Inferential Statistics and Distributions 13–7
8250FC~1.DOC TI-83 international English Bob Fedorisko Revised: 10/26/05 1:39 PM Printed: 10/27/05 2:57
PM Page 7 of 36
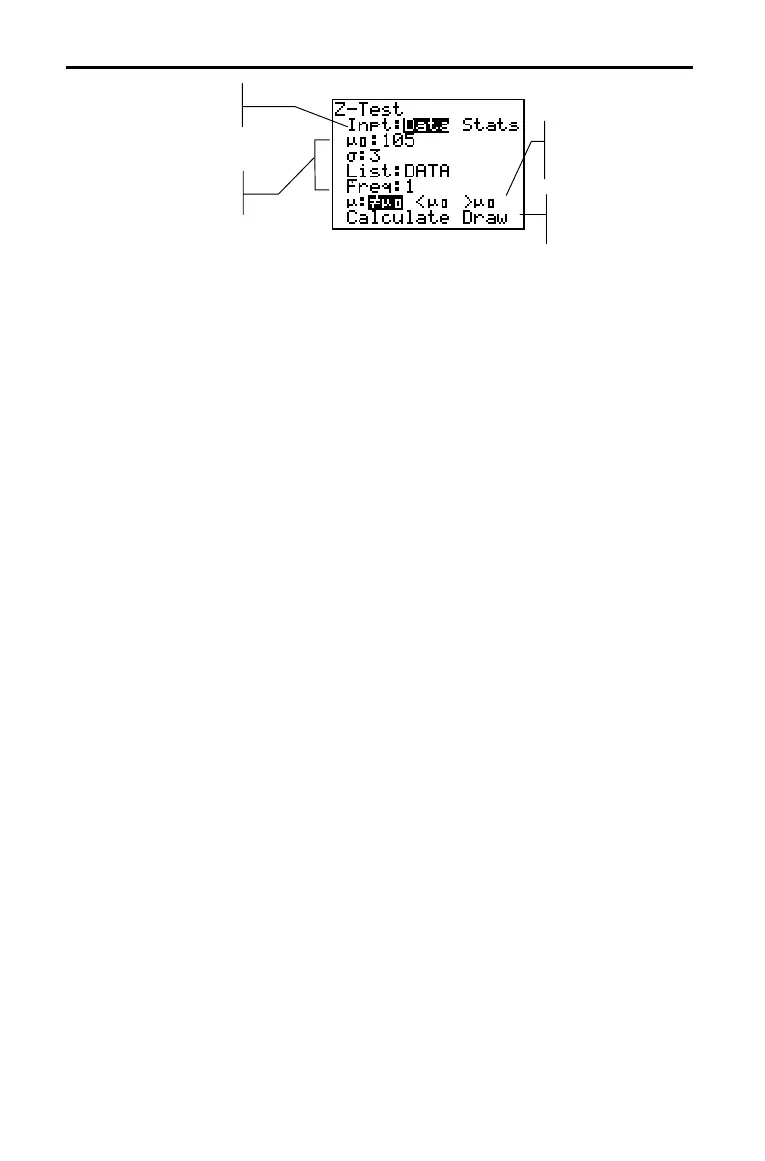
Most inferential stat editors prompt you to select one of two
types of input. (
1.PropZInt and 2.PropZTest, 1.PropZInt and
2.PropZInt, c
2
.Test, and LinRegTTest do not.)
• Select
Data to enter the data lists as input.
• Select
Stats to enter summary statistics, such as þ
þþ
þ, Sx, and
n, as input.
To select Data or Stats, move the cursor to either Data or Stats,
and then press Í.
Inferential stat editors require a value for every argument. If you
do not know what a particular argument symbol represents, see
the tables on pages 13.26 and 13.27.
When you enter values in any inferential stat editor, the
TI-82 STATS stores them in memory so that you can run many
tests or intervals without having to reenter every value.
Most of the inferential stat editors for the hypothesis tests
prompt you to select one of three alternative hypotheses.
• The first is a
ƒ alternative hypothesis, such as mƒm0 for the
Z.Test.
• The second is a
< alternative hypothesis, such as m1<m2 for
the 2.SampTTest.
• The third is a
> alternative hypothesis, such as p1>p2 for the
2.PropZTest.
To select an alternative hypothesis, move the cursor to the
appropriate alternative, and then press Í.
Selecting Data or
Stats
Entering the
Values for
Arguments
Selecting an
Alternative
Hypothesis
(ƒ < >)
Enter values for
arguments
Select an alternative
hypothesis
Select Calculate
or Draw output
Select Data or
Stats input

 Loading...
Loading...











