10.1 Selecting Motors and Inverters
10-5
Chapter 10 SELECTING OPTIMAL MOTOR AND INVERTER CAPACITIES
(1) Calculating the load torque during constant speed running (For detailed calculation, refer to Section
10.1.3 [1])
It is essential to calculate the load torque during constant speed running for all loads.
First calculate the load torque of the motor during constant speed running and then select a tentative
capacity so that the continuous rated torque of the motor during constant speed running becomes
higher than the load torque. To perform capacity selection efficiently, it is necessary to match the
rated speeds (base speeds) of the motor and load. To do this, select an appropriate reduction-gear
(mechanical transmission) ratio and the number of motor poles.
If the acceleration or deceleration time is not restricted, the tentative capacity can apply as a defined
capacity.
(2) Calculating the acceleration time (For detailed calculation, refer to Section 10.1.3 [2])
When there are some specified requirements for the acceleration time, calculate it according to the
following procedure:
1) Calculate the moment of inertia for the load and motor
Calculate the moment of inertia for the load, referring to Section 10.1.3 [2], "Acceleration and
deceleration time calculation." For the motor, refer to the related motor catalogs.
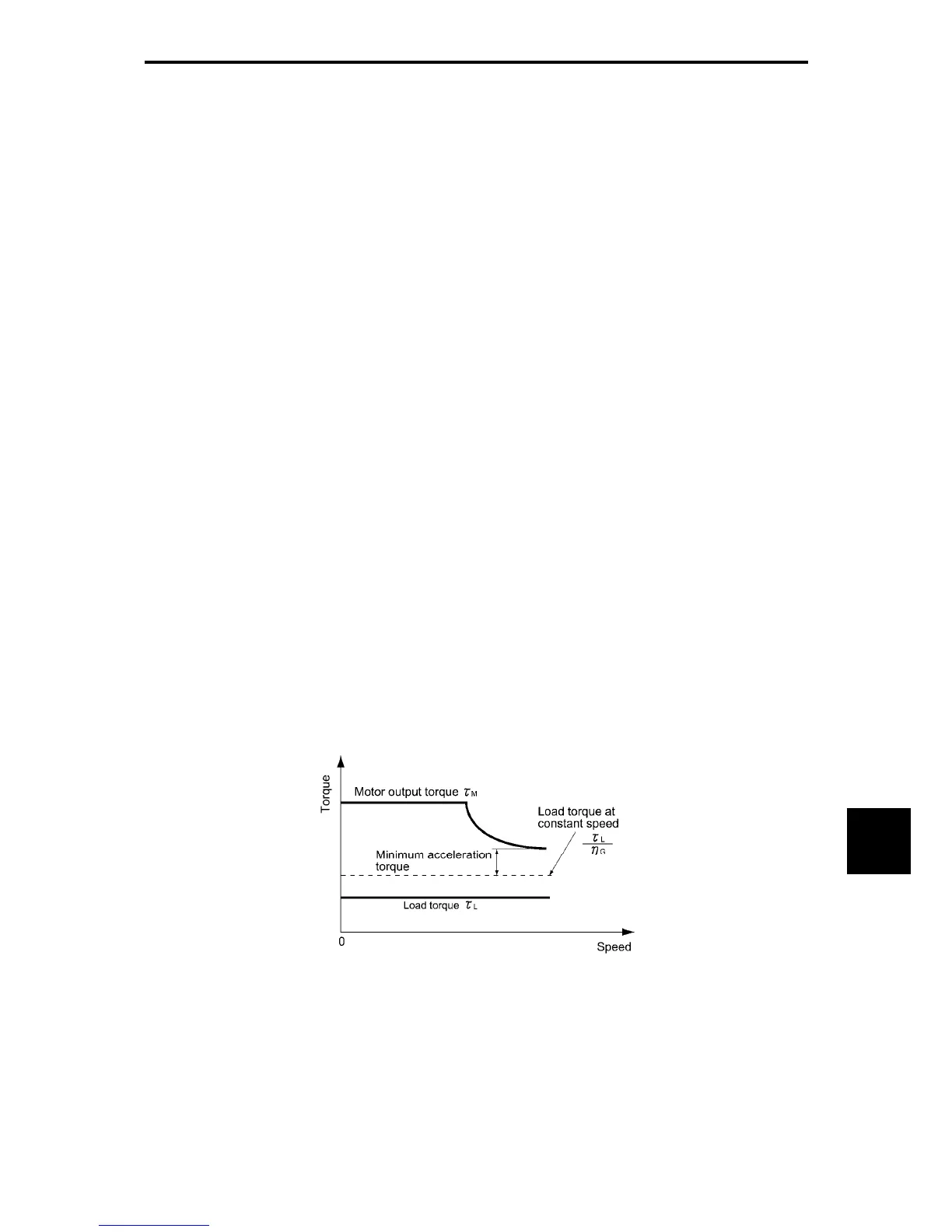
2) Calculate the minimum acceleration torque (See Figure 10.1-4)
The acceleration torque is the difference between the motor short-time output torque (base
frequency: 60 Hz) explained in Section 10.1.1 (2), "Maximum driving torque in a short time" and
the load torque (τ
L
/η
G
) during constant speed running calculated in the above (1). Calculate
the minimum acceleration torque for the whole range of speed.
3) Calculate the acceleration time
Assign the value calculated above to the equation (10.15) in Section 10.1.3 [2], "Acceleration
and deceleration time calculation" to calculate the acceleration time. If the calculated
acceleration time is longer than the expected time, select the inverter and motor having one
class larger capacity and calculate it again.
Figure 10.1-4 Example Study of Minimum Acceleration Torque

 Loading...
Loading...











