4. Configuration
99
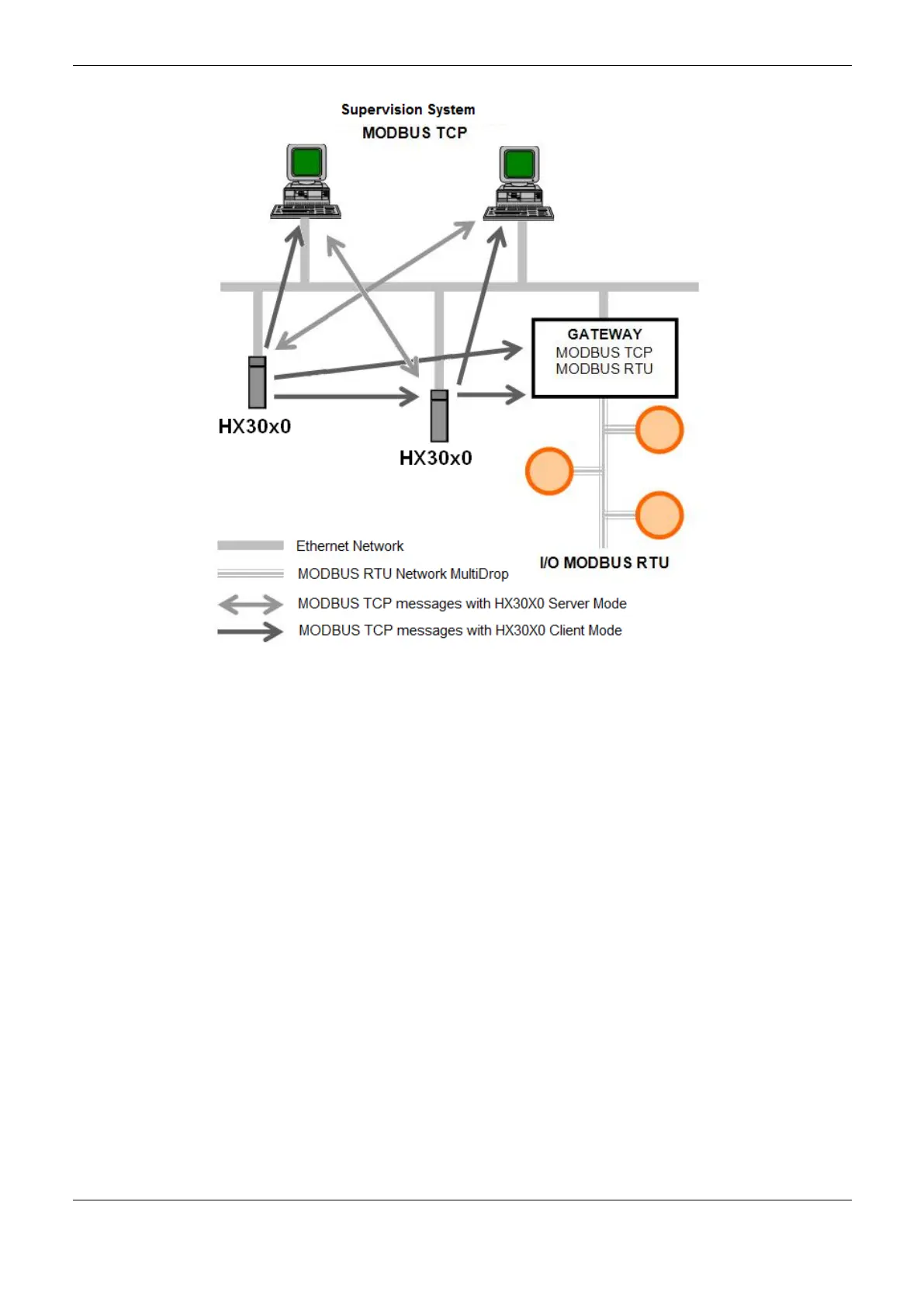
Figure 4-28. MODBUS TCP Communication Network
The association of MODBUS variables with CPU symbolic variables is made by the user through
relations definition via MasterTool IEC XE configuration tool. It’s possible to configure up to 32
relations for the server mode and up to 128 relations for the client mode. The relations in client mode,
on the other hand, must respect the data maximum size of a MODBUS function: 125 registers (input
registers or holding registers) or 2000 bits (coils or input status). This information is detailed in the
description of each protocol.
All relations, in client mode or server mode, can be disabled through direct representation variables
(%Q) identified as Mapping Disabling by MasterTool IEC XE. The disabling may occur through
general bits which affect all relations of an operation mode, or through specific bits, affecting
specific relations.
For the server mode relations, IP addresses clusters can be defined with writing and reading
allowance, called filters. This is made through the definition of an IP network address and of a subnet
mask, resulting in a group of client IPs which can read and write in the relation variables.
Reading/writing functions are filtered, in other words, they cannot be requested by any client,
independent from the IP address. This information is detailed in the MODBUS Ethernet Server
protocol.
When the MODBUS TCP protocol is used in the client mode, it’s possible to use the multiple
requests feature, with the same TCP connection to accelerate the communication with the servers.
When this feature isn’t desired or isn’t supported by the server, it can be disabled (relation level
action). It is important to emphasize that the maximum number of TCP connections between the
client and server is 63. If some parameters are changed, inactive communications can be closed,
which allows the opening of new connections.

 Loading...
Loading...