11.4 Option
11-36
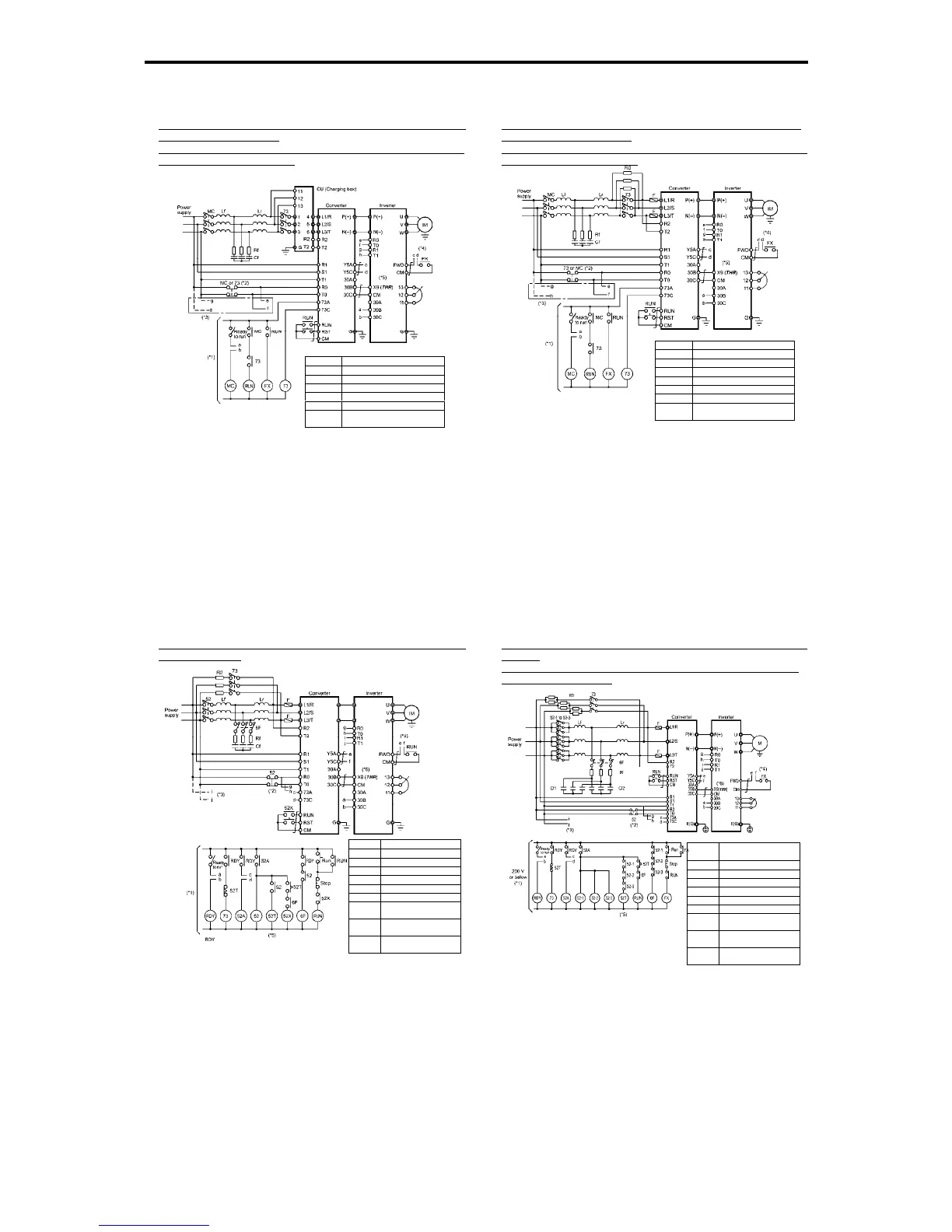
Basic connection diagrams
z RHC7.5-2C to RHC90-2C (Applicable inverters: Three-phase 200 V
class series, 7.5 to 90 kW)
z RHC7.5-4C to RHC220-4C (Applicable inverters: Three-phase 400
V class series, 7.5 to 220 kW)
*When a charging box is connected
(*1) For the 400 V class power supply, connect a stepdown transformer to limit
the voltage of the sequence circuit to 220 V or below.
(*2) Be sure to connect the auxiliary power input terminals R0 and T0 of the PWM
converter to the main power input lines via B contacts of magnetic contactors
of the charging circuit (73 or MC).
If 73 uses SC-05, SC-4-0, or SC-5-1, connect an auxiliary contact unit to the
MC's B contact or 73.
