Chapter 1. Overview
1-4
1
Overview
●
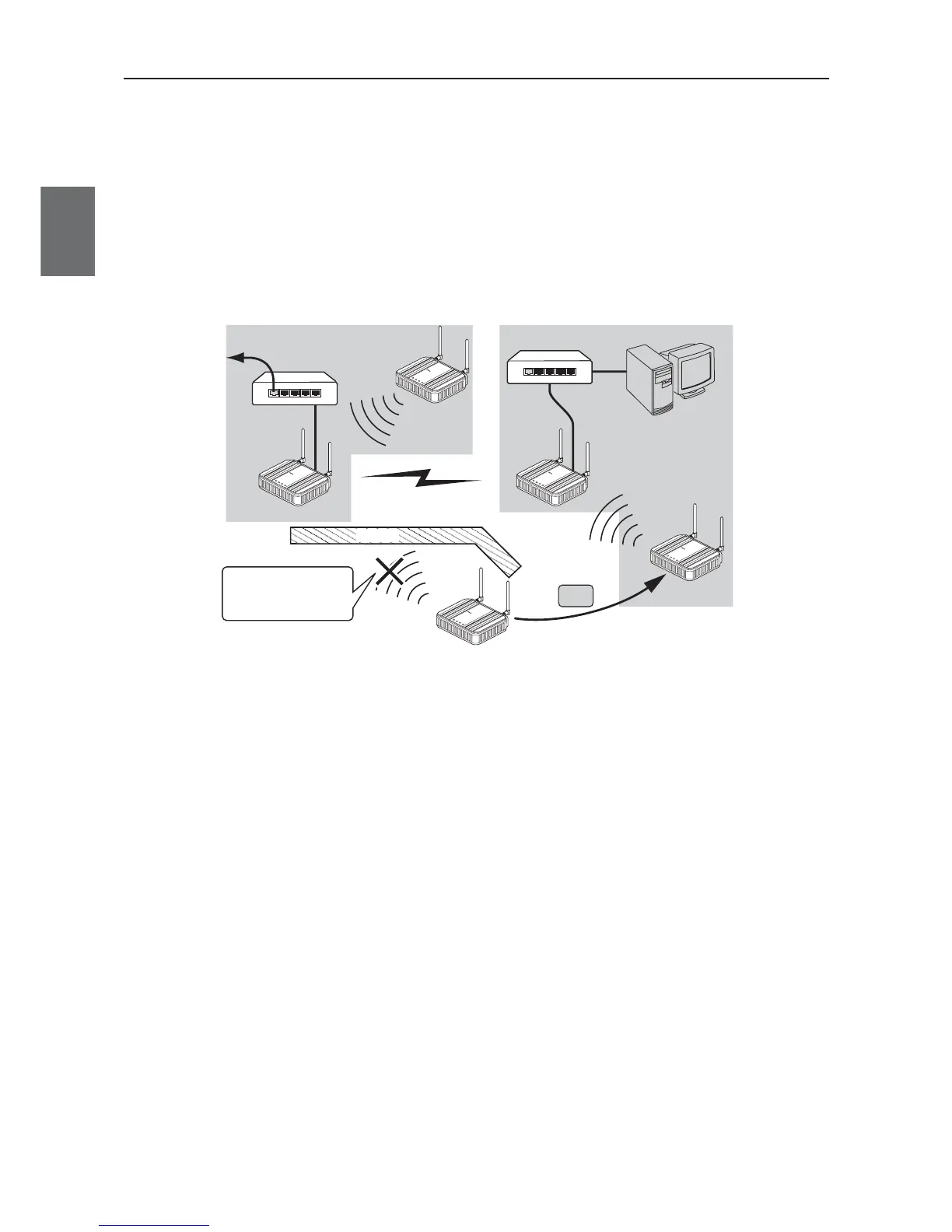
AP-to-AP (access point) bridging
In addition to communication between an access point and a client (slave), communication between access
points (between A and B in the figure) is available.This function is called AP-to-AP bridging.
AP-to-AP bridging can be up to 54Mbps [IEEE802.11a /IEEE802.11g], allowing connection between access
points.
Furthermore, an obstacle can be avoided that prevent direct communication between a client (slave, C in the
figure) and its closest access point (A), by moving close to other access point (B) without any obstacle.
This function can be used also as a relay function (P.1.9, B) to expand a communication zone by wireless
connection.
* All access points that use AP-to-AP bridging must be configured to use the same channel.
* Up to 6 units can communicate with an access point at the same time.
* To use encryption, the same encryption key must be configured for the access points.
* Only "WEP RC4" and "OCB AES" can be used as encryption for AP-to-AP bridging.
* BSSID of respective access point must be registered for those that use AP-to-AP bridging.
In the figure above, [BSSID] of [B] must be registered to [A] and [BSSID] of [A] to [B].
* Configuring the same channel and SSID allows detection of BSSID of the others, making registration easier.
* To use roaming, the same SSID must be configured for the access points (A and B).
* AP-to-AP bridging requires the same setup of Super AG (Yes or No).
* AP-to-AP bridging is not available at the channel where DFS function is provided.
 Loading...
Loading...