5.4 Details of Function Codes
5-220
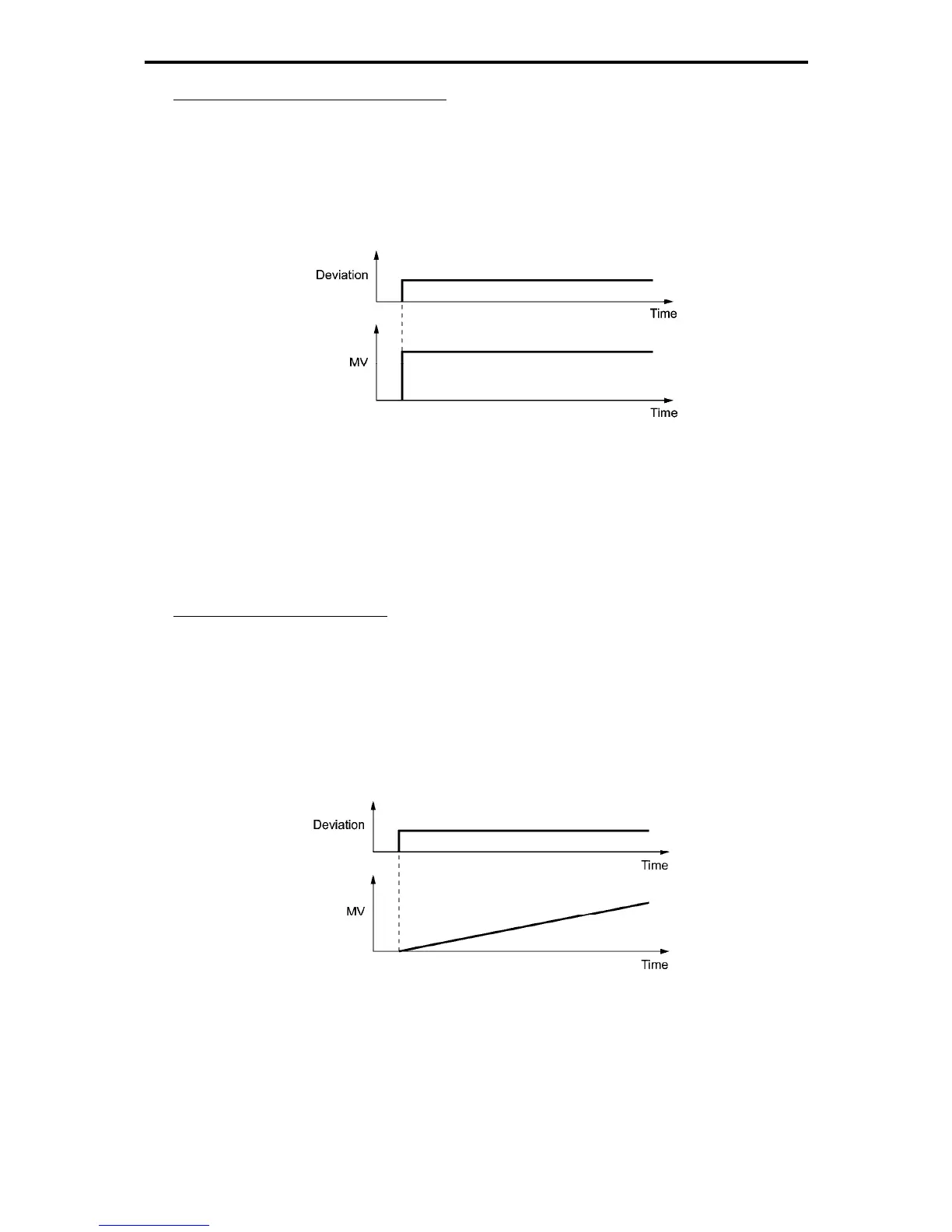
P (Proportional) action (Proportional operation)
When the operation amount (output frequency) and the deviation are in a proportional relationship, that is
called a P action. P action outputs the operation amount that is proportional to the deviation. However, the P
action alone cannot eliminate deviation.
Gain is data that determines the system response level against the deviation in P action. An increase in gain
speeds up response, but an excessive gain may oscillate the inverter output. A decrease in gain delays
response, but it stabilizes the inverter output.
Fig. 5.4-99
I integral time (J04)
J04 specifies the integral time for the PID controller.
- Data setting range: 0.0 to 3600.0 (sec)
0.0 means that the integral component is ineffective.
I (Integral) action (Integral operation)
When the operation amount (output frequency) change speed is proportional to the integral value of
deviation, that is called an I action. In I action, the operation amount that the deviation is integrated is output.
Therefore, I action is effective in bringing the feedback amount close to the commanded value. However, for
the system whose deviation rapidly changes, this action cannot react quickly.
The effectiveness of I action is expressed by integral time as parameter. The longer the integral time, the
slower the response. The reaction to the external disturbance also becomes slow. The shorter the integral
time, the faster the response. Setting too short integral time, however, makes the inverter output tend to
oscillate against the external disturbance.
Fig. 5.4-100
D differential time (J05)
J05 specifies the differential time for the PID controller.
- Data setting range: 0.00 to 600.00 (sec)
0.00 means that the integral component is ineffective.

 Loading...
Loading...











