1 DC 10.0.0.0/24 r 10.0.0.254 1 ether2
2 DC 192.168.0.0/24 r 192.168.0.254 0 ether1
3 DC 1.1.1.2/32 r 0.0.0.0 0 farsync1
[admin@MikroTik] ip route>
The configuration of the MikroTik router at the other end is similar:
[admin@MikroTik] ip address> add address 1.1.1.2/32 interface fsync \
\... network 1.1.1.1 broadcast 255.255.255.255
[admin@MikroTik] ip address> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 10.1.1.12/24 10.1.1.12 10.1.1.255 Public
1 1.1.1.2/32 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 fsync
[admin@MikroTik] ip address> /ping 1.1.1.1
1.1.1.1 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=31 ms
1.1.1.1 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms
1.1.1.1 64 byte pong: ttl=255 time=26 ms
3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 26/27.6/31 ms
[admin@MikroTik] ip address>
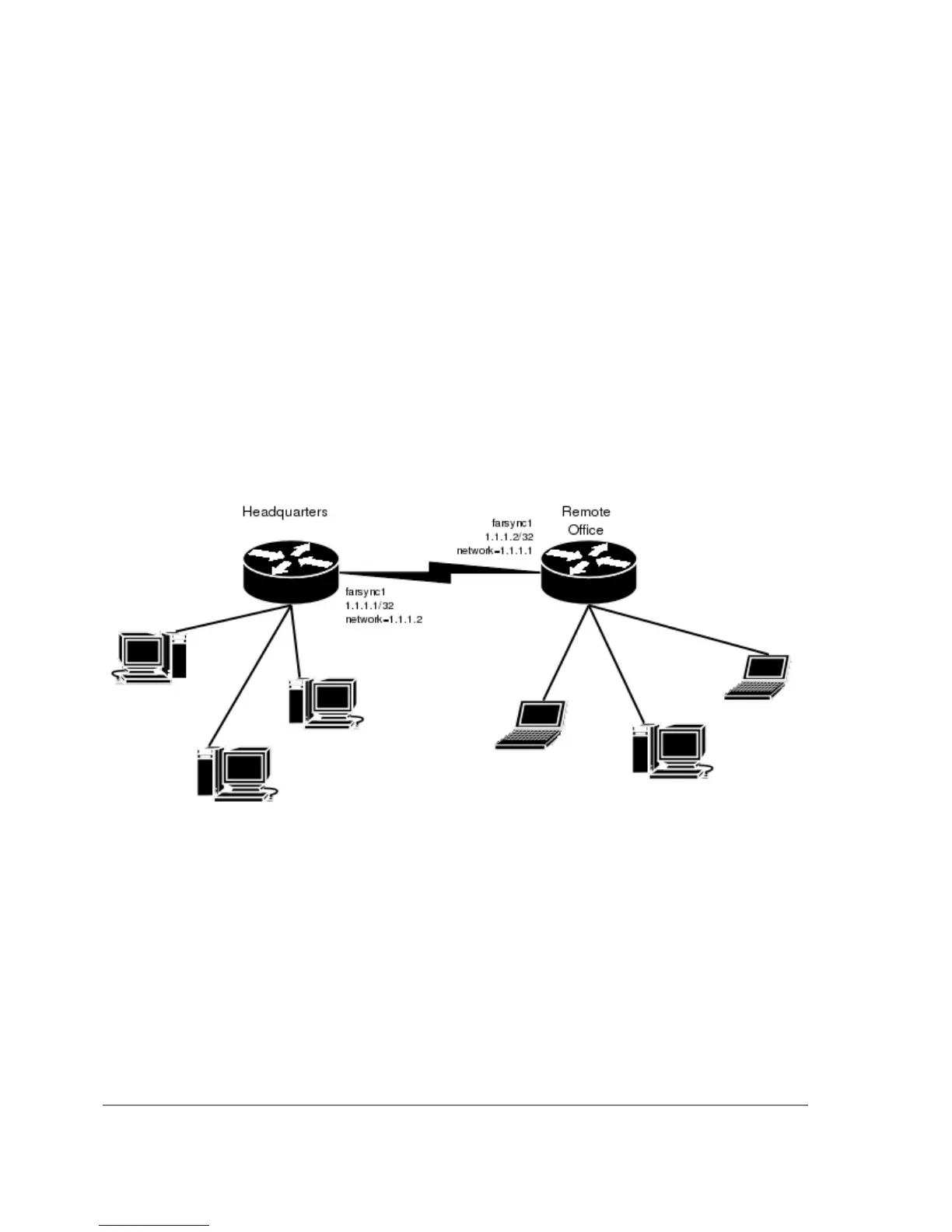
MikroTik router to MikroTik router P2P using X.21 line
Consider the following example:
The default value of the property clock-source must be changed to internal for one of the cards.
Both cards must have media-type property set to X21.
IP address configuration on both routers is as follows (by convention, the routers are named hq
and office respectively):
[admin@hq] ip address> pri
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 192.168.0.1/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 ether1
1 1.1.1.1/32 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.2 farsync1
[admin@hq] ip address>
[admin@office] ip address>
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 10.0.0.112/24 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.255 ether1
Page 192 of 695
Copyright 1999-2007, MikroTik. All rights reserved. Mikrotik, RouterOS and RouterBOARD are trademarks of Mikrotikls SIA.
Other trademarks and registred trademarks mentioned herein are properties of their respective owners.
 Loading...
Loading...