Modbus Examples
Example #1
DMC-4040 connected as a Modbus master to a RIO-47120 via Modbus. The DMC-4040 will set or clear all 16 of
the RIO’s digital outputs
1. Begin by opening a connection to the RIO which in our example has IP address 192.168.1.120
IHB=192,168,1,120<502 (Issued to DMC-4040)
2. Dimension an array to store the commanded values. Set array element 0 equal to 170 and array element 1
equal to 85. (array element 1 configures digital outputs 15-8 and array element 0 configures digital outputs
7-0)
DM myarray[2]
myarray[0] = 170 (which is 10101010 in binary)
myarray[1] = 85 (which is 01010101in binary)
3. a) Send the appropriate MB command. Use function code 15. Start at output 0 and set/clear all 16 outputs
based on the data in myarray[]
MBB=,15,0,16,myarray[]
3. b) Set the outputs using the SB command.
SB2001;SB2003;SB2005;SB2007;SB2008;SB2010;SB2012;SB2014;
Results:
Both steps 3a and 3b will result in outputs being activated as below. The only difference being that step 3a will set
and clear all 16 bits where as step 3b will only set the specified bits and will have no affect on the others.
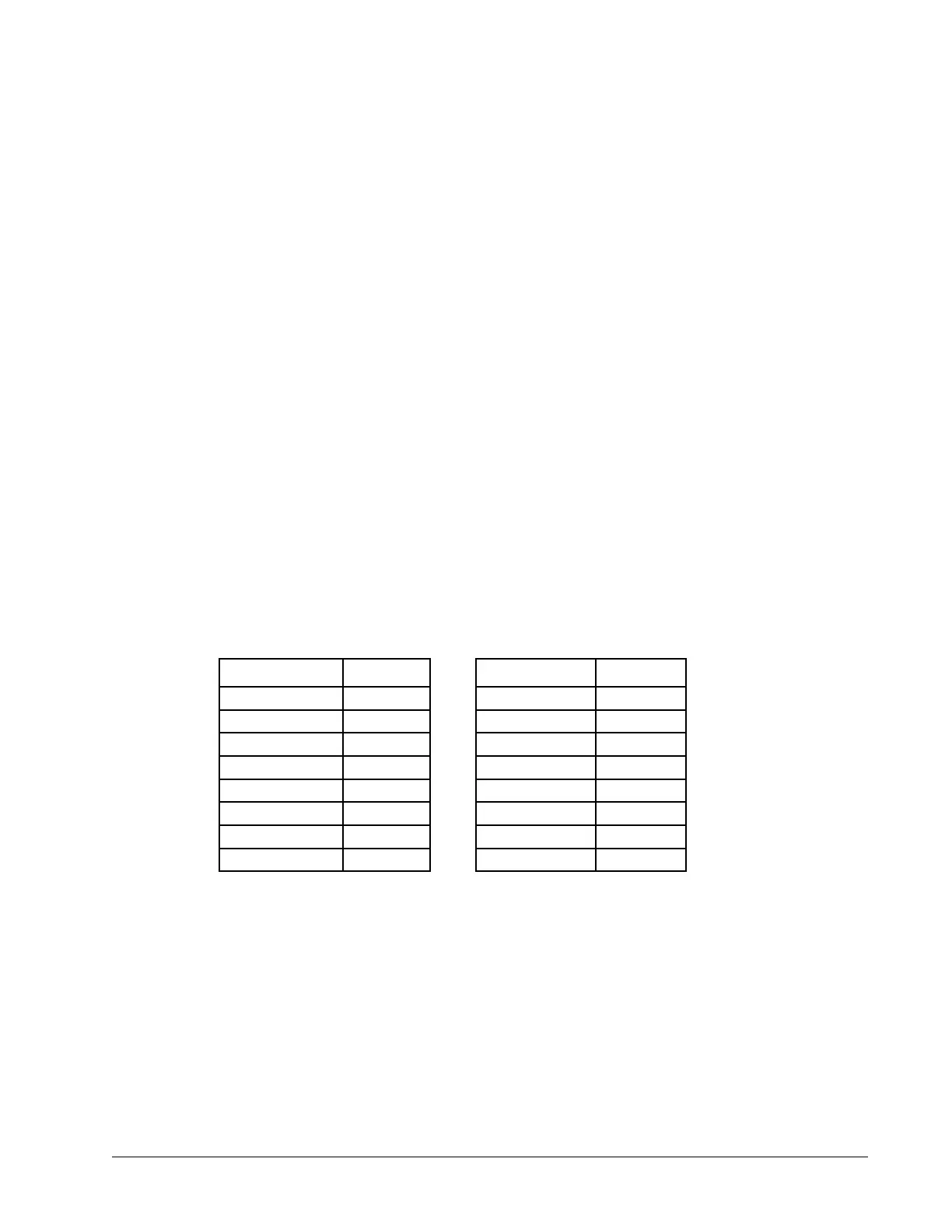
Bit Number Status Bit Number Status
0 0 8 1
1 1 9 0
2 0 10 1
3 1 11 0
4 0 12 1
5 1 13 0
6 0 14 1
7 1 15 0
Example #2
DMC-4040 connected as a Modbus master to a 3rd party PLC. The DMC-4040 will read the value of analog inputs
3 and 4 on the PLC located at addresses 40006 and 40008 respectively. The PLC stores values as 32-bit floating
point numbers which is common.
1. Begin by opening a connection to the PLC which has an IP address of 192.168.1.10 in our example
IHB=192,168,1,10<502
2. Dimension an array to store the results
DMC-40x0 User Manual Chapter 4 Software Tools and Communication • 54
 Loading...
Loading...