5.4 Details of Function Codes
5-221
Chapter 5 Function Code
Details of
Function Codes
F codes
E codes
C codes
P codes
H codes
A codes
b codes
r codes
J03 to J06
d codes
U codes
y codes
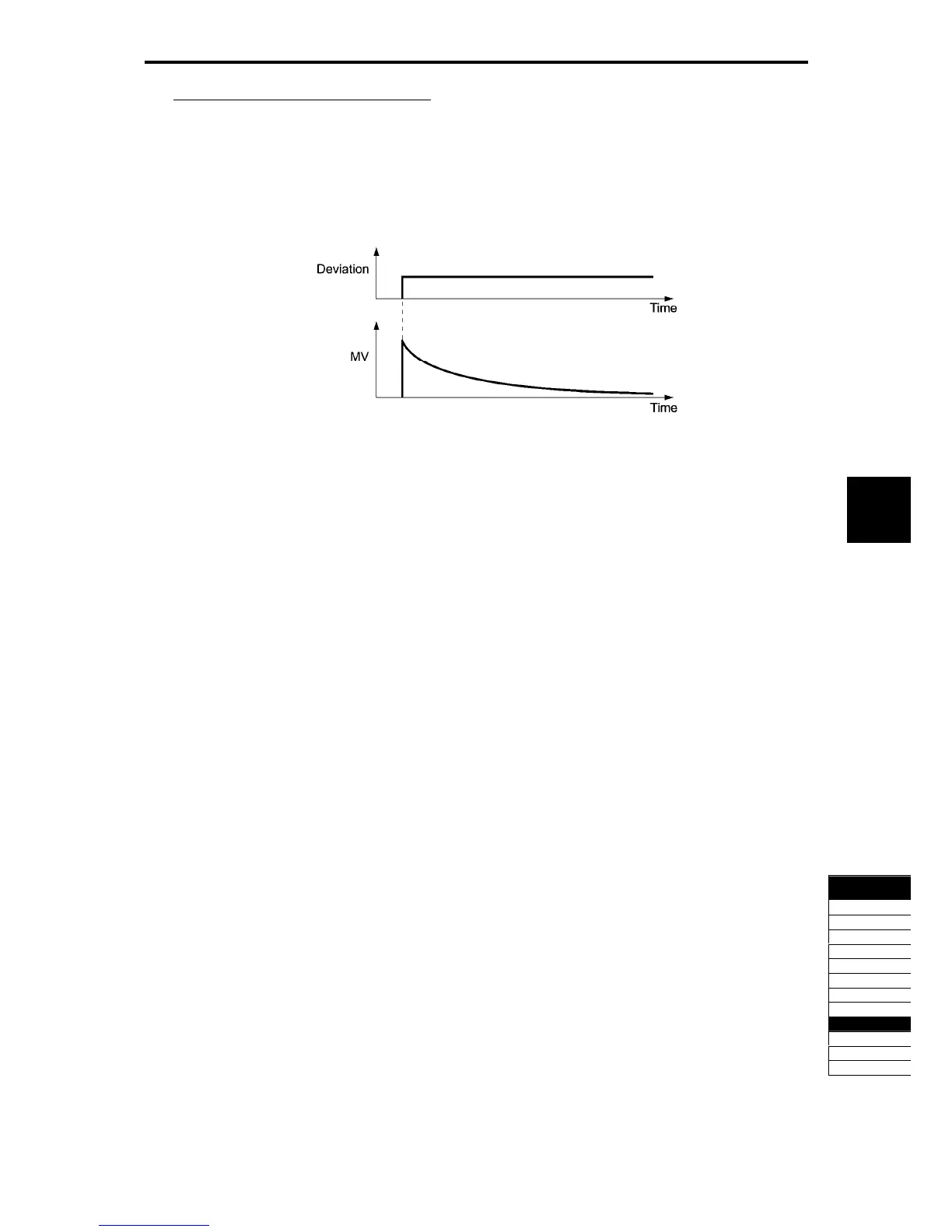
D (Differential) action (Differential operation)
When the operation amount (output frequency) is proportional to the differential value of deviation, that is
called the D action. D action makes the inverter quickly react to a rapid change of deviation.
The effectiveness of D action is expressed by differential time as parameter. Setting a long differential time
will quickly suppress oscillation caused by P action when a deviation occurs. Too long differential time
makes the inverter output oscillation more. Setting short differential time will weakens the suppression effect
when the deviation occurs.
Fig. 5.4-101
The combined control of P, I, and D actions are described below.
(1) PI control
PI control, which is a combination of P and I actions, is generally used to minimize the remaining deviation
caused by executing only P action. PI control always acts to minimize the deviation even if a commanded
value changes or external disturbance steadily occurs. However, the longer the integral time of I action, the
slower the system response to quick-changed control. P action can be used alone for loads with very large
part of integral components.
(2) PD control
In PD control, when a deviation occurs, the operation amount that is larger than the operation amount of only
D operation suddenly occurs, and increase of the deviation can be kept low. When the deviation becomes
small, the behavior of P action becomes small. A load including the integral component in the controlled
system may oscillate due to the action of the integral component if P action alone is applied. In such case,
PD control is used to reduce the oscillation caused by P action, for keeping the system stable. Therefore, PD
control is applied to a system that does not contain any damping actions in its process.
(3) PID control
PID control is implemented by combining P action with the deviation suppression of I action and the
oscillation suppression of D action. PID control features minimal control deviation, high precision and high
stability. In particular, PID control is effective to a system that has a long response time to the occurrence of
deviation.
Follow the procedure below to set data to PID control function codes.
It is highly recommended that you adjust the PID control value while monitoring the system response
waveform with an oscilloscope or equivalent. Repeat the following procedure to determine the optimal set
value.
• Increase the data of J03 for PID control (Gain) within the range where the feedback signal does not
oscillate.
• Decrease the data of J04 for PID control (Integral time) within the range where the feedback signal does
not oscillate.
• Increase the data of J05 for PID control (Differential time) within the range where the feedback signal
does not oscillate.

 Loading...
Loading...











