851
Configuring IP Unicast Routing
Configuring BGP
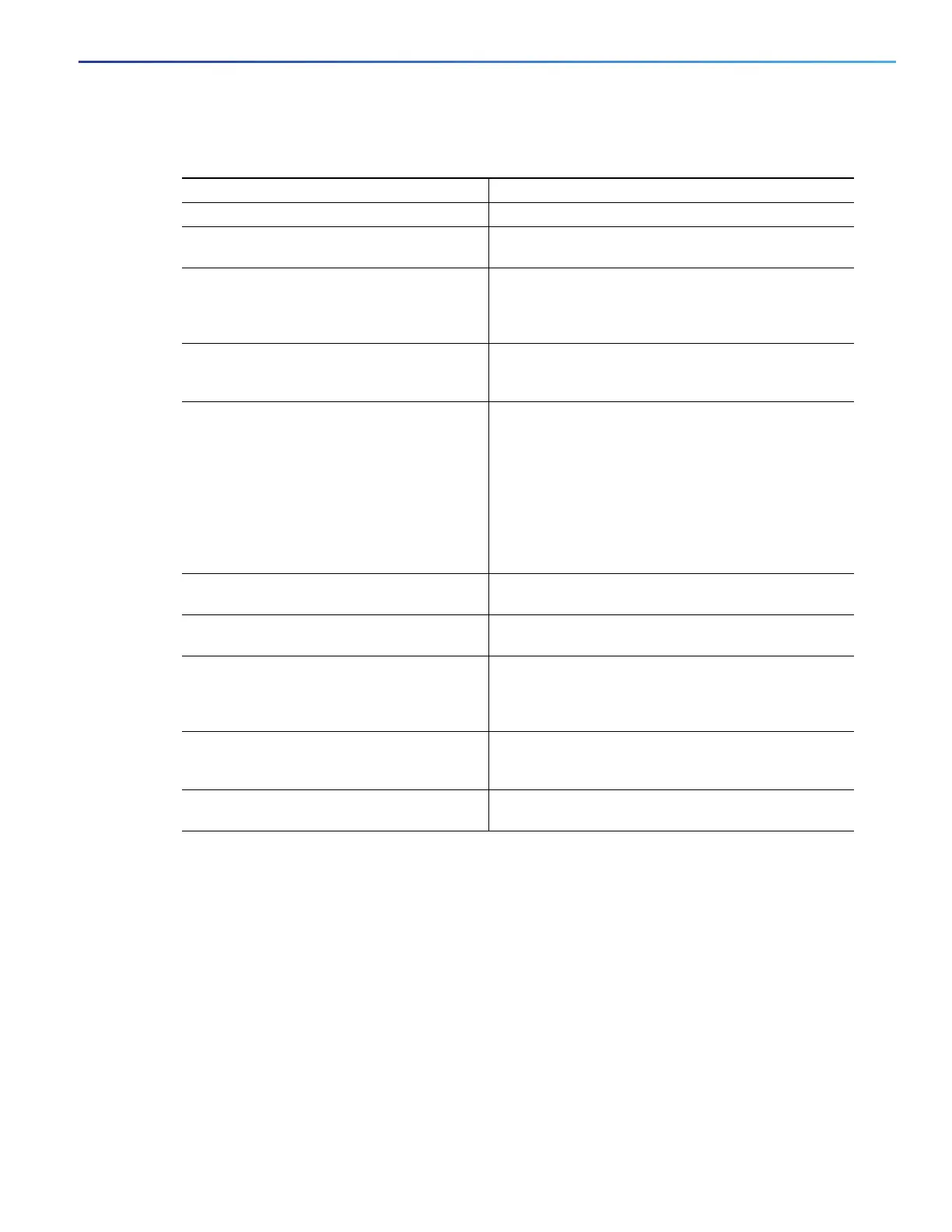
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
1. configure terminal Enter global configuration mode.
2. ip routing Enable IP routing (required only if IP routing is
disabled).
3. router bgp autonomous-system Enable a BGP routing process, assign it an AS number,
and enter router configuration mode. The AS number
can be from 1 to 65535, with 64512 to 65535
designated as private autonomous numbers.
4. network network-number [mask
network-mask] [route-map
route-map-name]
Configure a network as local to this AS, and enter it in
the BGP table.
5. neighbor {ip-address | peer-group-name}
remote-as number
Add an entry to the BGP neighbor table specifying that
the neighbor identified by the IP address belongs to
the specified AS.
For EBGP, neighbors are usually directly connected,
and the IP address is the address of the interface at the
other end of the connection.
For IBGP, the IP address can be the address of any of
the router interfaces.
6. neighbor {ip-address | peer-group-name}
remove-private-as
(Optional) Remove private AS numbers from the
AS-path in outbound routing updates.
7. no synchronization (Optional) Disable synchronization between BGP and
an IGP.
8. no auto-summary (Optional) Disable automatic network summarization.
By default, when a subnet is redistributed from an IGP
into BGP, only the network route is inserted into the
BGP table.
9. bgp fast-external-fallover (Optional) Automatically reset a BGP session when a
link between external neighbors goes down. By
default, the session is not immediately reset.
10. bgp graceful-restart (Optional) Enable NSF awareness on switch. By
default, NSF awareness is disabled.

 Loading...
Loading...