50-4
Software Configuration Guide—Release IOS XE 3.3.0SG and IOS 15.1(1)SG
OL-25340-01
Chapter 50 Configuring DHCP Snooping, IP Source Guard, and IPSG for Static Hosts
About DHCP Snooping
Option 82 Data Insertion
In residential, metropolitan Ethernet-access environments, DHCP can centrally manage the IP address
assignments for a large number of subscribers. When the DHCP Option 82 feature is enabled on the
switch, a subscriber device is identified by the switch port through which it connects to the network (in
addition to its MAC address). Multiple hosts on the subscriber LAN can be connected to the same port
on the access switch and are uniquely identified.
Note The DHCP Option 82 feature is supported only when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and on the
VLANs to which subscriber devices using this feature are assigned.
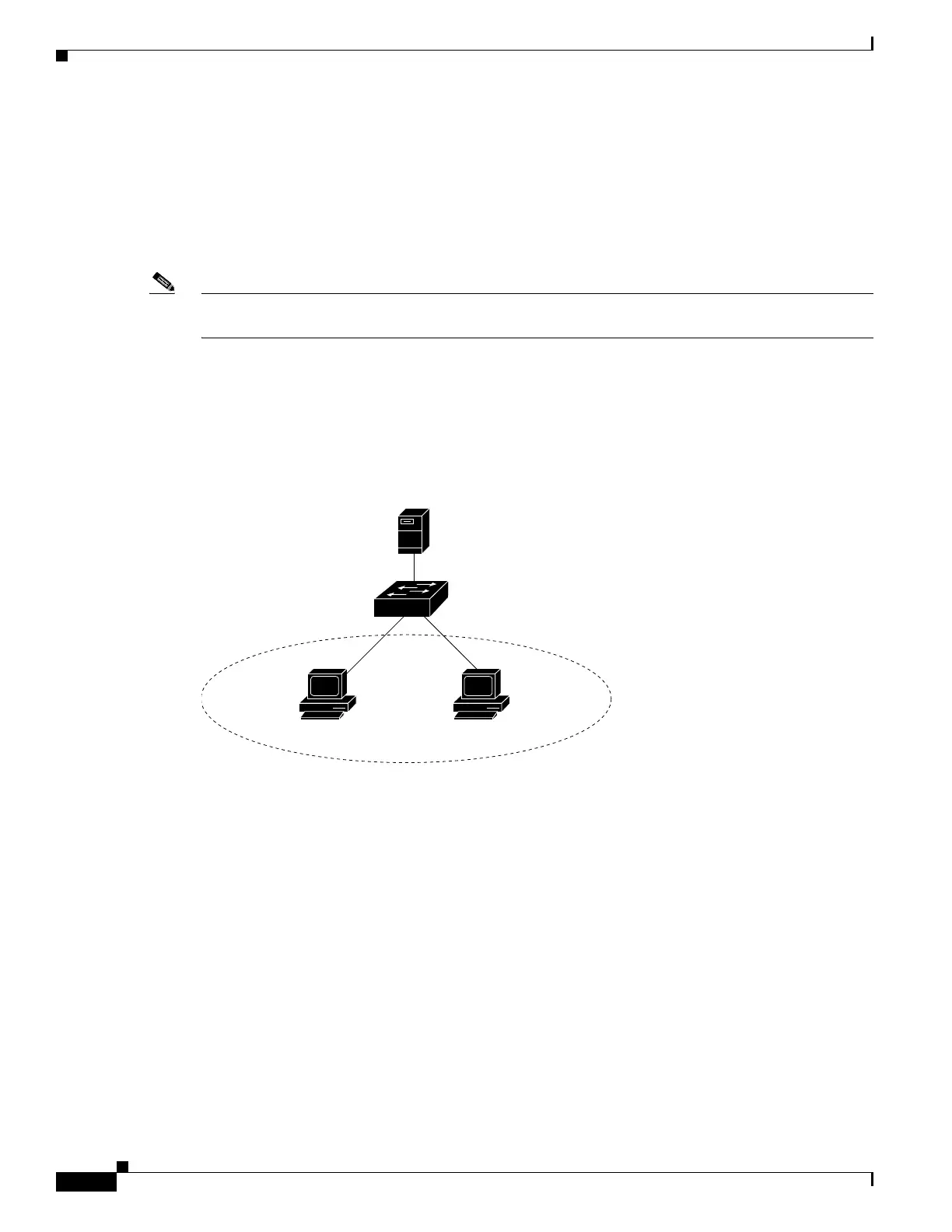
Figure 50-1 is an example of a metropolitan Ethernet network in which a centralized DHCP server
assigns IP addresses to subscribers connected to the switch at the access layer. Because the DHCP clients
and their associated DHCP server do not reside on the same IP network or subnet, a DHCP relay agent
(the Catalyst switch) is configured with a helper address to enable broadcast forwarding and to transfer
DHCP messages between the clients and the server.
Figure 50-1 DHCP Relay Agent in a Metropolitan Ethernet Network
When you enable the DHCP snooping information Option 82 on the switch, this sequence of
events occurs:
• The host (DHCP client) generates a DHCP request and broadcasts it on the network.
• When the switch receives the DHCP request, it adds the Option 82 information in the packet. By
default, the remote ID suboption is the switch MAC address, and the circuit ID suboption is the port
identifier, vlan-mod-port, from which the packet is received. Beginning with Cisco IOS
Release 12.2(40)SG, you can configure the remote ID and circuit ID. For information on
configuring these suboptions, see the “Enabling DHCP Snooping and Option 82” section on
page 50-10.
• If the IP address of the relay agent is configured, the switch adds this IP address in the DHCP packet.
• The switch forwards the DHCP request that includes the Option 82 field to the DHCP server.
• The DHCP server receives the packet. If the server is Option 82-capable, it can use the remote ID,
the circuit ID, or both to assign IP addresses and implement policies, such as restricting the number
of IP addresses that can be assigned to a single remote ID or circuit ID. The DHCP server then
echoes the Option 82 field in the DHCP reply.
Subscribers
Catalyst switch
(DHCP relay agent)
Host A
(DHCP client)
Access layer
DHCP
server
Host B
(DHCP client)
98813
VLAN 10

 Loading...
Loading...




















