106
• A host that is running IGMPv1 or IGMPv2, however, cannot specify multicast source addresses in its
report. In this case, you must configure the IGMP SSM mapping feature to translate the (*, G)
information in the IGMPv1 or IGMPv2 report into (G, INCLUDE, (S1, S2...)) information.
Figure 35 Network diagram
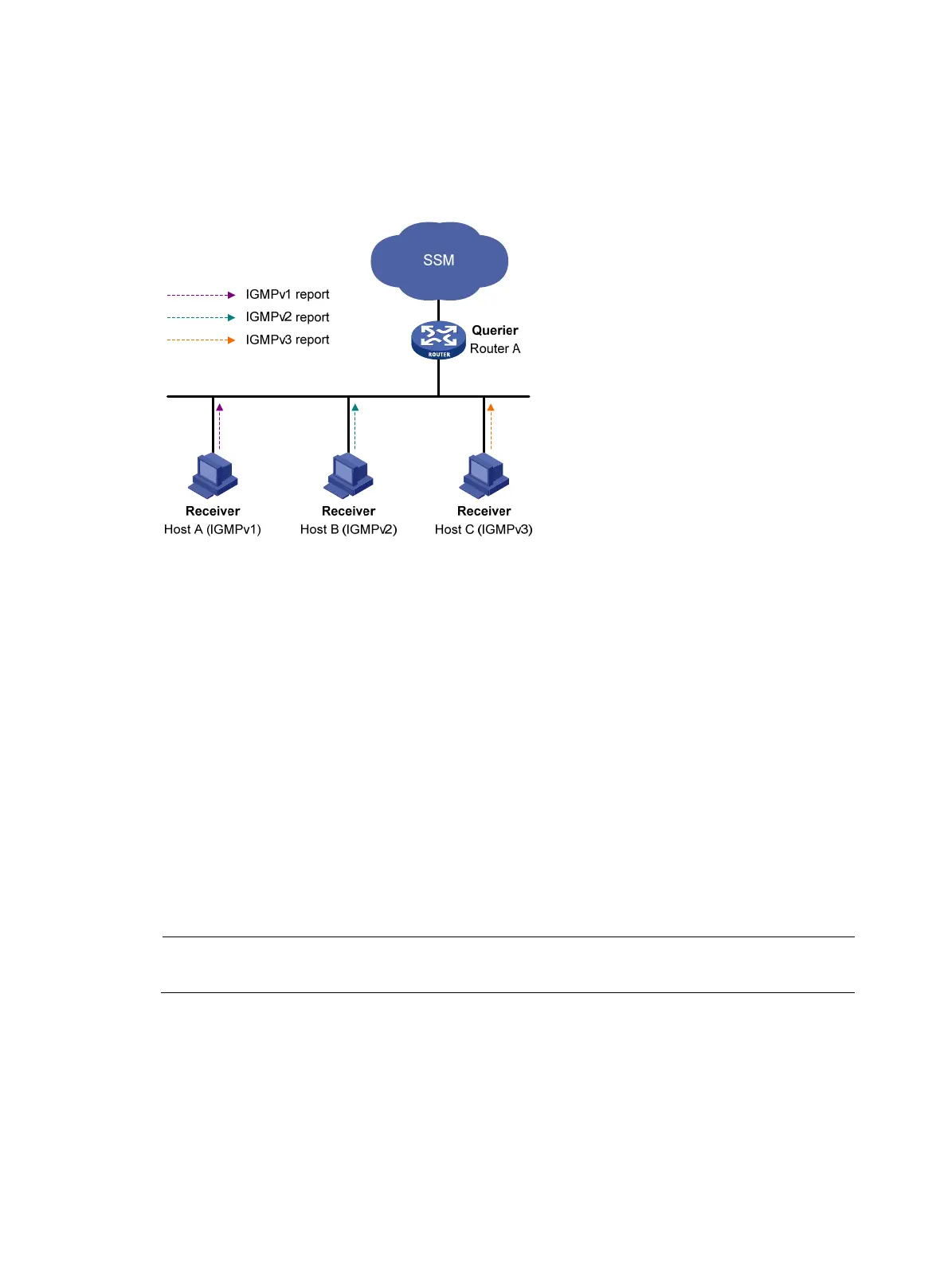
As shown in Figure 35, on an SSM network, Host A, Host B, and Host C are running IGMPv1, IGMPv2,
and IGMPv3 respectively. To provide SSM service for all the hosts if IGMPv3 is not available on Host A
and Host B, you must configure the IGMP SSM mapping feature on Router A.
With the IGMP SSM mapping feature configured, when Router A receives an IGMPv1 or IGMPv2 report,
it checks the multicast group address G carried in the message and does the following:
• If G is not in the SSM group range, Router A cannot provide the SSM service but can provide the
ASM service.
• If G is in the SSM group range but no IGMP SSM mappings that correspond to the multicast group
G have been configured on Router A, Router A cannot provide SSM service and drops the message.
• If G is in the SSM group range and the IGMP SSM mappings have been configured on Router A for
multicast group G, Router A translates the (*, G) information in the IGMP report into (G, INCLUDE,
(S1, S2...)) information based on the configured IGMP SSM mappings and provides SSM service
accordingly.
NOTE:
The IGMP SSM mapping feature does not process IGMPv3 reports.
For more information about the SSM group range, see "Configuring PIM (available only on the
S5500-EI)."
IGMP proxying
In some simple tree-shaped topologies, it is not necessary to configure complex multicast routing
protocols, such as PIM, on the boundary devices. Instead, you can configure IGMP proxying on these

 Loading...
Loading...











