Workload and Performance
44 iSeries Handbook
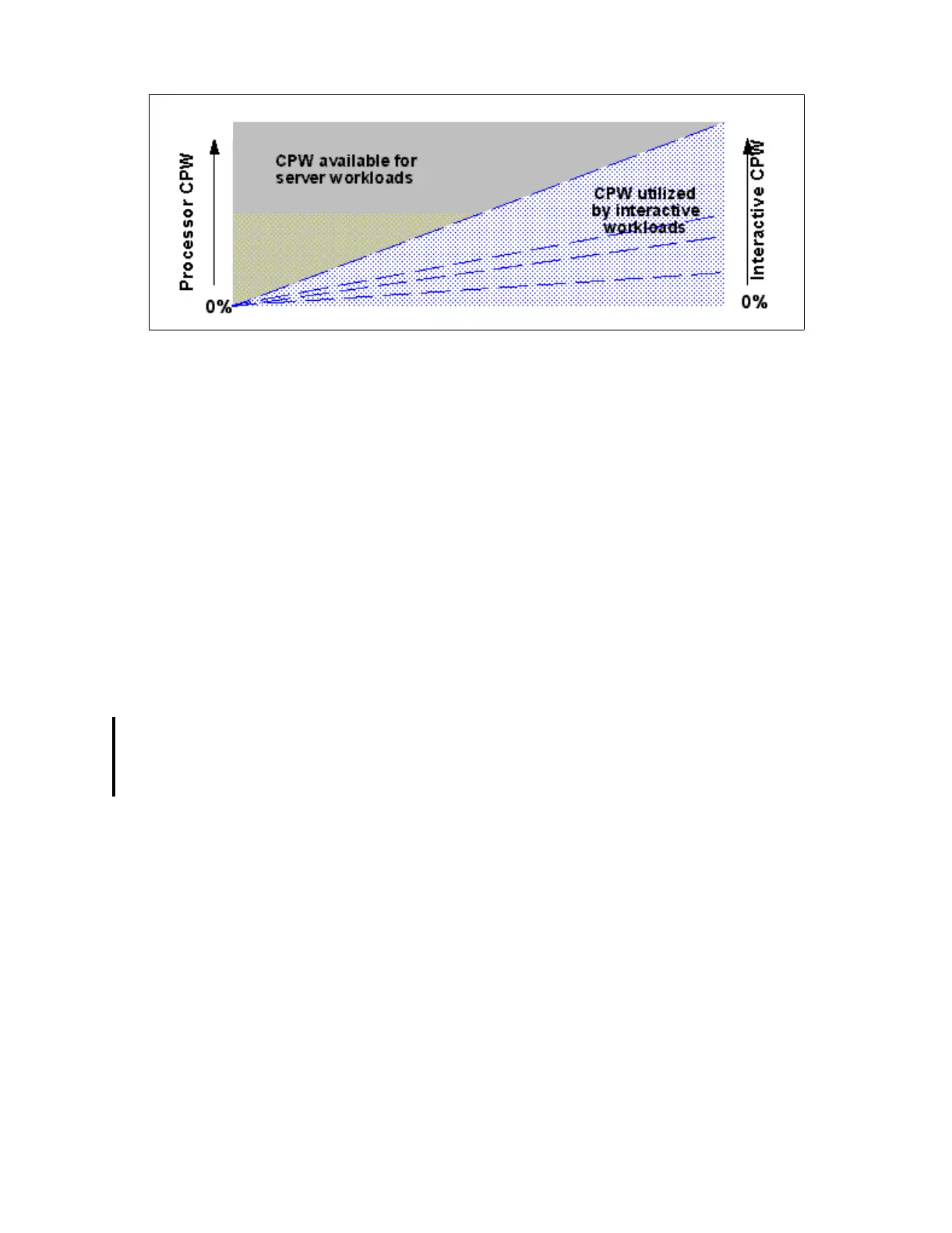
This chart shows the CPW that is available for server workloads as the interactive workload
increases. On the left side of the chart, the scale runs from 0 to 100%, which represents the
amount of Processor CPW available for server workloads (non 5250-type workload). On the
right side of the chart, a similar scale reflects the amount of Interactive CPW used by
Interactive workloads (5250 based). Each of the dotted lines dissecting the rectangle
represents various levels of Interactive CPW that can be purchased when ordering an
interactive feature for 270 and 8xx servers. Interactive features are not available on the Model
250.
At any point, the amount of CPW used to perform interactive workloads reduces the CPW
available for server workloads by an equal and proportionate amount. For example, for a
system with a processor CPW of 810 and an interactive feature CPW of 240, it is possible to
use up to 240 CPW for an interactive workload and still have 570 CPW available for the
non-interactive workload. On the other hand, if none of the AS/400e is used for interactive
workloads, all of the Processor CPW is available to perform server workloads. No tuning or
management is required.
For best performance, all critical system resources should be kept in balance with proper
configuration. This includes processors (quantity and speed), number of disk arms, amount of
memory, balanced HSL usage and more. For example, high I/O requirements on Optical HSL
may be better handled by copper HSL.
Capacity Upgrade on Demand (CUoD)
iSeries Capacity Upgrade on Demand offers the ability to non-disruptively activate one or
more additional central processors of specific models of iSeries Models 830 and 840. CUoD
adds capacity in increments of one processor, up to the maximum number of On Demand
processors built into the Model 840. CUoD has significant value for installations for customers
who want to upgrade without disruption.

 Loading...
Loading...











