62
Performing Switch Setup Configuration
Information About Performing Switch Setup Configuration
Switch Default Settings
DHCP-Based Autoconfiguration Overview
DHCP provides configuration information to Internet hosts and internetworking devices. This protocol consists of two
components: one for delivering configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a device and a mechanism for allocating
network addresses to devices. DHCP is built on a client-server model, in which designated DHCP servers allocate
network addresses and deliver configuration parameters to dynamically configured devices. The switch can act as both
a DHCP client and a DHCP server.
During DHCP-based autoconfiguration, your switch (DHCP client) is automatically configured at startup with IP address
information and a configuration file.
With DHCP-based autoconfiguration, no DHCP client-side configuration is needed on your switch. However, you need
to configure the DHCP server for various lease options associated with IP addresses. If you are using DHCP to relay the
configuration file location on the network, you might also need to configure a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server
and a Domain Name System (DNS) server.
The DHCP server for your switch can be on the same LAN or on a different LAN than the switch. If the DHCP server is
running on a different LAN, you should configure a DHCP relay device between your switch and the DHCP server. A relay
device forwards broadcast traffic between two directly connected LANs. A router does not forward broadcast packets,
but it forwards packets based on the destination IP address in the received packet.
DHCP-based autoconfiguration replaces the BOOTP client functionality on your switch.
DHCP Client Request Process
When you boot up your switch, the DHCP client is invoked and requests configuration information from a DHCP server
when the configuration file is not present on the switch. If the configuration file is present and the configuration includes
the ip address dhcp interface configuration command on specific routed interfaces, the DHCP client is invoked and
requests the IP address information for those interfaces.
Figure 2 on page 63 shows the sequence of messages that are exchanged between the DHCP client and the DHCP
server.
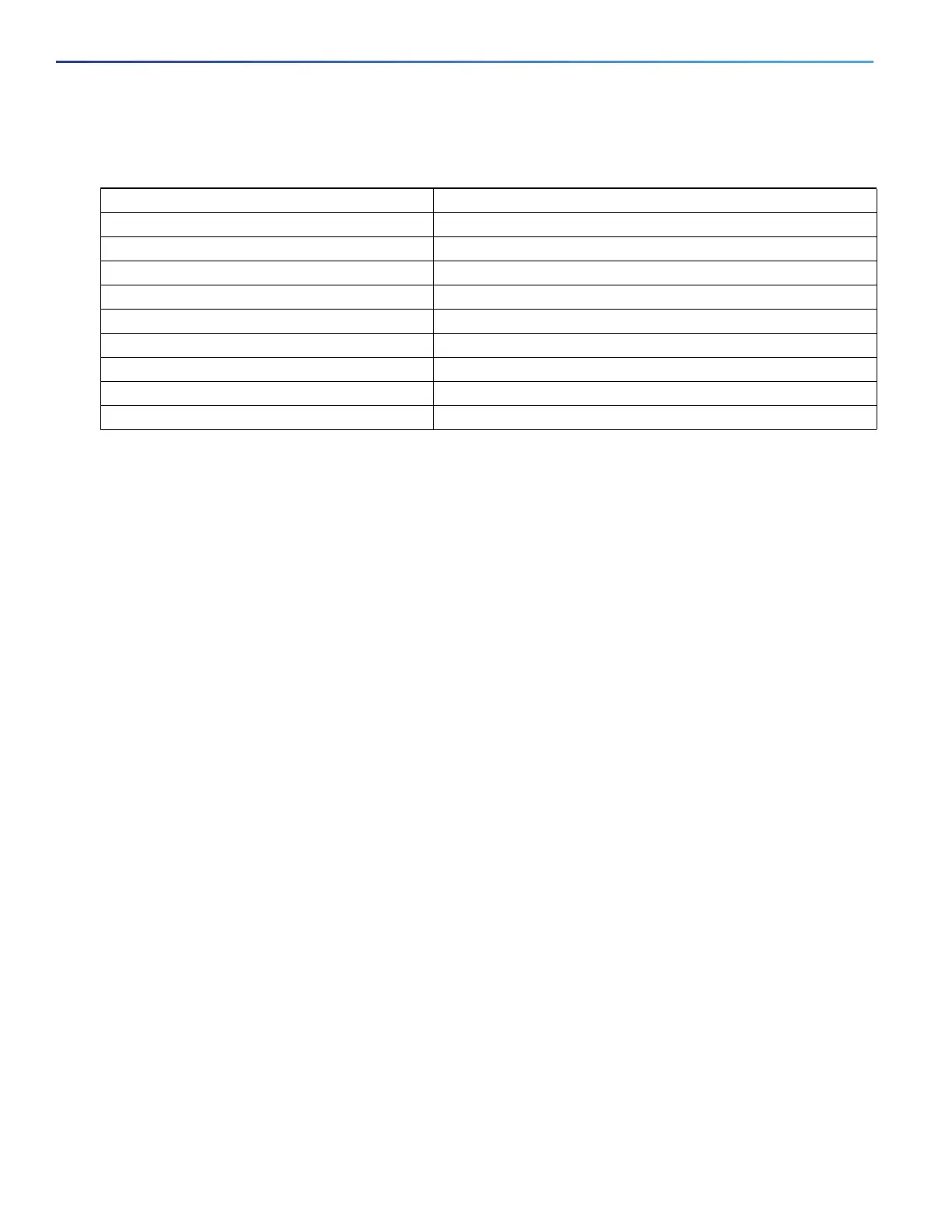
Feature Default Setting
IP address and subnet mask No IP address or subnet mask is defined.
Default gateway No default gateway is defined.
Enable secret password No password is defined.
Hostname The factory-assigned default hostname is Switch.
Telnet password No password is defined.
Cluster command switch functionality Disabled.
Cluster name No cluster name is defined.
Manual boot No.
Boot optimization Enabled.

 Loading...
Loading...