TSAT 3000 - Telemetry and data transfer via SATellite
TSAT 3000 Configuration Parameter Description, January 2013 Page 11 of 124
1. SCOPE
This document describes the configuration parameters in the .SAT file used to store CCU
configuration. The purpose, and legal values, of each parameter is described.
2. GENERAL
Unless otherwise stated, all MIB parameters described here are present in the TSAT 3000 CCU
software versions C30.0.0 to C31.9.0. Generally, unless otherwise stated by some of the qualifiers
below, all MIB parameters may be read and written, all MIB parameters will survive a RESTART of
the CCU, and all CURRENT MIB parameters may be changed while the CCU is running (change will
take effect immediately). The exception qualifiers are:
BOOT:
You cannot change the CURRENT value. Operator has to change the CACHE value,
flush CACHE to FILE and RESET the CCU to activate the new configuration.
Read-Only:
No CACHE or DEFAULT value. You can only read the CURRENT value.
Volatile:
No CASHE value. You can both read and write CURRENT value, but it will not
survive a RESTART of the CCU.
No-Current:
Some of the MIB parameters (i.e. the Backup Frequency parameters) don’t have
CURRENT values.
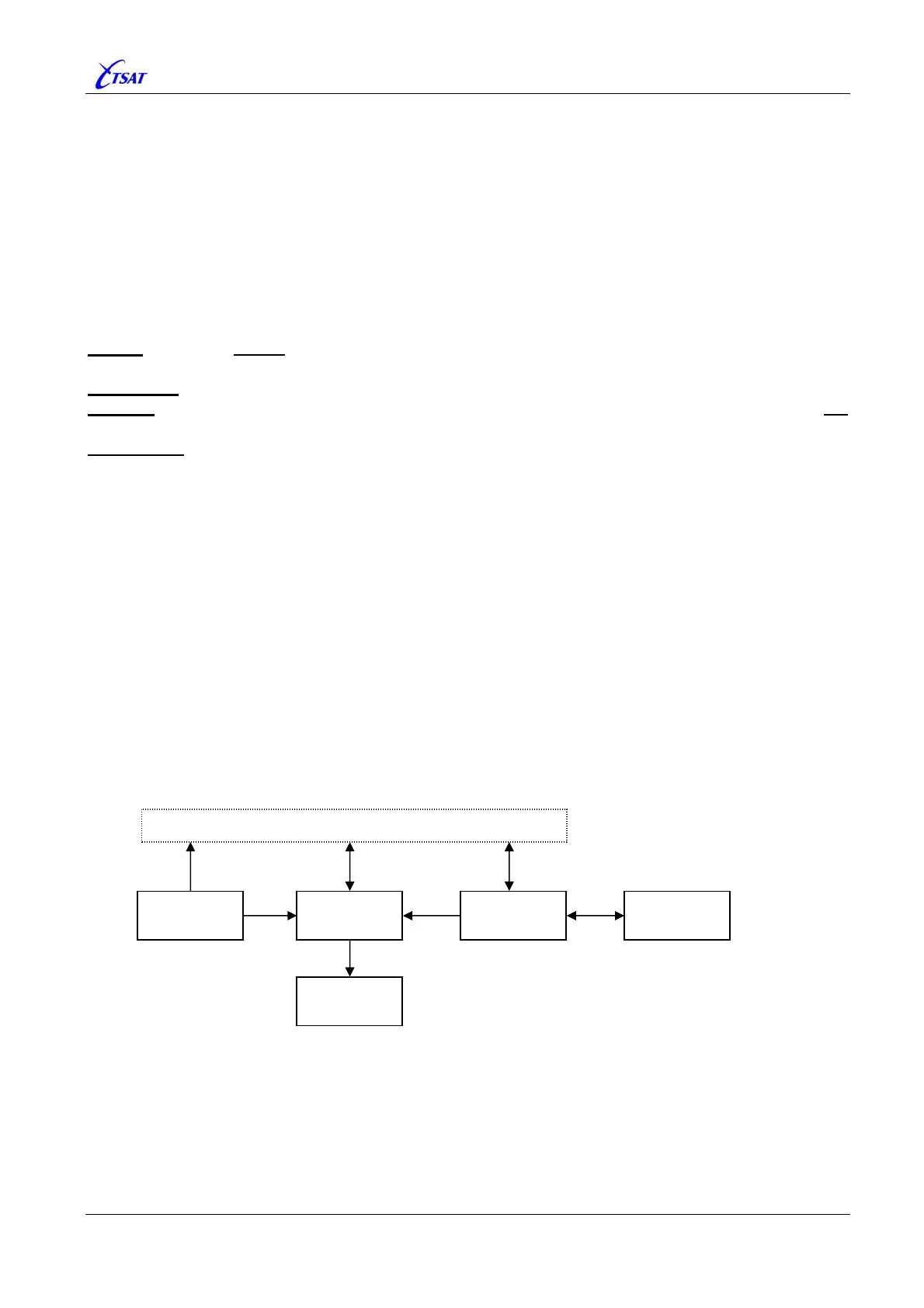
Within the CCU, each MIB variable may have up to 5 different values:
• DEFAULT is a table with default values stored in PROM.
• FILE is a table of MIB variables that will survive a restart of the CCU, and stored in the .SAT
configuration file. MIB variables that doesn’t have an FILE value will not survive a CCU reset,
and are also called ‘Volatile’ variables.
• CACHE is a RAM copy of the FILE table. It is initialised from the FILE values during start-up of
the CCU, and it will be copied back to the FILE when the operator is doing a SAVE (also called
FLUSH) operation.
• CURRENT is the table with values that is actually used. It is initialised from DEFAULT
immediately after CCU reset, and when the variables has been successfully copied from FILE to
CACHE, it will be initialised from CACHE (replace the DEFAULT configuration).
• LOCAL is local copies (or transformations) of the CURRENT variables that may be used within
some of the software modules. MIB variables that have a LOCAL value are also called ‘BOOT’
variables. I.e: The operator must change the CACHE value, flush the CACHE to FILE and
RESET the CCU to activate the new configuration.
From the ‘Management Information Base’ and ‘CCU Configuration’ windows in the Supervisory
Terminal the operator may select to:
• READ the DEFAULT, CURRENT or CACHE variables. The LOCAL values cannot be read.
• WRITE the variable to CURRENT or CACHE. The DEFAULT or LOCAL values cannot be written.
• SAVE the content of CACHE to FILE (also called FLUSH).
FILE
CACHE
CURRENT
LOCAL
Supervisory Terminal
DEFAULT
 Loading...
Loading...