(*3) Be sure to connect the auxiliary power input terminals R0 and T0 of the
inverter to the main power input lines via B contacts of magnetic contactors
of the charging circuit (73 or MC). For 200 V class series of inverters with a
capacity of 37 kW or above and 400 V class series with 75 kW or above,
connect the fan power input terminals R1 and T1 of the inverter to the main
power input lines without going through the MC's B contacts or 73.
(*4) Construct a sequence in which a run command is given to the inverter after
the PWM converter becomes ready to run.
(*5) Assign the external alarm THR to any of terminals [X1] to [X9] on the
inverter.
z RHC7.5-2C to RHC90-2C (Applicable inverters: Three-phase 200
V class series, 7.5 to 90 kW)
z RHC7.5-4C to RHC220-4C (Applicable inverters: Three-phase 400
V class series, 7.5 to 220 kW)
(*1) For the 400 V class power supply, connect a stepdown transformer to limit
the voltage of the sequence circuit to 220 V or below.
(*2) Be sure to connect the auxiliary power input terminals R0 and T0 of the
PWM converter to the main power input lines via B contacts of magnetic
contactors of the charging circuit (73 or MC).
If 73 uses SC-05, SC-4-0, or SC-5-1, connect an auxiliary contact unit to the
MC's B contact or 73.
(*3) Be sure to connect the auxiliary power input terminals R0 and T0 of the
inverter to the main power input lines via B contacts of magnetic contactors
of the charging circuit (73 or MC). For 200 V class series of inverters with a
capacity of 37 kW or above and 400 V class series with 75 kW or above,
connect the fan power input terminals R1 and T1 of the inverter to the main
power input lines without going through the MC's B contacts or 73.
(*4) Construct a sequence in which a run command is given to the inverter after
the PWM converter becomes ready to run.
(*5) Assign the external alarm THR to any of terminals [X1] to [X9] on the
inverter.
z RHC280-4C to RHC400-4C (Applicable inverters: Three-phase 400
V, 280 to 400 kW)
(*1) Connect a stepdown transformer to limit the voltage of the sequence circuit
to 220 V or below.
(*2) Be sure to connect the auxiliary power input terminals R0 and T0 of the PWM
converter and the inverter to the main power input lines via B contacts of
magnetic contactors of the power supply circuit (52).
(*3) Connect the fan power input terminals R1 and T1 of the inverter to the main
power input lines without going through the B contacts of 52, since the
inverter's AC fans are supplied with power from these terminals.
(*4) Construct a sequence in which a run command is given to the inverter after
the PWM converter becomes ready to run.
(*5) Set the timer 52T at 1 sec.
(*6) Assign the external alarm THR to any of terminals [X1] to [X9] on the
inverter.
z RHC400-4C in VT mode (Applicable inverters: Three-phase 400 V,
400 kW)
z RHC500-4C and RHC630-4C (Applicable inverters: Three-phase
400 V, 500 and 630 kW)
(*1) Connect a stepdown transformer to limit the voltage of the sequence circuit
to 220 V or below.
(*2) Be sure to connect the auxiliary power input terminals R0 and T0 of the
PWM converter and the inverter to the main power input lines via B contacts
of magnetic contactors of the power supply circuit (52).
(*3) Connect the fan power input terminals R1 and T1 of the inverter to the main
power input lines without going through the B contacts of 73 or 52, since the
inverter's AC fans are supplied with power from these terminals.
(*4) Construct a sequence in which a run command is given to the inverter after
the PWM converter becomes ready to run.
(*5) Set the timer 52T at 1 sec.
(*6) Assign the external alarm THR to any of terminals [X1] to [X9] on the
inverter.
(*7) Wiring for terminals L1/R, L2/S, L3/T, R2, T2, R1, S1, and T1 should match
with the phase sequence.
Figure 11.4-8
Symbol Part name
Lr Boosting reactor
Lf Filtering reactor
Cf Filtering capacitor
Rf Filtering resistor
CU Charging box
73
Magnetic contactor for
charging circuit
Symbol Part name
Lr Boosting reactor
Lf Filtering reactor
Cf Filtering capacitor
Rf Filtering resistor
R0 Charging resistor
F Fuse
73
Magnetic contactor for
charging circuit
Symbol Part name
Lr Boosting reactor
Lf Filtering reactor
Cf Filtering capacitor
Rf Filtering resistor
R0 Charging resistor
F Fuse
73
Magnetic contactor for
charging circuit
52
Magnetic contactor for
power supply
6F
Magnetic contactor for
filtering circuit
Sym
bol
Part name
Lr Boosting reactor
Lf Filtering reactor
Cf Filtering capacitor
Rf Filtering resistor
R0 Charging resistor
F Fuse
73
Magnetic contactor for
charging circuit
52
Magnetic contactor for
power supply
6F
Magnetic contactor for
filtering circuit

 Loading...
Loading...











