3-42
95-8533
18.2
Det-Tronics S
³
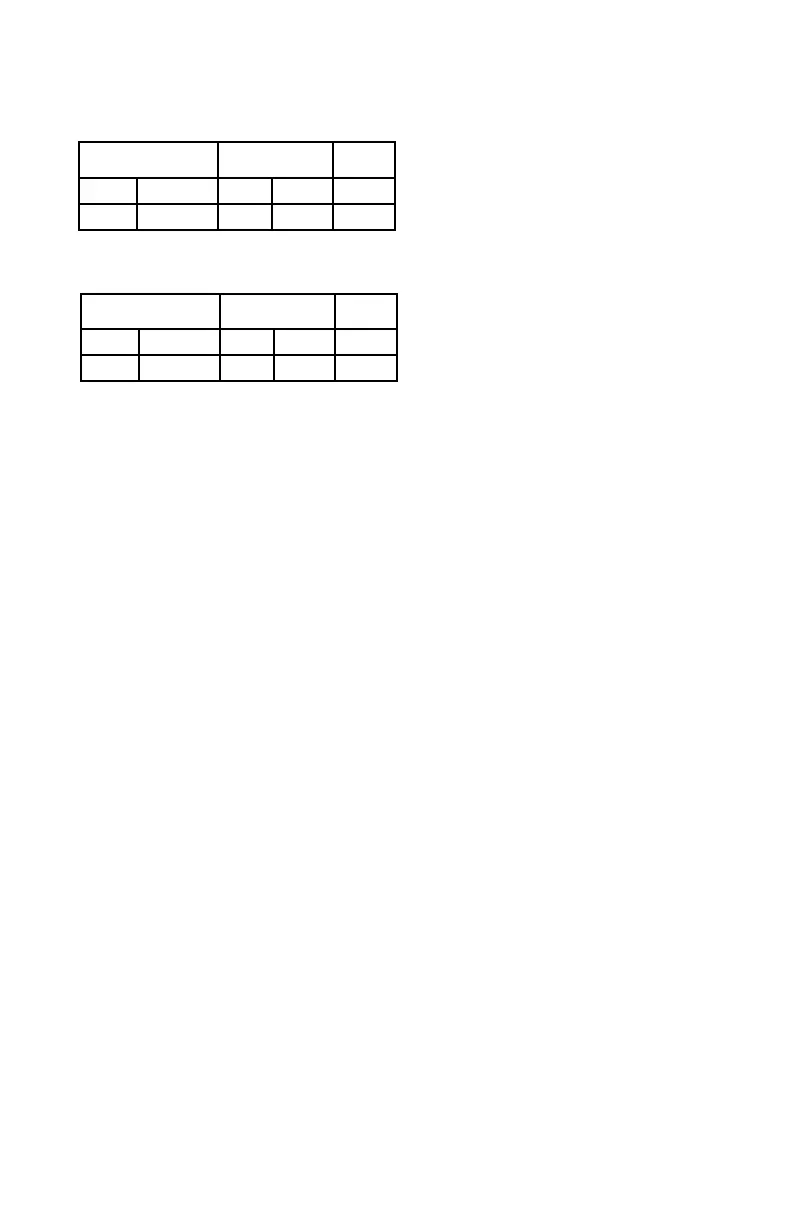
Safety System Software is used
for device configuration. The following tables
show the minimum software/firmware releases:
GAS DETECTOR LOCATION
AND INSTALLATION
Gas detection devices must be properly
located to provide maximum protection.
Determining the proper number of devices and
placement varies depending on the specific
requirements of the area of protection.
The following should be considered when
locating a gas detection device:
1. Gas type. If it is lighter than air (acetylene,
hydrogen, methane, etc.), place the
sensor above the potential source. Place
the sensor close to the floor for gases that
are heavier than air (benzene, butane,
butylene, propane, hexane, pentane, etc.)
or for vapors resulting from flammable liquid
spills.
NOTE
Air currents can cause a gas that is
heavier than air to rise. Also, if the gas is
hotter than ambient air, it could also rise.
2. How rapidly will the gas diffuse into the air?
Select a location for the sensor as close as
possible to the anticipated source of a gas
leak.
3. Ventilation characteristics. Air movement
will cause gas to accumulate more heavily
in one area than another. The devices
should be placed in areas where the
most concentrated accumulation of gas is
anticipated.
4. Devices should be pointed down to prevent
the buildup of moisture or contaminants on
the filter.
5. Devices must be accessible for testing and
calibration.
NOTE
The use of the Sensor Separation Kit will
be required in some installations.
ENVIRONMENTS AND SUBSTANCES
THAT AFFECT GAS DETECTOR
PERFORMANCE
Catalytic sensors should be located where
they are safe from potential sources of
contamination that can cause a decrease in
the sensitivity of the device including:
A. Substances that can clog the pores of the
flame arrestor and reduce the gas diffusion
rate to the sensor including:
Dirt and oil, corrosive substances such as
Cl2 (Chlorine) or HCl, paint overspray, or
residue from cleaning solutions that can
clog the flame arrestor.
NOTE
A dust cover should be installed to
protect the flame arrester whenever
these conditions exist.
B. Substances that cover or tie up the active
sites on the catalytic surface of the active
sensing element such as volatile metal
organics, gases, or vapors of hydrides,
and volatile compounds containing
phosphorous, boron, silicone, etc.
Examples:
RTV silicone sealants
Silicone oils and greases
Tetraethyl lead
Phosphine
Diborane
Silane
Trimethyl chlorsilane
Hydrogen fluoride
Boron trifluoride
*for part number 007606-002
For Gas Applications
Controller Firmware* AIM S
³
Rev. Version Rev. Version Version
B 3.06 B 1.02 2.9.1.1
*for part number 008983-001
For Flame Applications
Controller Firmware* AIM S
³
Rev. Version Rev. Version Version
C 5.52 D 1.07 4.0.0.0

 Loading...
Loading...