CG Drives & Automation,01-5326-01r5 Functional Description 129
Example:
“Motor speed [225]” 3000 rpm
Minimum speed [341] 600 rpm
Maximum speed [343] 3000 rpm
Acceleration time [331] 10 seconds
Deceleration time [332] 10 seconds
Acc>Min speed[335] 40 seconds
Dec<Min speed[336] 40 seconds
A. The drive will start from 0 rpm and accelerate to
Minimum speed [341] = 600 rpm in 8 seconds
according to ramp time parameter
Acc>Min speed [335].
Calculated as following:
600 rpm is 20% of 3000 rpm => 20% of 40 s = 8 s.
B. The acceleration continues from minimum speed level
600 rpm to maximum speed level 3000 rpm with
acceleration rate according to ramp time Acceleration
time [331].
Calculate by following:
3000 - 600= 2400 rpm which is 80 % of 3000 rpm =>
acceleration tim is 80 % x 10 s = 8 s.
This means that the total acceleration time from 0 -
3000 rpm will take 8 + 8 = 16 seconds.
Deceleration Time from Minimum
Speed [336]
If a minimum speed is programmed, this parameter will be
used to set the deceleration time from the minimum speed
to 0 rpm at a stop command. The ramp time is defined as
the time it takes for the motor to decelerate from the
nominal motor speed to 0 rpm.
Communication information
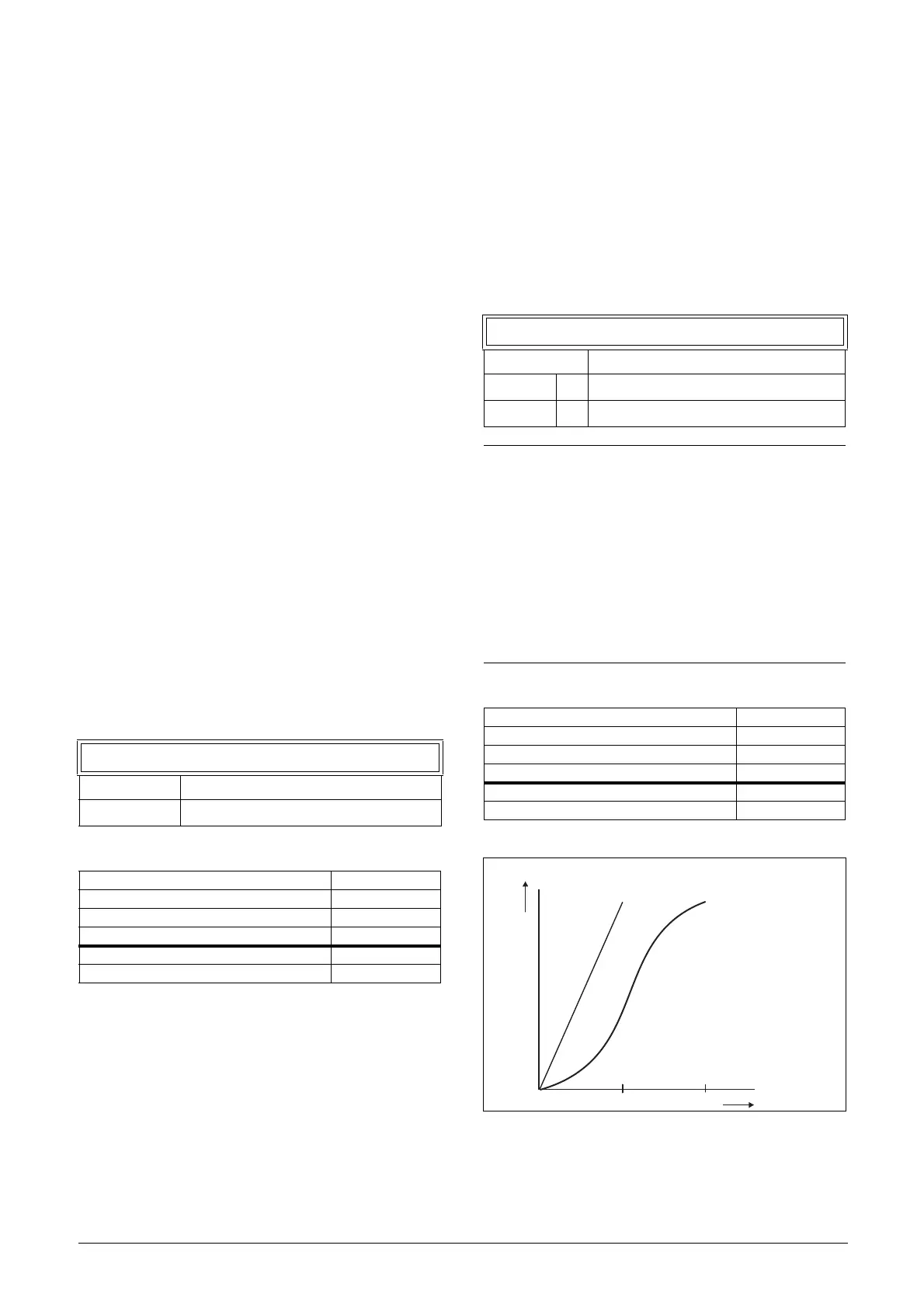
Acceleration Ramp Type [337]
Sets the type of all the acceleration ramps in a parameter set.
See Fig. 101. Depending on the acceleration and
deceleration requirements for the application, the shape of
both the ramps can be selected. For applications where speed
changes need to be started and stopped smoothly, such as a
conveyor belt with materials that can drop following a quick
speed change, the ramp shape can be adapted to a S-shape
and prevent speed change shocks. For applications that are
not critical in this, the speed change can be fully linear over
the complete range.
Communication information
Fig. 101 Shape of acceleration ramp
336 Dec<Min Spd
Default: 10.0 s
Range: 0-3600 s
Modbus Instance no/DeviceNet no: 43106
Profibus slot/index 169/10
EtherCAT and CANopen index (hex) 4c22
Profinet IO index 19490
Fieldbus format Long, 1=0.01 s
Modbus format EInt
337 Acc Rmp
Default: Linear
Linear 0 Linear acceleration ramp.
S-Curve 1 S-shape acceleration ramp.
NOTE: For S-curve ramps the ramp times, [331] and
[332], defines the maximum acceleration and
deceleration rated, i.e. linear part of S-curve, just as
for the linear ramps. The S-curves are implemented
so that for a speed step below sync speed the ramps
are fully
S-shaped while for larger steps the middle part will
be linear. Therefore will a S-curve ramp from 0 –sync
speed take 2 x Time while a step from 0–2 x sync
speed will take 3 x Time (middle part 0.5sync speed –
1.5sync speed linear). Also valid for menu [338],
Deceleration ramp type.
Modbus Instance no/DeviceNet no: 43107
Profibus slot/index 169/11
EtherCAT and CANopen index (hex) 4c23
Profinet IO index 19491
Fieldbus format UInt
Modbus format UInt

 Loading...
Loading...