4. Configuration
121
still not used. The default cannot be defined for the Data Size field as it will vary according to
selected MODBUS data type.
The configurations in the “Filters...” button, described on Table 4-85, are related to the TCP
communication filters:
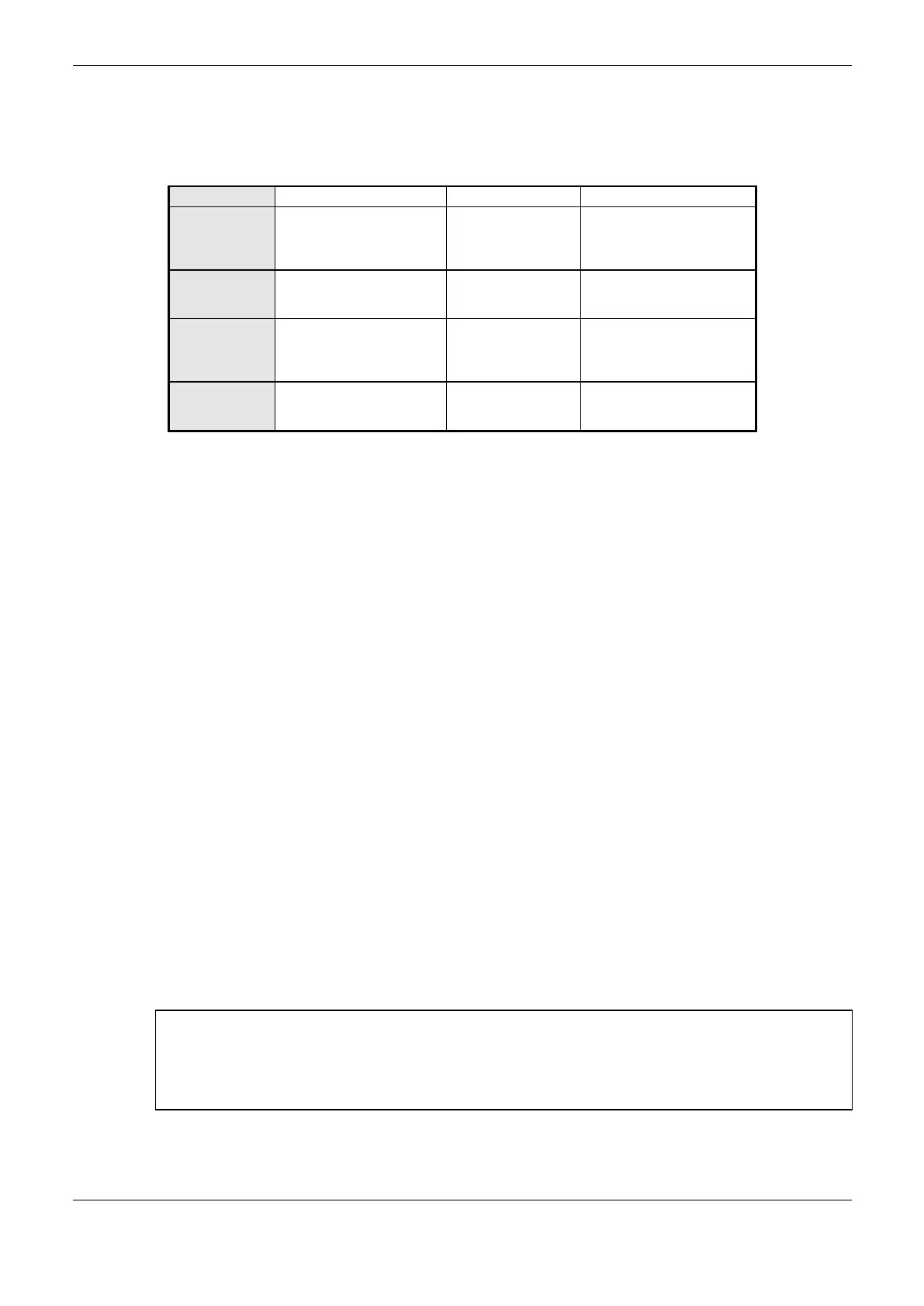
Specifies a IP interval with
writing access to the
declared variables in the
MODBUS relation
0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Specifies a subnet mask
and the parameter Write
Filter IP
0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Specifies a IP interval with
reading access to the
declared variables in the
MODBUS relation
0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Specifies a subnet mask
and the parameter Read
Filter IP
0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Table 4-85. IP Filters of Modbus Server
Note:
Filters: the filters are used to establish an IP addresses interval which have writing or reading access
in the MODBUS relations, individually configured. The permission criteria is made through an AND
logic operation between the Write Filter Mask and the client IP address. In case the result is the same
as the Write Filter IP, the client has writing right. E.g. if the Write Filter IP = 192.168.15.0 and the
Write Filter Mask = 255.255.255.0, then only clients with IP = 192.168.15.x will have writing right.
The same proceeding is applied to the Read Filter parameters to define the reading rights.
In the previously defined relations, the maximum MODBUS data size can be 65536 (maximum value
configured in the Data Size field). However, the request which arrives in the MODBUS Ethernet
Server must address a subgroup of this mapping and this group must have, at most, the data size
depending on the function code which is defined below:
Read coils (FC 1): 2000
Read input status (FC 2): 2000
Read holding registers (FC 3): 125
Read input registers (FC 4): 125
Write single coil (FC 5): 1
Write single holding register (FC 6): 1
Force multiple coils (FC 15): 1968
Write holding registers (FC 16): 123
Mask Write (FC 22): 1
Read/ Write holding registers (FC 23):
o Read: 121
o Write: 121
ATTENTION:
Differently from other application tasks, when a depuration mark in the MainTask is reached, the
task of an Ethernet Server MODBUS instance and any other MODBUS task will stop running at the
moment that it tries to perform a writing in a memory area. It occurs in order to keep the consistency
of the memory areas data while a MainTask is not running.
 Loading...
Loading...