EtherHaul Operation, Administration and Maintenance Manual
Page 94
Priority – determines the priority of the reference clock source in the event that
there is an equal ql among the interfaces. The priority can be any value from 1
to 254, where 1 is the highest priority.
One entry, for host, cannot be deleted and has the fixed priority of 255 (the
lowest priority).
You cannot configure more than one interface with the same pri ority.
QL-Mode – enable/disable. When ql-mode is disabled, ESMC messages are
ignored and the status is determined by the set ql-config attribute.
QL-CFG – ql config. Determines the quality level (ql) of the interface (values as in
the ql table above).
QL-Actual – R/O field. The quality level of the interface.
SSM-VID – the VLAN ID ssm messages are sent over (default none=untagged).
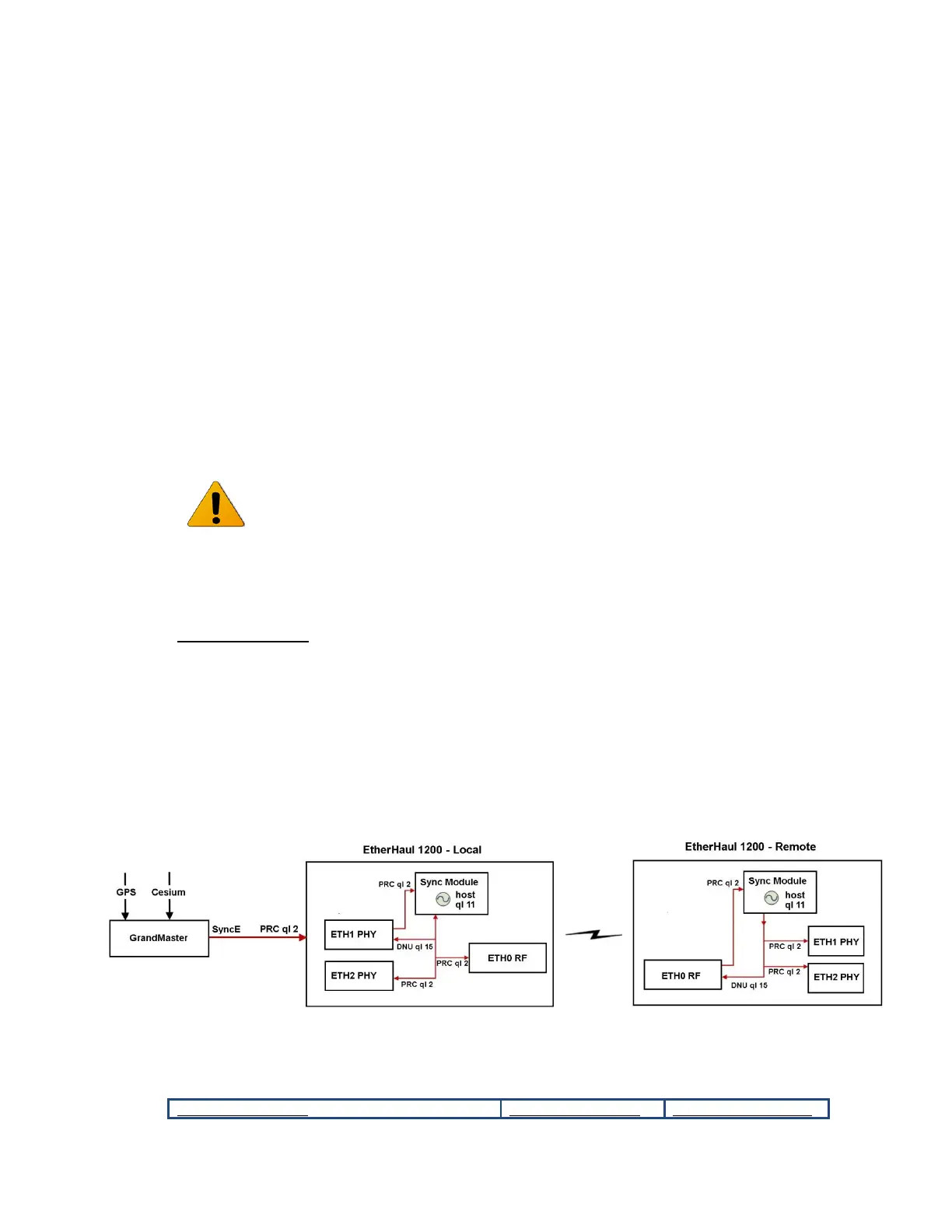
10.1.2 Typical SyncE Scenario
Normal Operation
The local EtherHaul receives timing information on Eth1 from the network (source) with
quality level PRC (2: ql-prc) and distributes it to all interfaces.
The remote EtherHaul receives timing information from the radio port (Eth0). Its quality
level is PRC (2: ql-prc).
QL-Mode is enabled, meaning quality level is extracted from the ESMC messages.
DNU (15: ql-dnu, Do Not Use) is returned to the source in order to prevent timing loops.
Figure 10-3 Typical SyncE Scenario – Normal Operation
The configuration for this scenario is:
It can take the system few minutes to lock on the new clock source after initial syncE
setup.

 Loading...
Loading...