347
Configuring MSTP
How to Configure MSTP
Configuring the Root Switch
Before You Begin
After configuring the switch as the root switch, we recommend that you avoid manually configuring the hello time,
forward-delay time, and maximum-age time through the spanning-tree mst hello-time, spanning-tree mst
forward-time, and the spanning-tree mst max-age global configuration commands.
This task is optional.
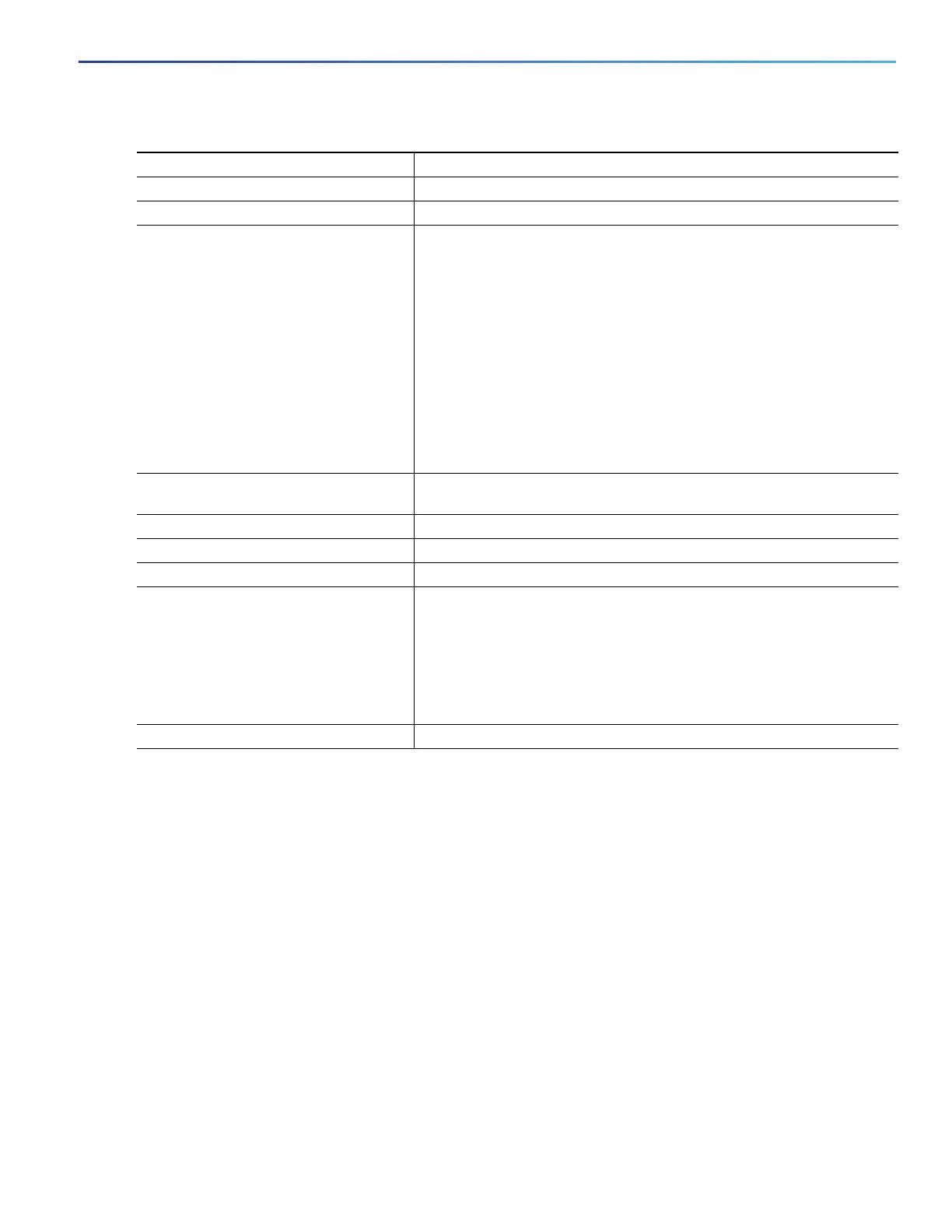
Command Purpose
1. configure terminal Enters global configuration mode.
2. spanning-tree mst configuration Enters MST configuration mode.
3. instance instance-id vlan vlan-range Maps VLANs to an MST instance.
instance-id—range is 0 to 4096.
vlan vlan-range—range is 1 to 4096.
When you map VLANs to an MST instance, the mapping is
incremental, and the VLANs specified in the command are added to
or removed from the VLANs that were previously mapped.
To specify a VLAN range, use a hyphen; for example, instance 1 vlan
1-63 maps VLANs 1 through 63 to MST instance 1.
To specify a VLAN series, use a comma; for example, instance 1 vlan 10,
20, 30 maps VLANs 10, 20, and 30 to MST instance 1.
4. name name Specifies the configuration name. The name string has a maximum length
of 32 characters and is case sensitive.
5. revision version Specifies the configuration revision number. The range is 0 to 65535.
6. show pending Verifies your configuration by displaying the pending configuration.
7. exit Applies all changes, and returns to global configuration mode.
8. spanning-tree mode mst Enables MSTP. RSTP is also enabled.
Caution: Changing spanning-tree modes can disrupt traffic because
all spanning-tree instances are stopped for the previous mode and
restarted in the new mode.
You cannot run both MSTP and PVST+ or both MSTP and rapid PVST+ at
the same time.
9. end Returns to privileged EXEC mode.

 Loading...
Loading...