335
Configuring MSTP
Information About Configuring MSTP
The IST connects all the MSTP switches in the region and appears as a subtree in the CIST that encompasses the entire
switched domain. The root of the subtree is the CIST regional root. The MST region appears as a virtual switch to adjacent
STP switches and MST regions.
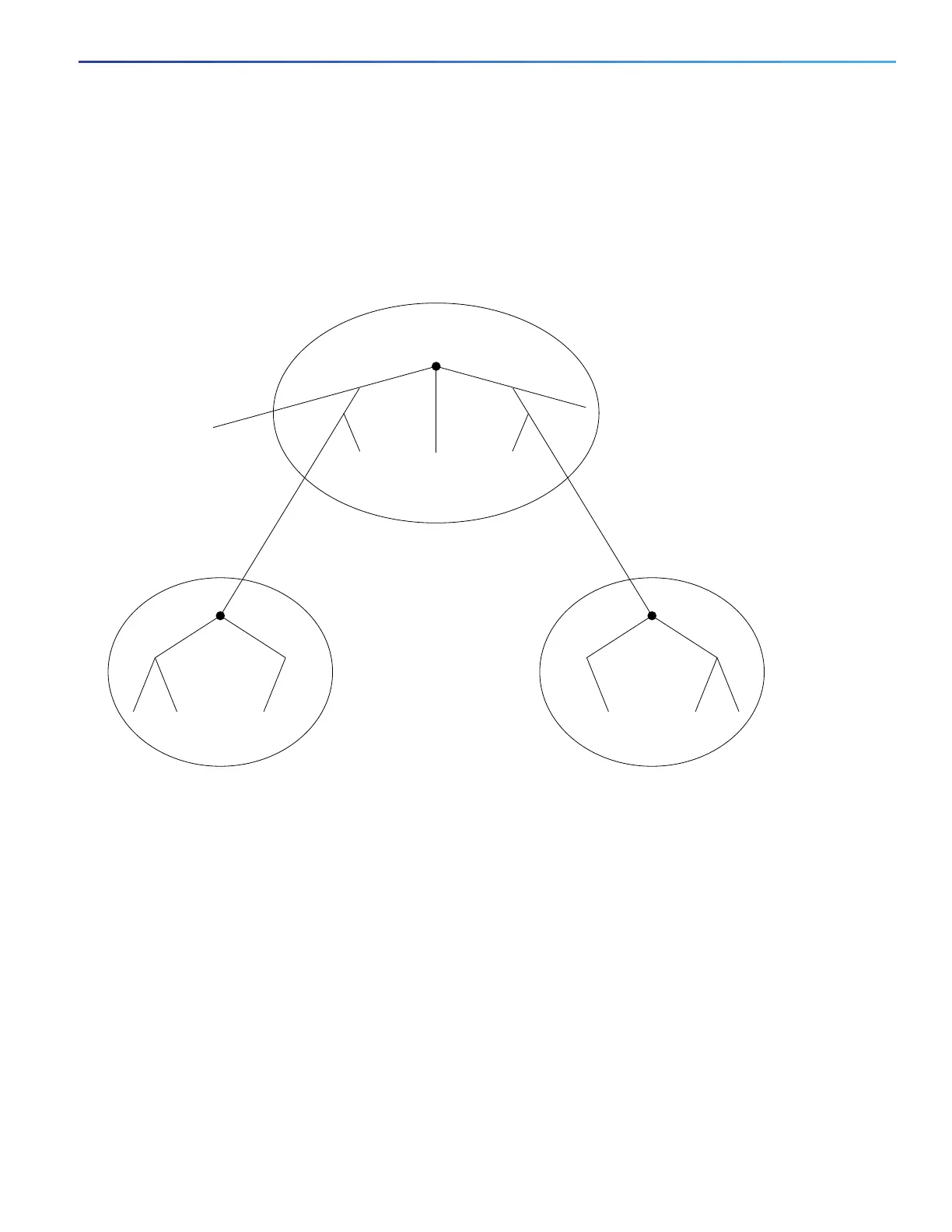
Figure 1 on page 3 shows a network with three MST regions and a legacy IEEE 802.1D switch (D). The CIST regional root
for region 1 (A) is also the CIST root. The CIST regional root for region 2 (B) and the CIST regional root for region 3 (C)
are the roots for their respective subtrees within the CIST. The RSTP runs in all regions.
Figure 39 MST Regions, CIST Masters, and CST Root
Only the CST instance sends and receives BPDUs, and MST instances add their spanning-tree information into the
BPDUs to interact with neighboring switches and compute the final spanning-tree topology. Because of this, the
spanning-tree parameters related to BPDU transmission (for example, hello time, forward time, max-age, and max-hops)
are configured only on the CST instance but affect all MST instances. Parameters related to the spanning-tree topology
(for example, switch priority, port VLAN cost, and port VLAN priority) can be configured on both the CST instance and
the MST instance.
MSTP switches use Version 3 RSTP BPDUs or IEEE 802.1D STP BPDUs to communicate with legacy IEEE 802.1D
switches. MSTP switches use MSTP BPDUs to communicate with MSTP switches.
IEEE 802.1s Terminology
Some MST naming conventions used in Cisco’s prestandard implementation have been changed to identify some internal
or regional parameters. These parameters are significant only within an MST region, as opposed to external parameters
that are relevant to the whole network. Because the CIST is the only spanning-tree instance that spans the whole
network, only the CIST parameters require the external rather than the internal or regional qualifiers.
The CIST root is the root switch for the unique instance that spans the whole network, the CIST.
IST master
and CST root
IST master IST master
A
MST Region 1
D
Legacy IEEE 802.1D
B
MST Region 2 MST Region 3
C
92983

 Loading...
Loading...