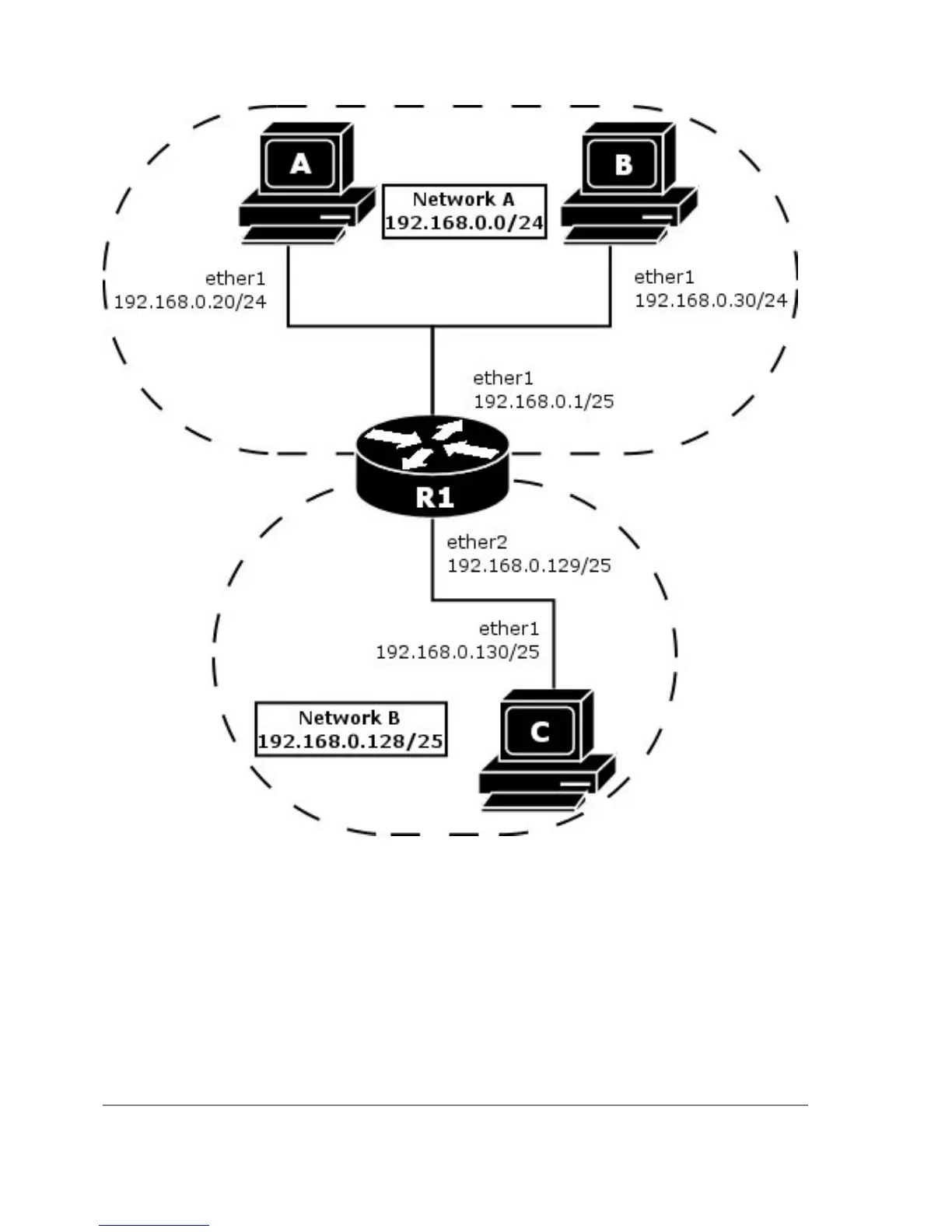
Suppose the host A needs to communicate to host C. To do this, it needs to know host's C MAC
address. As shown on the diagram above, host A has /24 network mask. That makes host A to
believe that it is directly connected to the whole 192.168.0.0/24 network. When a computer needs to
communicate to another one on a directly connected network, it sends a broadcast ARP request.
Therefore host A sends a broadcast ARP request for the host C MAC address.
Broadcast ARP requests are sent to the broadcast MAC address FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. Since the ARP
request is a broadcast, it will reach all hosts in the network A, including the router R1, but it will not
reach host C, because routers do not forward broadcasts by default. A router with enabled proxy
ARP knows that the host C is on another subnet and will reply with its own MAC adress. The router
with enabled proxy ARP always answer with its own MAC address if it has a route to the
destination.
Page 104 of 695
Copyright 1999-2007, MikroTik. All rights reserved. Mikrotik, RouterOS and RouterBOARD are trademarks of Mikrotikls SIA.
Other trademarks and registred trademarks mentioned herein are properties of their respective owners.
 Loading...
Loading...