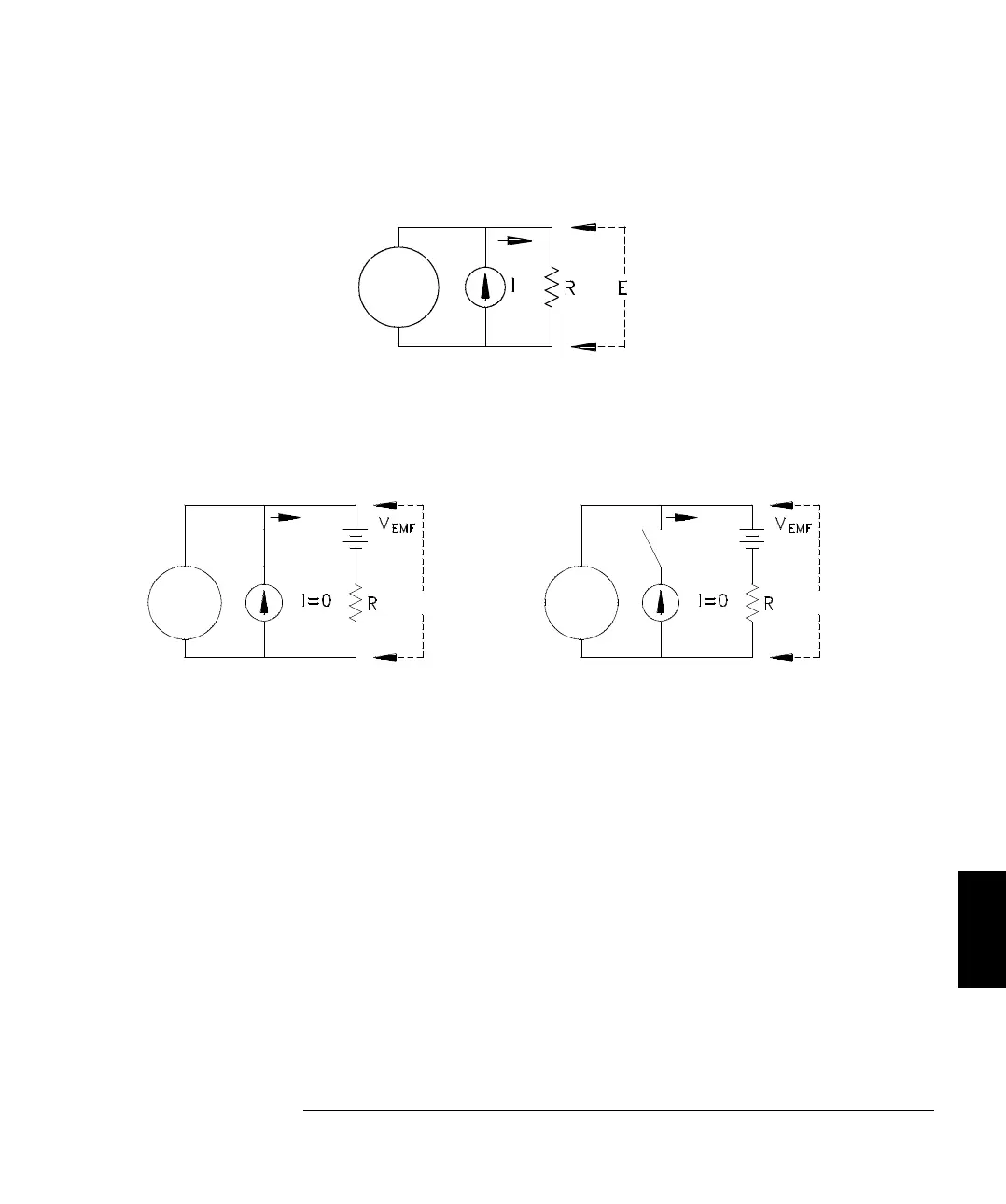
Offset Compensation
A resistance measurement involves measuring a voltage (E) induced
across the resistance by a known current source.
Thermal EMF caused by dissimilar metals can create a parasitic voltage
in the measurement circuit (V
EMF
). (See page 251 for a description of
thermal EMF). The thermal EMF can be caused by the input lead
connections or internally in resistor R. In general, this voltage will not
change with the current applied to the resistor.
The voltage measured, and so the resistance calculated, is in error by
V
EMF
. Using offset compensation can reduce the errors caused by V
EMF
.
To make an offset compensated measurement, the meter makes two
voltage measurements, one with the current source on and one with the
current source off, and subtracts the two measurements. The actual voltage
drop across the resistor, and the calculated resistance are obtained by:
First Reading − Second Reading = ( I ∗ R + V
EMF
) − V
EMF
= I ∗ R
Offset compensation can be used in 2-Wire or 4-Wire ohms measurements.
Ideal
Meter
Ideal
Meter
Ideal
Meter
E=IR+V
EMF
E=(0*R)+V
EMF
= V
EMF
7
Chapter 7 Measurement Tutorial
Measurement Techniques and Sources of Error
259

 Loading...
Loading...











