RAID 6RAID 6
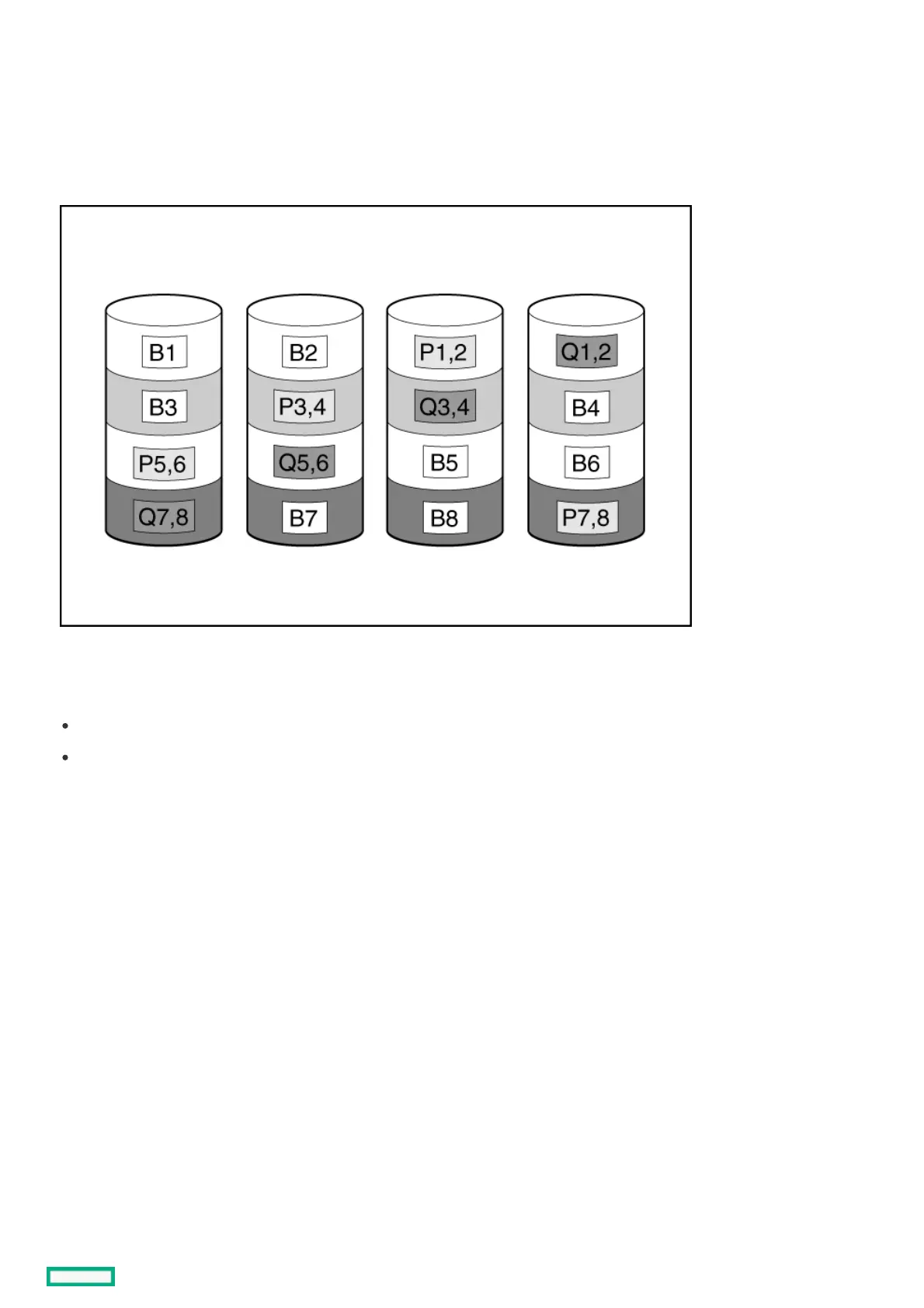
RAID 6 protects data using double parity. With RAID 6, two different sets of parity data are used (denoted by Px,y and Qx,y in the
figure), allowing data to still be preserved if two drives fail. Each set of parity data uses a capacity equivalent to that of one of the
constituent drives. The usable capacity is C x (n - 2) where C is the drive capacity with n drives in the array.
A minimum of 4 drives is required.
The maximum number of drives supported for RAID 6 is 32.
This method is most useful when data loss is unacceptable but cost is also an important factor. The probability that data loss will occur
when an array is configured with RAID 6 (Advanced Data Guarding (ADG)) is less than it would be if it were configured with RAID 5.
This method has the following benefits:
It is useful when data protection and usable capacity are more important than write performance.
It allows any two drives to fail without loss of data.
 Loading...
Loading...