1125100 WPC 1000 User Manual
2-30 Installation
board (see Figure 2-11, page 2-20). Wiring connections are shown in Table 2-4 and in Figure
4 at the end of the manual.
Wiring the Auxiliary Output
WPC 1000 provides an output called Auxiliary 1 (pin #14 on the WPC 1000 Control board).
Auxiliary 1 is normally closed (N/C), or On. The output opens, or turns Off, when a fault
condition occurs, an E-stop string opens, or a light curtain is interrupted while the press is
running. The output can also be programmed to turn Off during an Interrupted Stroke (see
page 4-3 for an explanation of Interrupted Stroke).
Auxiliary Output 1 can be wired to a customer-supplied control relay and used to stop
auxiliary equipment such as scrap choppers, conveyors, etc. when one of the conditions
described above causes the press to stop. When a warning beacon is connected to the control
relay, the beacon illuminates when a fault occurs and Aux. Output 1 opens.
Wiring, state changes, and change conditions for Auxiliary Output 1 are provided in
Table 2-5. Wiring connections are also shown in Table 2-16, page 2-69 and in Figure 2 at the
back of the manual.
Aux. Output 1 response to an Interrupted Stroke is controlled by option switch 8 on the WPC
1000 Control board. Switch settings are shown in Table 2-6, page 2-31.
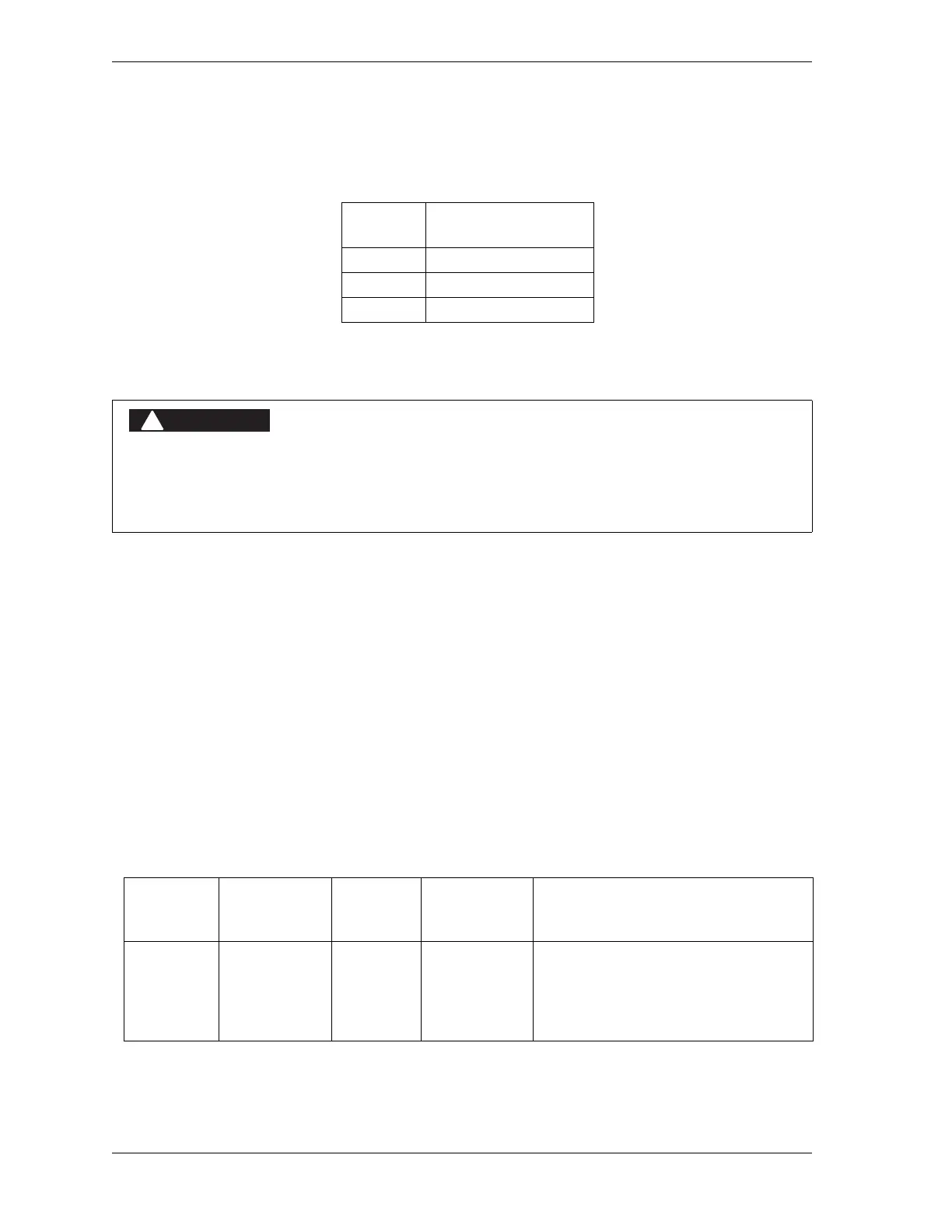
Table 2-4. Lockout Relay Wiring Connections (DSV/Lockout Relay Board)
TB301
Pin #
Signal
58 Lockout relay input
59 Lockout relay output
60 Lockout relay output
NON-SAFETY OUTPUT USED FOR SAFETY FUNCTIONS
Use Auxiliary Output 1 for a non-safety function only, such as convenience in automation. Aux. 1
cannot protect personnel from a moving hazard.
Failure to comply with these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
Table 2-5. Auxiliary Output 1 Wiring Connection and Change Conditions
Output Pin #
(WPC 1000
Cntrl Bd.)
Normal
State
Change
State
Change Conditions
Auxiliary 1 14 On (N/C) Off (or Open) • WPC 1000 fault
• E-stop string open
• Light curtain interruption
• Interrupted Stroke (controlled by
option switch 8–see Table 2-6)

 Loading...
Loading...