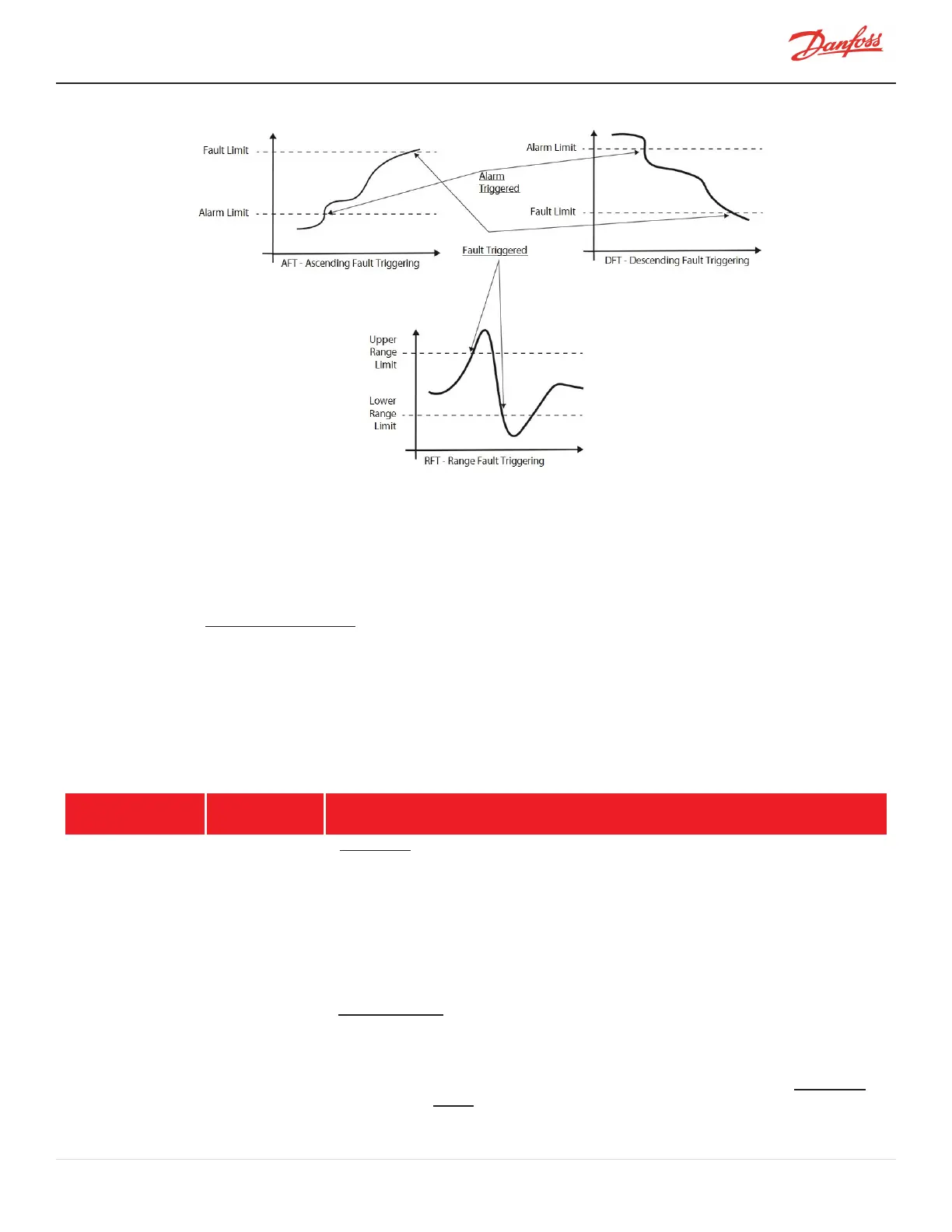
Figure 5-1 Fault Trigger Methods
Fault Reset:Afaultthatdoesnotrequireapowercycletoclear(non-critical)canberesetinthefollowingmanner:
Interlockmustbeclosed,settheDemandto"0"andafterwardstoavaluegreaterthan0.Nowthefaultisresetand
thecompressorisreadytorun.Theassumptionisthatthecauseofthefaulthasbeenrectified.
TheClearFaultsbuttonintheSMTCompressorMonitorcanbeusedinsoftwareversions4.0.0andlater.Alsoseethe
OEMProgrammingGuideforadditionalfaultresetoptions.
Afaultdemandingapowercycle(Lock-OutFault)isresettablebycyclingthemainspowertothecompressor.The
assumptionisthatthecauseofthefaulthasbeenrectified.Refertothefollowingtables:
l
Table5-6CompressorStatus
l
Table5-8Motor/SystemStatusonpage260
l
Table5-9BearingStatusonpage263
Table 5-6 Compressor Status
Compressor Status
Description
Trigger Method Troubleshooting
HighInverter
TemperatureFault
AFT Consequence:
l
IndicatestheInvertercoolingisinsufficient.Repeatedoccurrencesofthisalarmcan
resultinInverterfailure.
l
Ifthisfaultoccursthree(3)timeswithina30-minuteperiod,aLock-OutFaultwilloccur.
l
ThemeasuredInvertertemperaturemustdropbelowtheMaximumDriveStartup
Temperaturebeforearestartcanbeattempted,otherwisetheCompressorMonitorTool
ControlStatusmessage“Abovedrivetemperaturelimitwaitingtocooldown”willbe
displayed.
Recommendation:
l
Ensuretheliquidmotor-coolinglinehassufficientliquidsupplyandisnotblocked.
l
Preventprolongedoperationatapressureratiolessthan1.5.
o
LowLiftoperationrequiresadditionalconsiderations,refertotheApplications
Manual
l
Verifythesolenoidsareoperationalandnotblocked.RefertoSection4.6.3Solenoid
M-SV-001-EN Rev. H-1/23/2023 Page 255 of 294

 Loading...
Loading...











