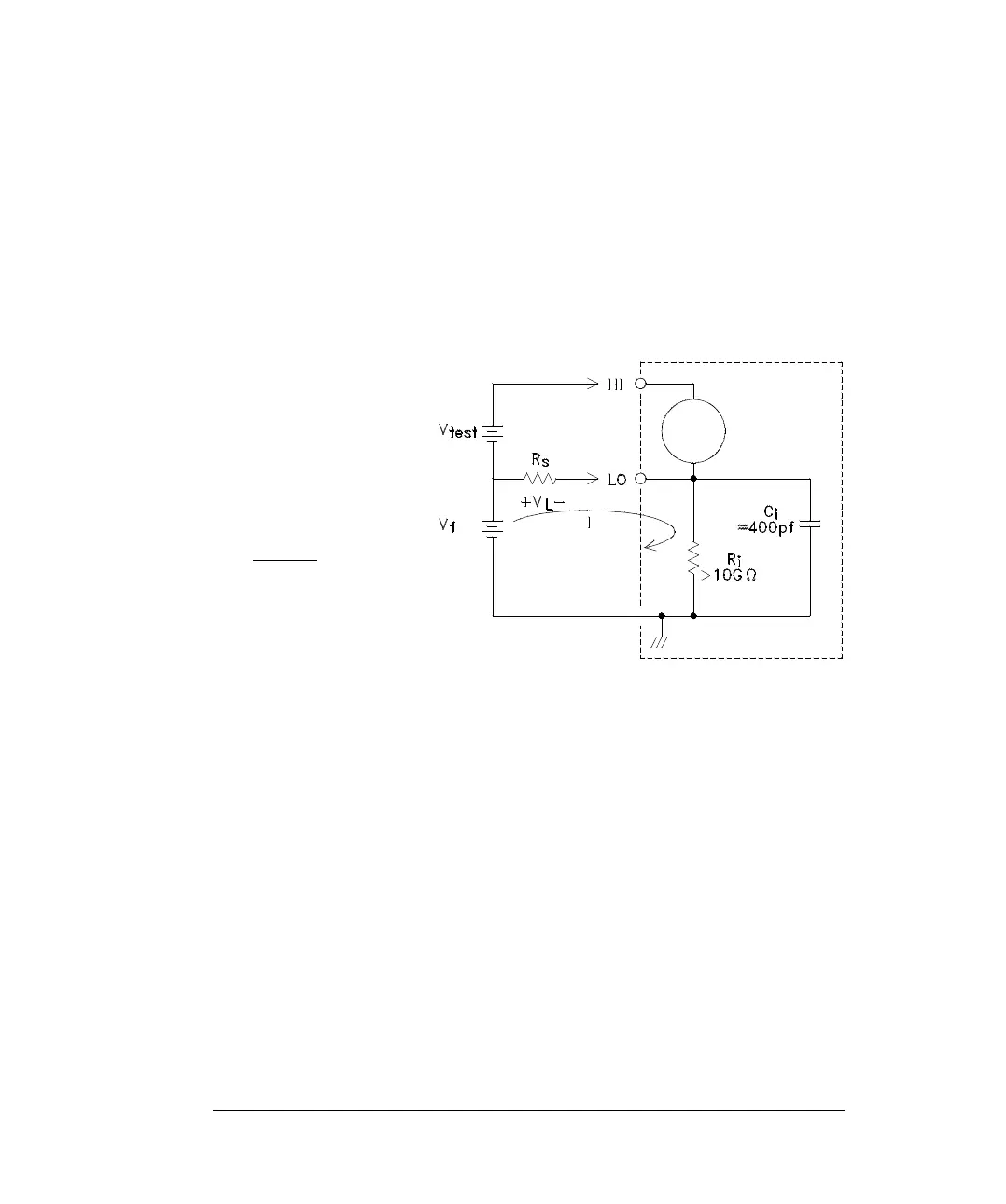
Common Mode Rejection (CMR)
Ideally, a meter is completely isolated from earth-referenced circuits.
However, there is finite resistance and capacitance between the meter’s
input LO terminal and earth ground. If the input terminals are both
driven by an earth referenced signal, V
f
, then a current will flow through
R
S
and create a voltage drop V
L
as shown below.
Any resulting voltage, V
L
, will appear as an input to the meter. As the
value of R
S
approaches 0, so does the error. Additionally, if V
f
is at the
power line frequency (50 Hz or 60 Hz), the noise can be greatly reduced
by setting the meter’s integration time (NPLC) to 1 or greater.
See page 252.
V
f
=
Common
Mode
Float
voltage
R
S
=
LO
Lead
Resistance
R
i
=
Meter
Isolation
Resistance
C
i
=
Meter
Isolation
Capacitance
Z
i
=
Parallel
Impedance
of
R
i
+
C
i
Error
(
V
L
)
=
V
f
x
R
S
R
S
+
Z
Ideal
Meter
Chapter 7 Measurement Tutorial
Measurement Techniques and Sources of Error
254

 Loading...
Loading...











