Theory of Operation
Mode l8500C/8500C+ Operators Manual
2-5
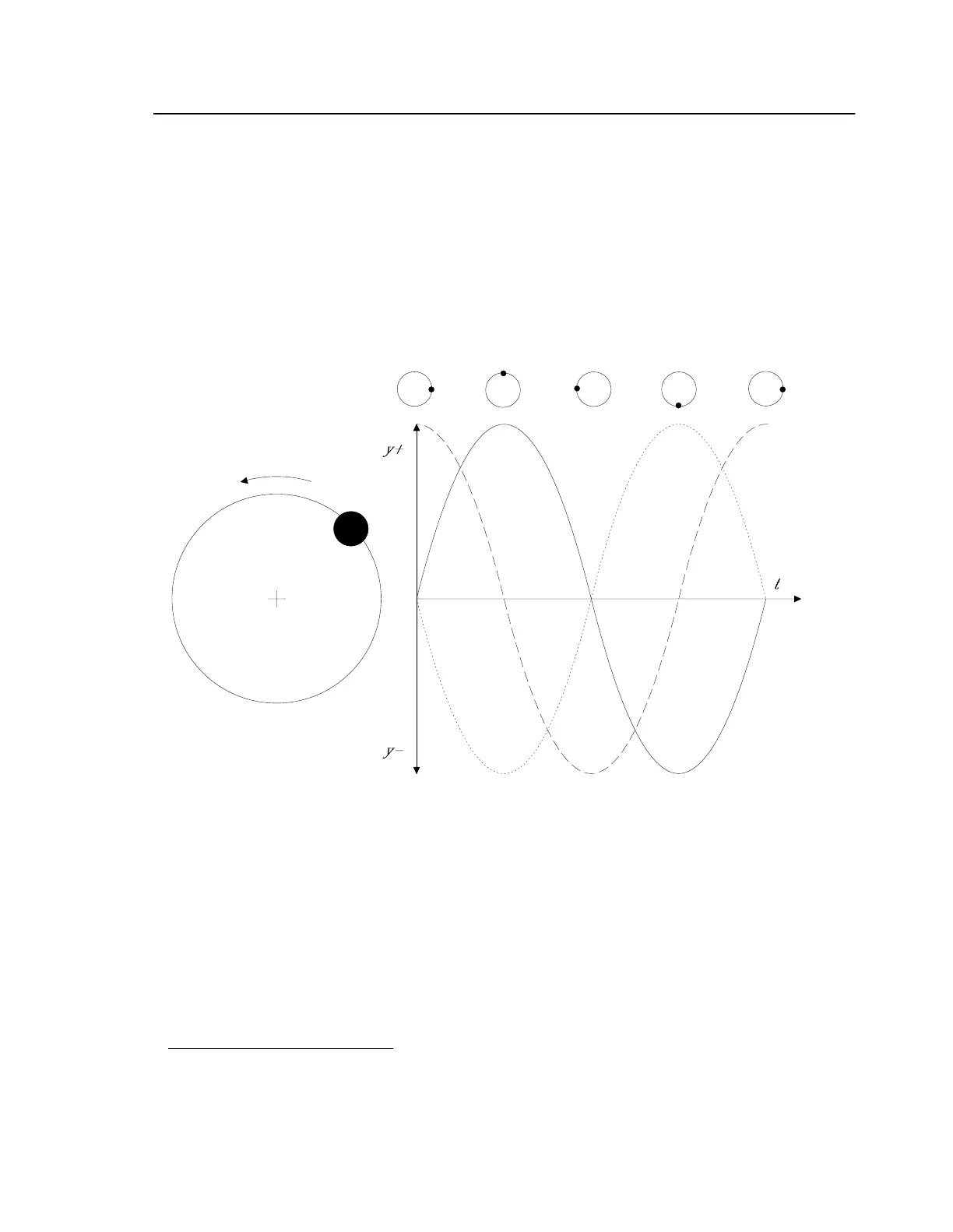
The 8500C/C+ determines the angular position and vibrational amplitude of an unbalanced rotor with
the help of a device called a
velocimete
. The Chadwick-Helmuth Mode l 7 310 Velocimeter is a
electroni
transducer
that measures displacement velocity, that is, the rate of change of displacement
with respect to time. The velocity,
v
, of a simple harmonic oscillator can be expressed mathematically
by
In this equation,
f
is the frequency of rotation,
r
the amplitude of vibration, and
θ
the phase angle. The
waveform produced by this equation can be seen in Figure2-4. No te the 90°phase shift from th
displacement waveform.
Figure 2-4. Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration in an Imbalanced Hub
A velocimeter is usually attached directly to a rotor system's support structure and oriented in th
direction of the vibration. It generates an electrical signal whose voltage varies from plus to minus as
the support structure moves up and down during each revolution. This varying voltage is directly
proportional to the amplitude of vibration and actually represents the physical motion of the point
where the velocimeter is attached. The 8500C/C+ samples this signal and transforms it, using fast
Fourier transform (FFT) software techniques. Then, the 8500C/C+ extracts the frequency component
of the vibration, otherwise called th
balance frequency
of the system.
1
1. Out-of-balance rotors are often subjected to several different kinds of vibration. The 8500C/C+
extracts a profile of these different vibration amplitudes across a broad range of frequencies and
displays the values in a plot of frequency against amplitude. The largest of the peaks is usually the
balance frequency of the lateral mass imbalance. This frequency must be selected by the user before
the balance can continue.
v2
π
fr
θ
cos=
0
Acceleration
Displacement
Velocity
 Loading...
Loading...