1-9
Chapter 1. Overview
1
Overview
■
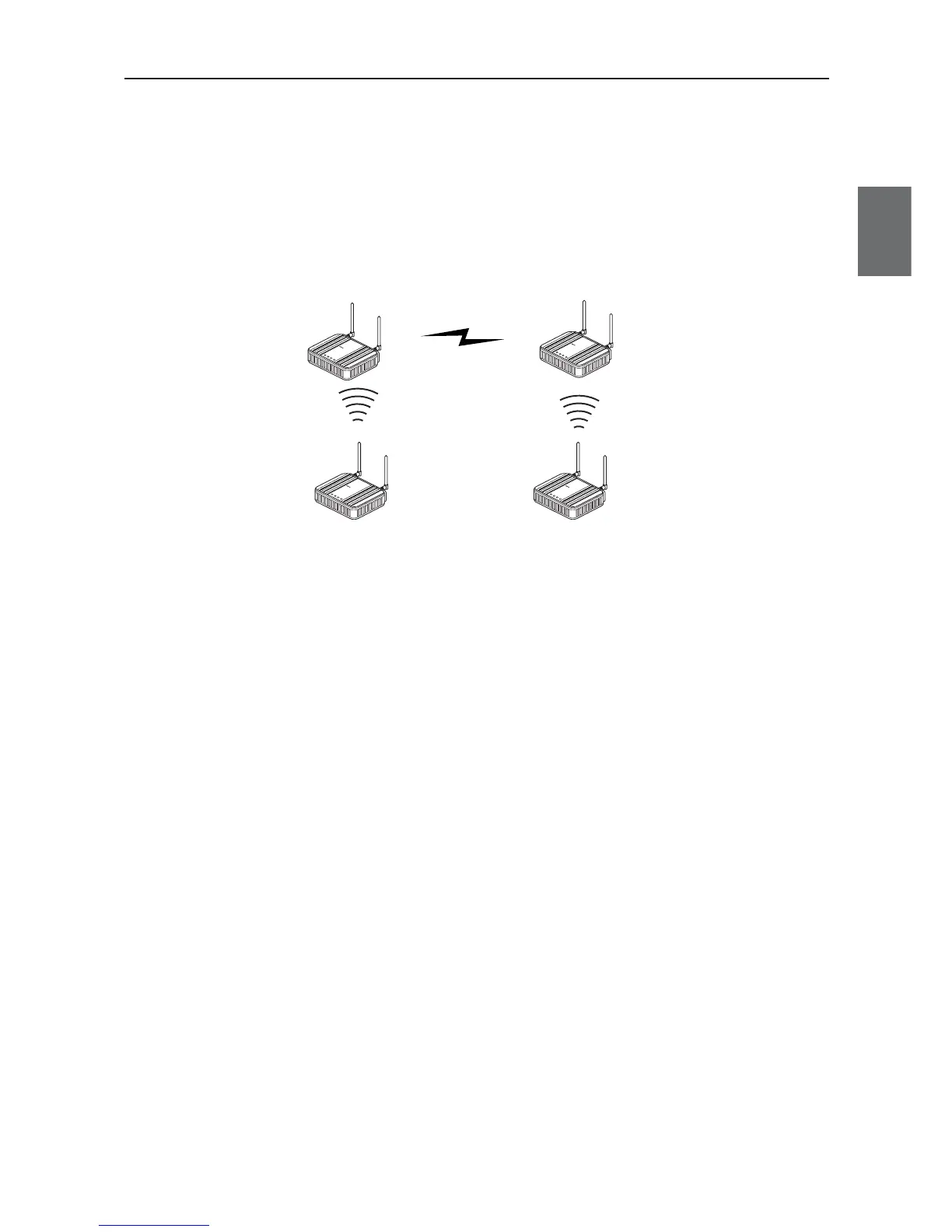
Relay Function
This function extends communication distance using other access point of AP-to-AP bridging as a wireless
repeater.
BSSID of respective access point must be registered for those that use AP-to-AP bridging.
Communication will be available between a distant access point and a client (slave) via a repeater.
* Up to 7 access points (including own unit) can be used for communication at the same time.
When one path is busy, other paths suspend communication. Because of this, all throughput is 1/6(1/ access number) by AP-to-AP
Bridging.
For the diagram of the maximum connection structure of communication AP-to-AP Bridging, see Ex 1 – 3 in “4-1 To Use AP-to-AP
Bridging” (P.4-2 and 4-3).
* All access points that use AP-to-AP bridging must be configured to use the same channel.
* For more information on AP-to-AP bridging, see "To Use AP-to-AP Bridging" (P.4-2).
Configuring the same SSID (3-3 Step 2. Configuring Wireless Network Name (SSID)(P.3-8)) allows detection of BSSID of the others,
making registration easier.
* If connection described below is made in addition to the example above, spanning tree function must be configured to avoid looping of
packets.(See P.1-5)
•A network has 3 or more wireless units using AP-to-AP bridging.
•Connecting access points (between A and B) using AP-to-AP bridging through a LAN cable
* AP-to-AP bridging is not available at the channel where DFS function is provided.
 Loading...
Loading...