7-2 Applications
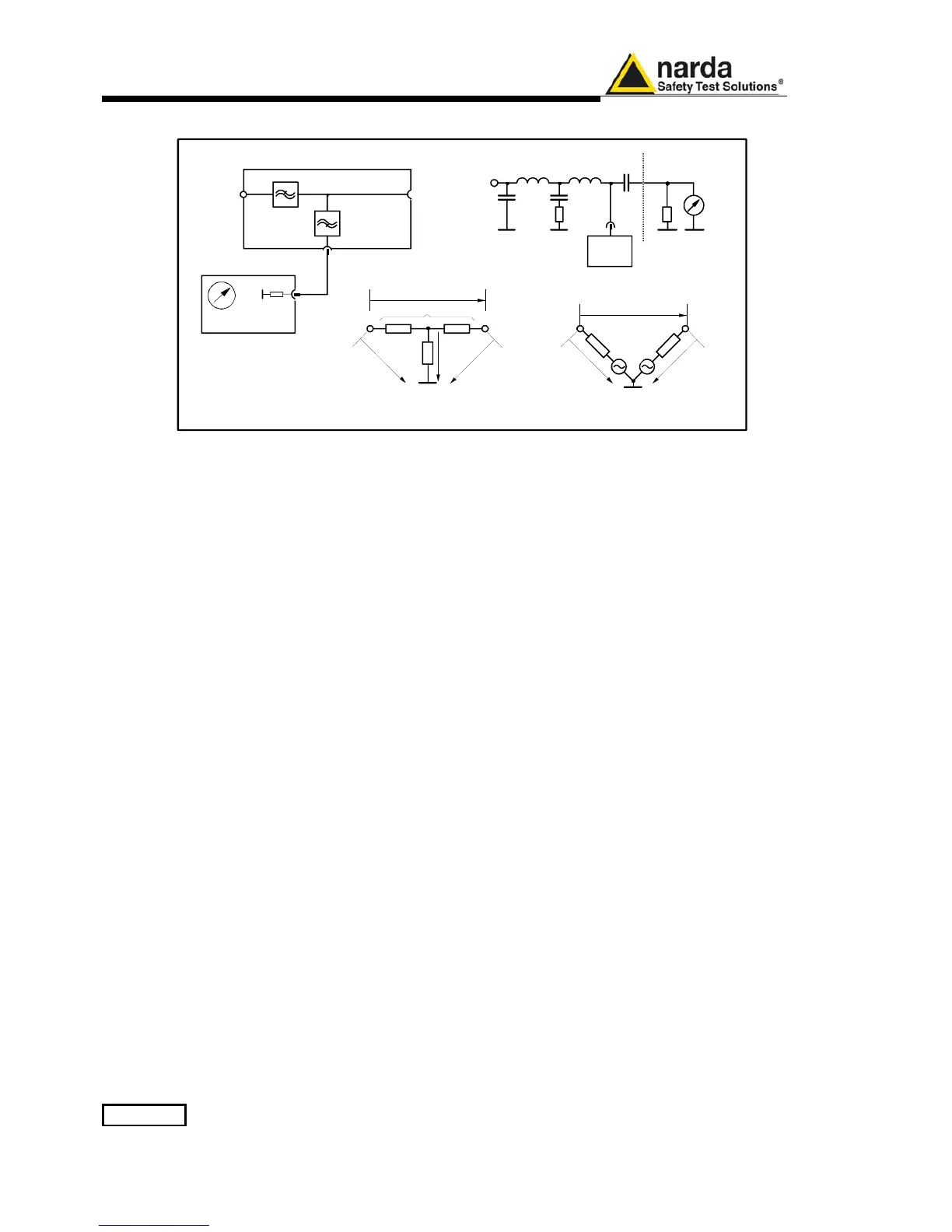
Fig. 7-1 AMN Principle: a) Δ-type or T-type LISN ; b) V-type LISN
7.1.2.1 AMN
AMNs are usually classified depending their configuration: V-type
Networks, Δ-type Networks, T-type Networks.
• The V-type Network is used for measuring the unsymmetrical RFI
voltage on AC and DC supply line. Standard impedances specified by
CISPR and other international standards are 50Ω // 50 μH+5Ω and 50Ω
// 5 μH+1Ω.
• The Δ-type Network is used for measuring the symmetrical RFI voltage
on balanced telecommunication lines. It is generally designed to permit
switchover between symmetrical and asymmetrical RFI measurements.
Its use is limited; Standards usually specify the T-type Network instead.
The most common impedance for Δ-type Network is 150Ω.
• The T-type Network is used for measuring the asymmetrical RFI
voltage on balanced (electrically symmetrical) audio frequency, control
and data lines. Standard impedance is 150Ω as well.
An Artificial Mains Network shall be designed in order to:
1. terminate each line (power, signal, etc.) of the EUT (Equipment Under
Test) with a standardized impedance;
2. permit the feeding of the EUT with the proper supply voltage and
current or with the signal and data required for operations;
3. isolate the side of the test circuit where EMI voltages are measured
against interference coming from mains network or from the auxiliary
equipment supplying the EUT with the required data;
4. provide a suitable test point – to be connected to the test receiver - to
pick up the RFI voltages from the conductor under test;
5. ensure that the impedance of the source (power, signal) is not varied in
a significant way, otherwise EUT response to the interference may
change.
lowpass
filter
highpass
filter
mains
DUT
test
receiver
RF load to
interference
DUT
50
Ω
8
μ
F
5
Ω
50
μ
H0.25
μ
F
test
receiver
mains
V-LISN
V
sym
V
asym
Z
asym
Z
sym
V
unsym
V
unsym
2
μ
F
250
μ
H
V
unsym
V
unsym
V
sym
L
1
L
2
L
1
L
2
L
1
a) b)
V-LISN
(only one
line is shown)

 Loading...
Loading...