SMP300 Series • Reference Information 142
Sending commands using a TCP/IP connection
1. Configure the network settings of a control PC to connect it to the same network as the
SMP300 Series. Connect the control PC to the network with an RJ‑45 cable.
2. Start the DataViewer program (see Start the DataViewer program on page141) and
follow the steps to connect to the SMP300 Series via TCP/IP.
3. On the Communication Setup window (see figure95):
1. Select the TCP/IP tab.
2. Enter the IP address of the SMP300 Series into the Hostname/IP Address field.
3. In the Telnet Port field, enter the port number for the connection.
NOTE: The default telnet port for SIS commands is port23.
4. Click OK. The Communication Setup dialog closes.
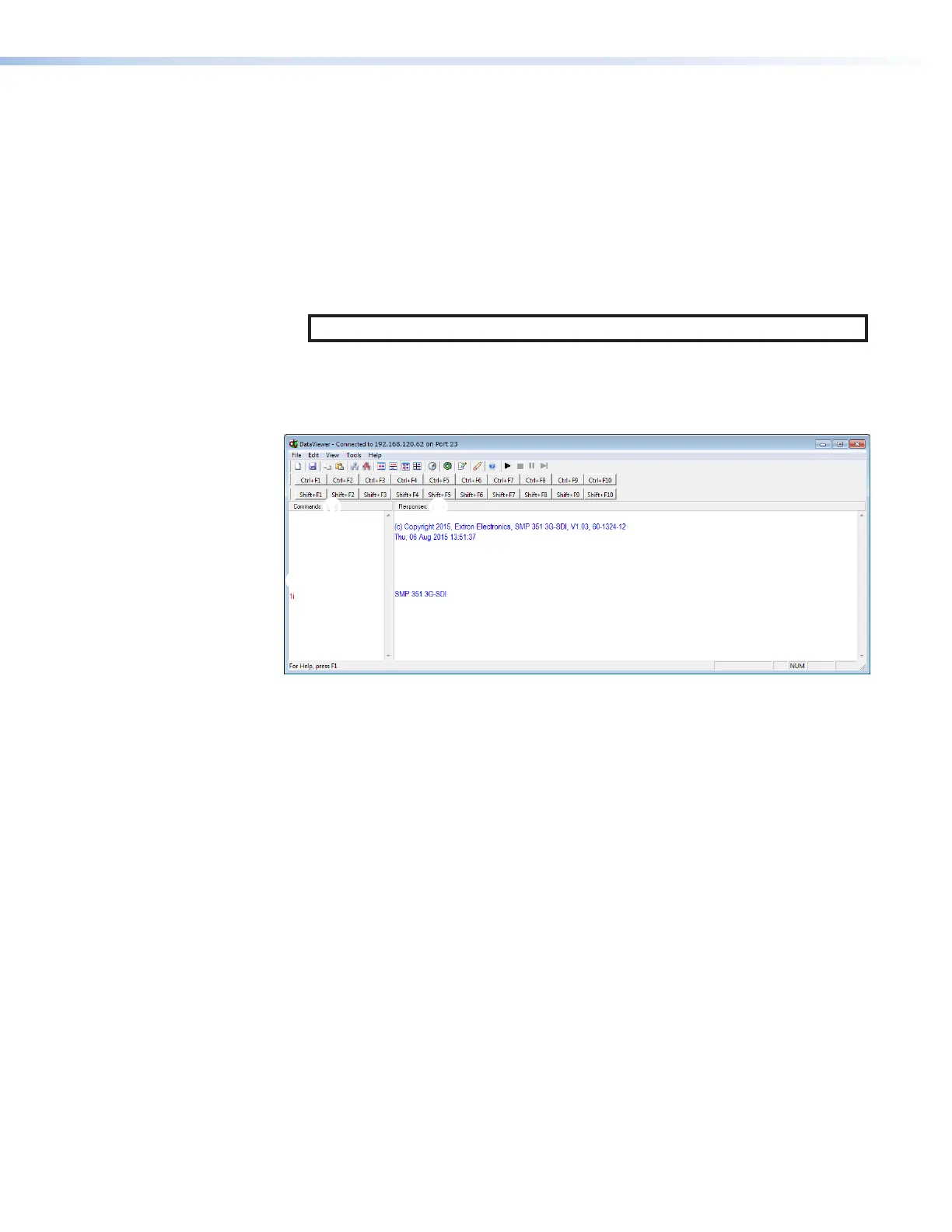
The main DataViewer dialog opens and the SMP300 Series responds with a copyright
statement containing the model number, part number, and current firmware version of
the connected SMP300 Series, along with the date (see figure96,
2
).
11 22
3
3 44
Figure 96. Enter Commands and View Responses
5. Use the Commands field to enter SIS commands (see figure96,
1
). View the responses
in the Responses field (
2
).
For example, enter 1I, the command to display the model name, in the Commands field
(
3
). The Responses field (
4
) returns the model name and number of the connected
device.
What is an IP Address?
A full explanation of IP addressing is beyond the scope of this user guide. However, the
following information is enough to get started.
An IP address is a 32‑bit binary number used to identify each device on an Ethernet
network. This number is usually represented by four decimal numbers (each in the range
0to 255) separated by dots, (for example, 198.123.34.240). This is called "dotted decimal
notation".
An IP address is divided into two parts:
• The network identifier
• The host identifier
On a given network, each address must have the same network identifier value, but have a
unique host identifier. There are, therefore, different classes of addresses that define:
• The range of valid addresses.
96
 Loading...
Loading...