122
Enable Digest Snooping on the ports of Device A and Device B that connect to Device C, so that the
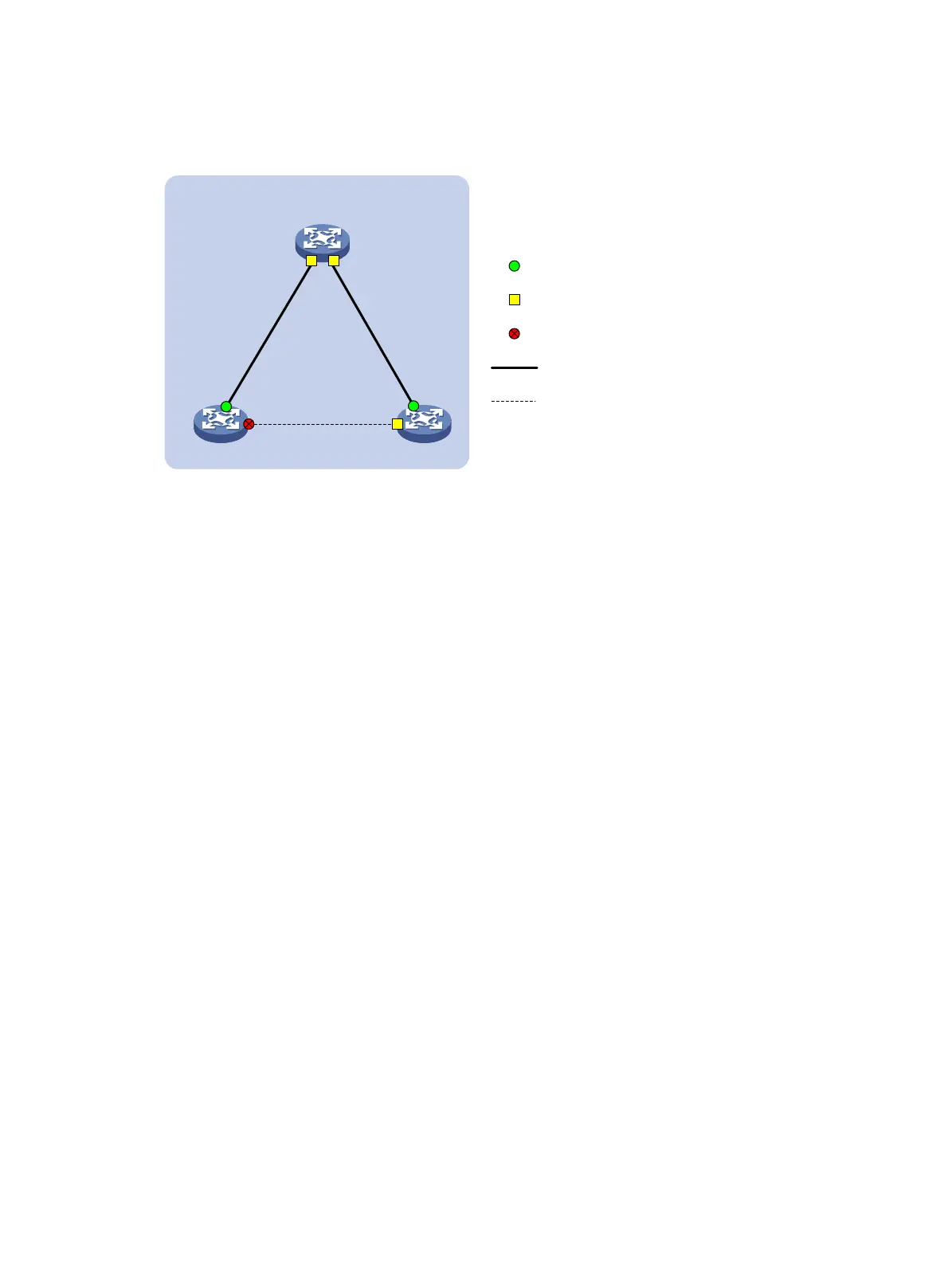
three devices can communicate with one another.
Figure 37 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
# Enable Digest Snooping on Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device A and enable global Digest
Snooping on Device A.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping
[DeviceA-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] stp global config-digest-snooping
# Enable Digest Snooping on Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device B and enable global Digest
Snooping on Device B.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping
[DeviceB-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceB] stp global config-digest-snooping
Configuring No Agreement Check
In RSTP and MSTP, the following types of messages are used for rapid state transition on
designated ports:
• Proposal—Sent by designated ports to request rapid transition
• Agreement—Used to acknowledge rapid transition requests
Both RSTP and MSTP devices can perform rapid transition on a designated port only when the port
receives an agreement packet from the downstream device. RSTP and MSTP devices have the
following differences:
• For MSTP, the root port of the downstream device sends an agreement packet only after it
receives an agreement packet from the upstream device.
• For RSTP, the downstream device sends an agreement packet whether or not an agreement
packet from the upstream device is received.
Device C
Root bridge
XGE1/0/1 XGE1/0/2
XGE1/0/1
XGE1/0/2
XGE1/0/1
XGE1/0/2
Root port
Designated port
Normal link
Blocked link
Blocked port
Device A Device B
MST region

 Loading...
Loading...














