448
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
Information About Port-Based Traffic Control
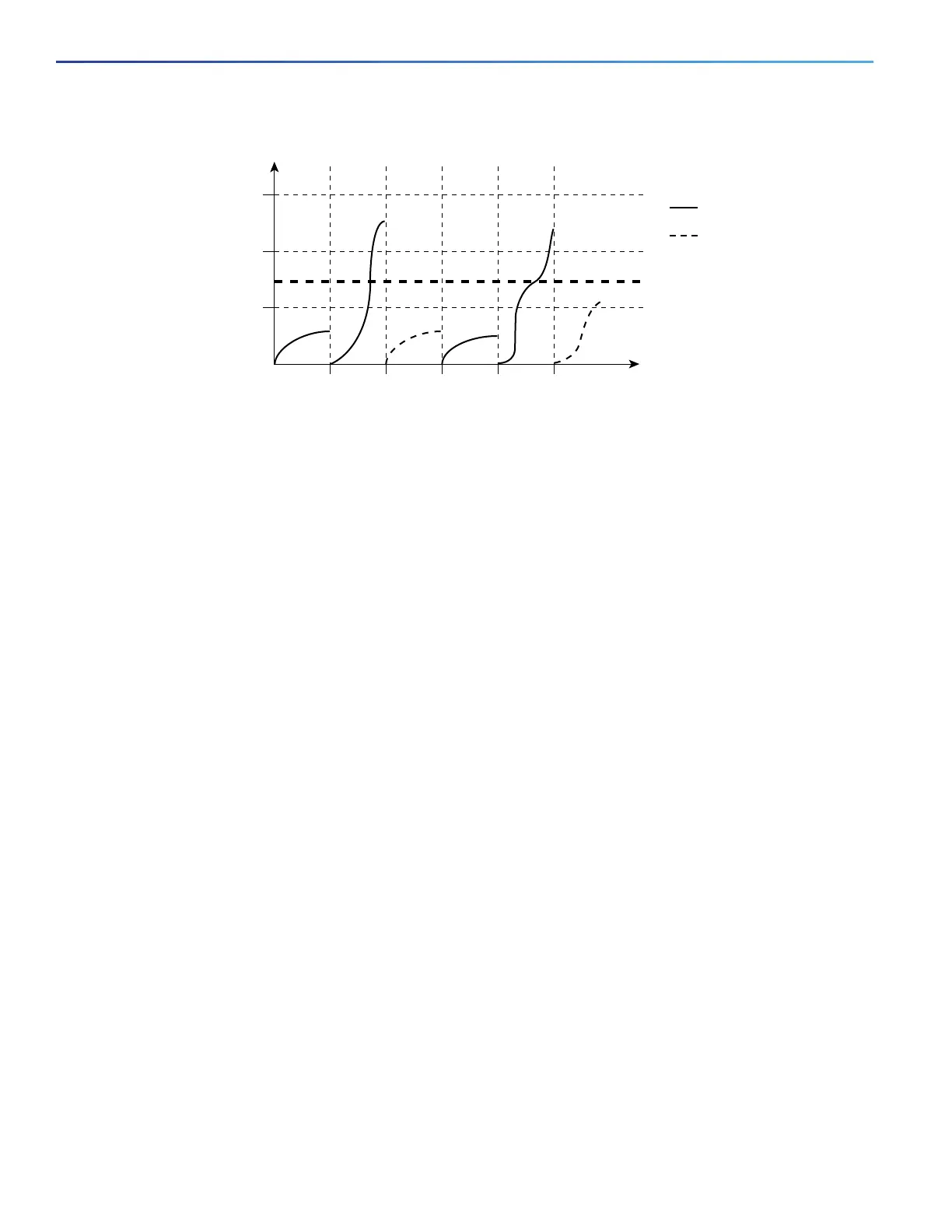
Figure 68 Broadcast Storm Control Example
The combination of the storm-control suppression level and the 1-second time interval controls the way the storm control
algorithm works. A higher threshold allows more packets to pass through. A threshold value of 100 percent means that
no limit is placed on the traffic. A value of 0.0 means that all broadcast, multicast, or unicast traffic on that port is blocked.
Note: Because packets do not arrive at uniform intervals, the 1-second time interval during which traffic activity is
measured can affect the behavior of storm control.
You use the storm-control interface configuration commands to set the threshold value for each traffic type.
Default Storm Control Configuration
By default, unicast, broadcast, and multicast storm control are disabled on the switch interfaces; that is, the suppression
level is 100 percent.
Storm Control and Threshold Levels
You configure storm control on a port and enter the threshold level that you want to be used for a particular type of traffic.
However, because of hardware limitations and the way in which packets of different sizes are counted, threshold
percentages are approximations. Depending on the sizes of the packets making up the incoming traffic, the actual
enforced threshold might differ from the configured level by several percentage points.
Note: Storm control is supported on physical interfaces. You can also configure storm control on an EtherChannel. When
storm control is configured on an EtherChannel, the storm control settings propagate to the EtherChannel physical
interfaces.
Small-Frame Arrival Rate
Incoming VLAN-tagged packets smaller than 67 bytes are considered small frames. They are forwarded by the switch,
but they do not cause the switch storm-control counters to increment. In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(44)SE and later, you
can configure a port to be error disabled if small frames arrive at a specified rate (threshold).
You globally enable the small-frame arrival feature on the switch and then configure the small-frame threshold for
packets on each interface. Packets smaller than the minimum size and arriving at a specified rate (the threshold) are
dropped since the port is error disabled.
If the errdisable recovery cause small-frame global configuration command is entered, the port is reenabled after a
specified time. (You specify the recovery time by using errdisable recovery global configuration command.)
Total
number of
broadcast
packets
or bytes
Forwarded traffic
0T1
Threshold
T2 T4 T5
46651
T3 Time
Blocked traffic

 Loading...
Loading...