278
Configuring L2PT
Overview
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT) can transparently send Layer 2 protocol packets from
geographically dispersed customer networks across a service provider network.
Background
Dedicated lines are used in a service provider network to build user-specific Layer 2 networks. As a
result, a customer network contains sites located at different sides of the service provider network.
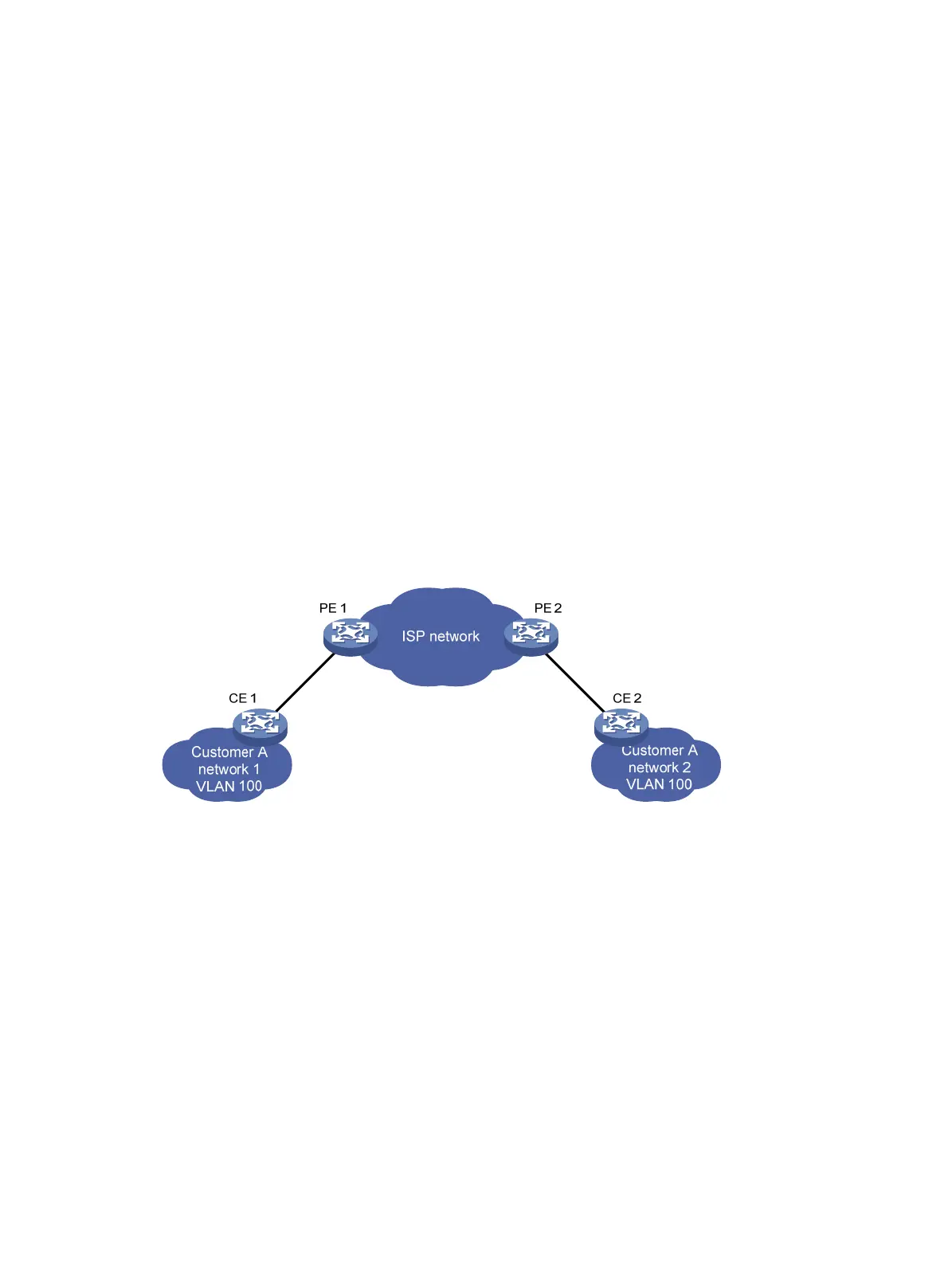
As shown in Figure 89, Custome
r A's network is divided into network 1 and network 2, which are
connected by the service provider network. For Customer A's network to implement Layer 2 protocol
calculations, the Layer 2 protocol packets must be transmitted across the service provider network.
Upon receiving a Layer 2 protocol packet, the PEs cannot determine whether the packet is from the
customer network or the service provider network. They must deliver the packet to the CPU for
processing. In this case, the Layer 2 protocol calculation in Customer A's network is mixed with the
Layer 2 protocol calculation in the service provider network. Neither the customer network nor the
service provider network can implement independent Layer 2 protocol calculations.
Figure 89 L2PT application scenarios
L2PT is introduced to resolve the problem. L2PT provides the following functions:
• Multicasts Layer 2 protocol packets from a customer network in a VLAN. Dispersed customer
networks can complete an independent Layer 2 protocol calculation, which is transparent to the
service provider network.
• Isolates Layer 2 protocol packets from different customer networks through different VLANs.
HPE devices support L2PT for the following protocols:
• CDP.
• DLDP.
• EOAM.
• GVRP.
• LACP.
• LLDP.
• MVRP.
• PAgP.

 Loading...
Loading...














