37-6
Software Configuration Guide—Release IOS XE 3.3.0SG and IOS 15.1(1)SG
OL-25340-01
Chapter 37 Configuring Bidirection Forwarding Detection
Information About Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
When the BFD protocol on the standby RP is notified of a switchover it changes its state to active,
registers itself with Cisco Express Forwarding so that it can receive packets, and then sends packets for
any elements that have expired.
BFD also uses checkpoint messages to ensure that sessions created by clients on the active RP are
maintained during a switchover. When a switchover occurs, BFD starts an SSO reclaim timer. Clients
must reclaim their sessions within the duration specified by the reclaim timer or else the session is
deleted.
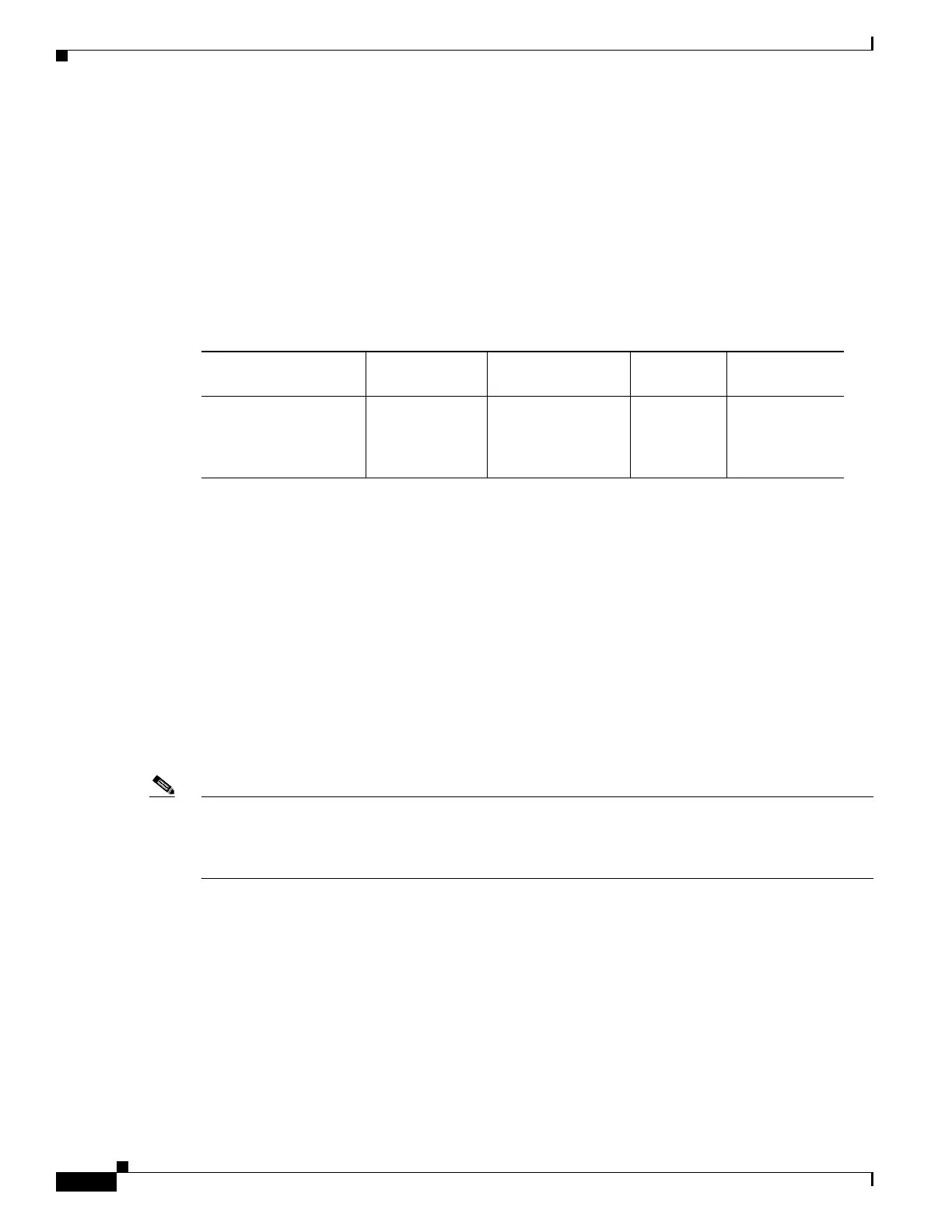
Timer values are different based on the number of BFD sessions and the platform.
Table 37-1 describes the timer value on Cisco 4500 series switches.
BFD Support for Static Routing
Unlike dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and BGP, static routing has no method of peer
discovery. Therefore, when BFD is configured, the reachability of the gateway is completely dependent
on the state of the BFD session to the specified neighbor. Unless the BFD session is up, the gateway for
the static route is considered unreachable, and therefore the affected routes will not be installed in the
appropriate Routing Information Base (RIB).
For a BFD session to establish successfully, BFD must be configured on the interface on the peer and
there must be a BFD client registered on the peer for the address of the BFD neighbor. When an interface
is used by dynamic routing protocols, the latter requirement is usually met by configuring the routing
protocol instances on each neighbor for BFD. When an interface is used exclusively for static routing,
this requirement must be met by configuring static routes on the peers.
BFD is supported on IPv4 and IPv6 static routes.
Note If a BFD configuration is removed from the remote peer while the BFD session is in the up state, the
updated state of the BFD session is not signaled to the static route. This will cause the static route to
remain in the RIB. The only workaround is to remove the static route BFD neighbor configuration so
that the static route no longer tracks BFD session state.
Benefits of Using BFD for Failure Detection
When you deploy any feature, it is important to consider all the alternatives and be aware of any
trade-offs being made.
The closest alternative to BFD in conventional EIGRP, BGP, and OSPF deployments is the use of
modified failure detection mechanisms for EIGRP, BGP, and OSPF routing protocols.
If you set EIGRP hello and hold timers to their absolute minimums, the failure detection rate for EIGRP
falls to within a one- to two-second range.
Table 37-1 BFD Timer Values on a Cisco 4500 Series Switches
Maximum Number of
BFD Sessions
BFD Session
Type
Minimum Timer
Value (ms) Clients Comments
128 Async/echo 50
multiplier 3
All A multiple of 5
is recommended
for SSO
switches.

 Loading...
Loading...




















