5-96
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide
OL-17037-01
Chapter 5 Configuring Security Solutions
Managing Rogue Devices
This page provides the following information: the MAC address of the rogue client, the MAC address of
the rogue access point to which this client is associated, the SSID and IP address of the rogue client, the
dates and times when the rogue client was first and last reported, and the current status of the rogue
client.
Step 10 From the Update Status drop-down box, choose one of the following options to specify how the
controller should respond to this rogue client:
• Contain—The controller contains the offending device so that its signals no longer interfere with
authorized clients.
• Alert—The controller forwards an immediate alert to the system administrator for further action.
The bottom of the page provides information on the access points that detected this rogue client.
Step 11 Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 12 If desired, you can test the controller’s connection to this client by clicking Ping.
Step 13 Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
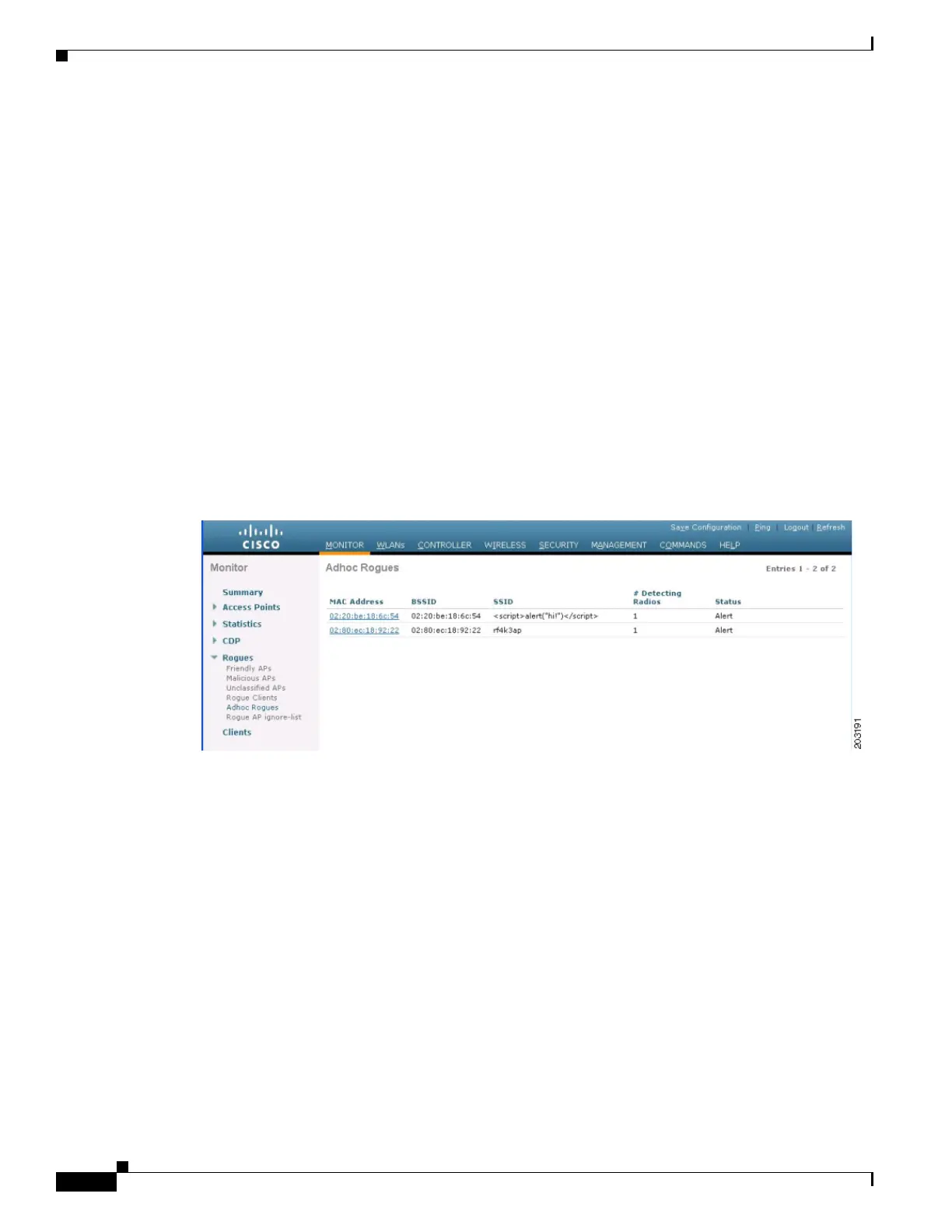
Step 14 To view any ad-hoc rogues detected by the controller, click Adhoc Rogues. The Adhoc Rogues page
appears (see Figure 5-50).
Figure 5-50 Adhoc Rogues Page
This page shows the following information: the MAC address, BSSID, and SSID of the ad-hoc rogue,
the number of radios that detected the ad-hoc rogue, and the current status of the ad-hoc rogue.
Step 15 To obtain more details about an ad-hoc rogue, click the MAC address of the rogue. The Adhoc Rogue
Detail page appears (see Figure 5-51).

 Loading...
Loading...











