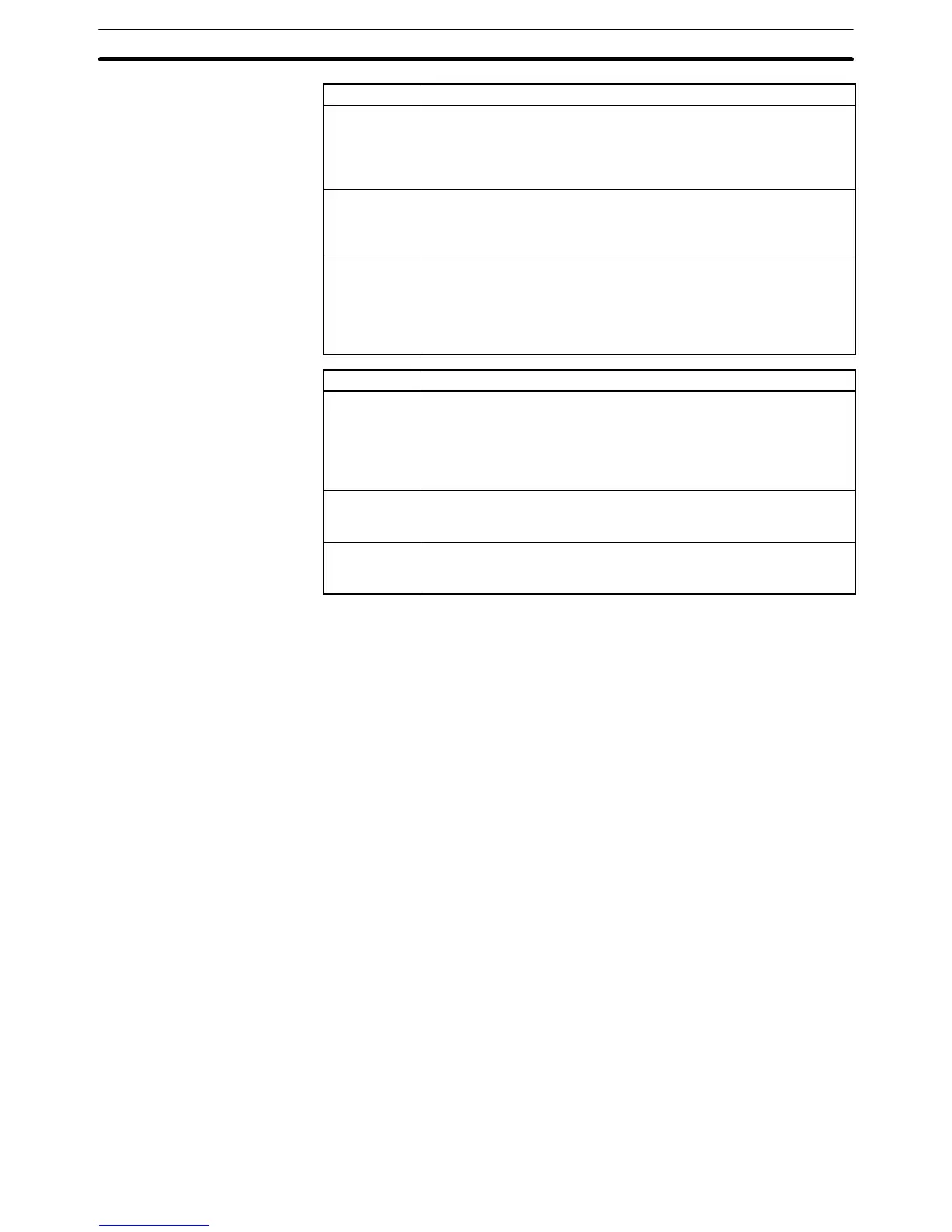
Message Meaning and appropriate response
IL-ILC ERR IL(02) and ILC(03) are not used in pairs. Correct the program so
that each IL(02) has a unique ILC(03). Although this error message
will appear if more than one IL(02) is used with the same ILC(03),
the program will executed as written. Make sure your program is
written as desired before proceeding.
JMP-JME
ERR
JMP(04) 00 and JME(05) 00 are not used in pairs. Although this
error message will appear if more than one JMP(04) 00 is used with
the same JME(05) 00, the program will be executed as written.
Make sure your program is written as desired before proceeding.
SBN-RET
ERR
If the displayed address is that of SBN(92), two different
subroutines have been defined with the same subroutine number.
Change one of the subroutine numbers or delete one of the
subroutines. If the displayed address is that of RET(93), RET(93)
has not been used properly. Check requirements for RET(93) and
correct the program.
Message Meaning and appropriate response
COIL DUPL The same bit is being controlled (i.e., turned ON and/or OFF) by
more than one instruction (e.g., OUT, OUT NOT, DIFU(13),
DIFD(14), KEEP(11), SFT(10)). Although this is allowed for certain
instructions, check instruction requirements to confirm that the
program is correct or rewrite the program so that each bit is
controlled by only one instruction.
JMP
UNDEFD
JME(05) has been used with no JMP(04) with the same jump
number. Add a JMP(04) with the same number or delete the
JME(05) that is not being used.
SBS
UNDEFD
A subroutine exists that is not called by SBS(91). Program a
subroutine call in the proper place, or delete the subroutine if it is
not required.
4-4 User-defined Errors
There are three instructions that the user can use to define his own errors or
messages. These instructions are used to send messages to the Programming
Console connected to the PC, cause a non-fatal or a fatal error.
FAILURE ALARM - FAL(06) FAL(06) is an instruction that causes a non-fatal error. The following will occur
when an FAL(06) instruction is executed:
1, 2, 3...
1. The ERR/ALM indicator on the CPU Unit will flash. PC operation will con-
tinue.
2. The instruction’s 2-digit BCD FAL number (01 to 99) will be written to
SR 25300 to SR 25307.
3. The FAL number and time of occurrence will be recorded in the PC’s error
log area if a Memory Cassette with a clock (RTC) is used.
The FAL numbers can be set arbitrarily to indicate particular conditions. The
same number cannot be used as both an FAL number and an FALS number.
To clear an FAL error, correct the cause of the error, execute FAL 00, and then
clear the error using the Programming Console.
FALS(07) is an instruction that causes a fatal error. The following will occur when
an FALS(07) instruction is executed:
1, 2, 3...
1. Program execution will be stopped and outputs will be turned OFF.
2. The ERR/ALM indicator on the CPU Unit will be lit.
3. The instruction’s 2-digit BCD FALS number (01 to 99) will be written to
SR 25300 to SR 25307.
4. The FALS number and time of occurrence will be recorded in the PC’s error
log area if a Memory Cassette with a clock (RTC) is used.
Level B Errors
Level C Errors
SEVERE FAILURE ALARM -
FALS(07)
User-defined Errors
Section 4-4
 Loading...
Loading...