-0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Real part (R) of Z in Ohms
Imaginary part (X) of Z in Ohms
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
^
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
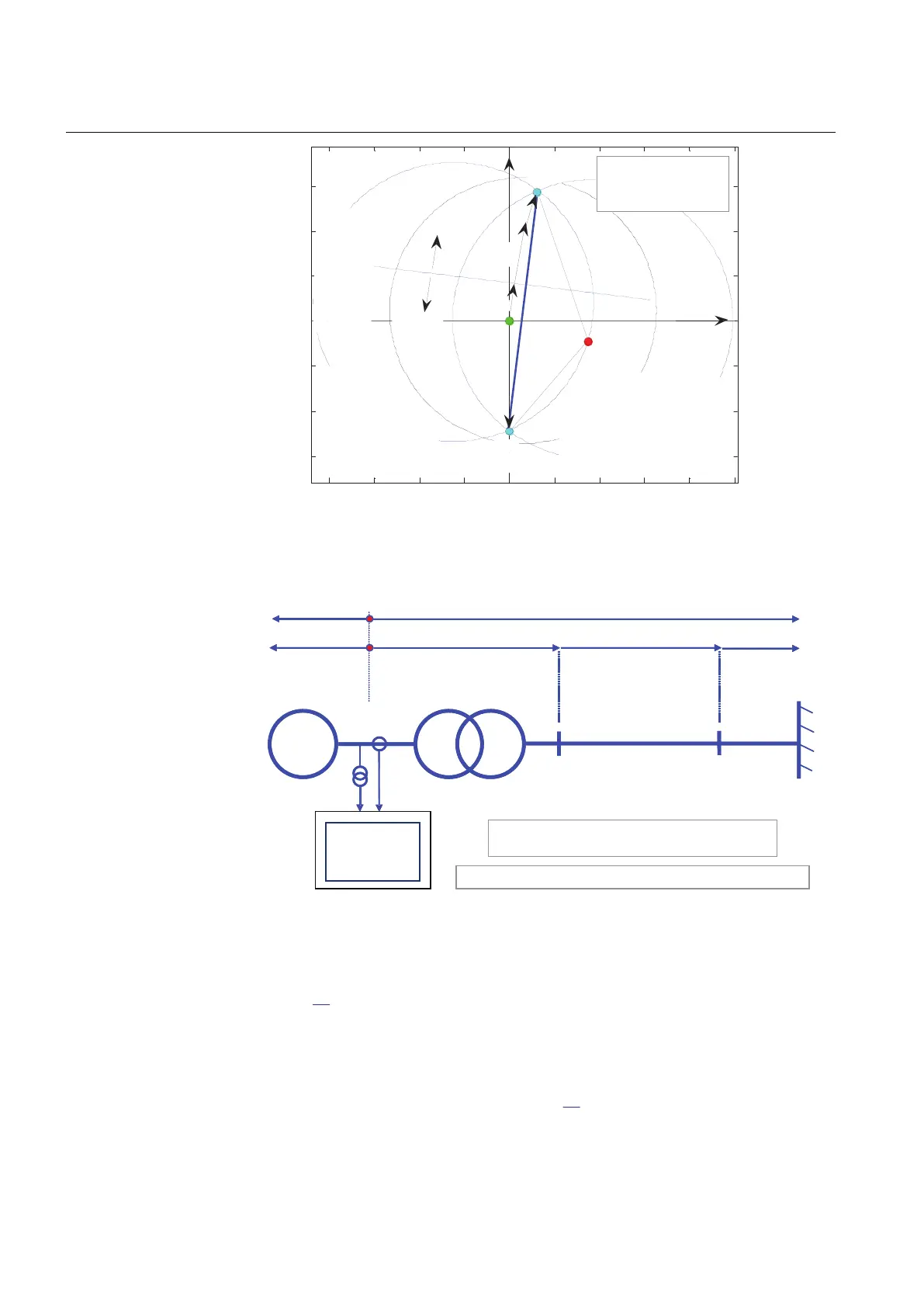
Ztr
Ze
Zgen
SE
RE
Z(R,X)
R
Zline
Zone 2
relay
←
Z-line
120°
←
Lens is the locus
of constant rotor (power)
angle, e.g. 120°.
Lens' width determined
by the setting StartAngle
X
Position of the OOS
relay is the origin of
the R - X plane
Zone 1
limit-of-reach
→
circle depends on
the position of the
points SE and RE
X-line
determined
by the
→
setting
ReachZ1
IEC10000112-1-en.vsd
IEC10000112 V1 EN-US
Figure 64: Construction of the lens characteristic for a power system
ll impedances must be referred to the generator voltage 13.8 k
ReverseZ(ReverseR, ReverseX)) ForwardZ(Forward
ll impedances must be referred to the generator voltage 13.8 k
IEC10000113 V2 EN-US
Figure 65: Example of an actual power system
To be able to automatically construct the lens characteristic for a system shown in
Figure 65, the actual power system must be modeled as a two-machine equivalent
system, or as a single machine – infinite bus equivalent system, the following
information is necessary: Zgen(Rgen, Xgen), Ztr(Rtr, Xtr), Zline(Rline, Xline),
Zeq(Req, Xeq), and the setting StartAngle , for example 120 degrees. All
impedances must be referred to the voltage level where the out-of-step protection
relay is placed; in the case shown in Figure
65 the relay is connected to the
terminals of the generator and, therefore, the previous quantities shall be referred to
Section 6 1MRK 506 382-UEN A
Impedance protection
142 Line distance protection REL650 2.2 IEC
Technical manual
 Loading...
Loading...











