SMP300 Series • Reference Information 143
• The parts of the address used to identify the network and host.
The most common IP address classes are:
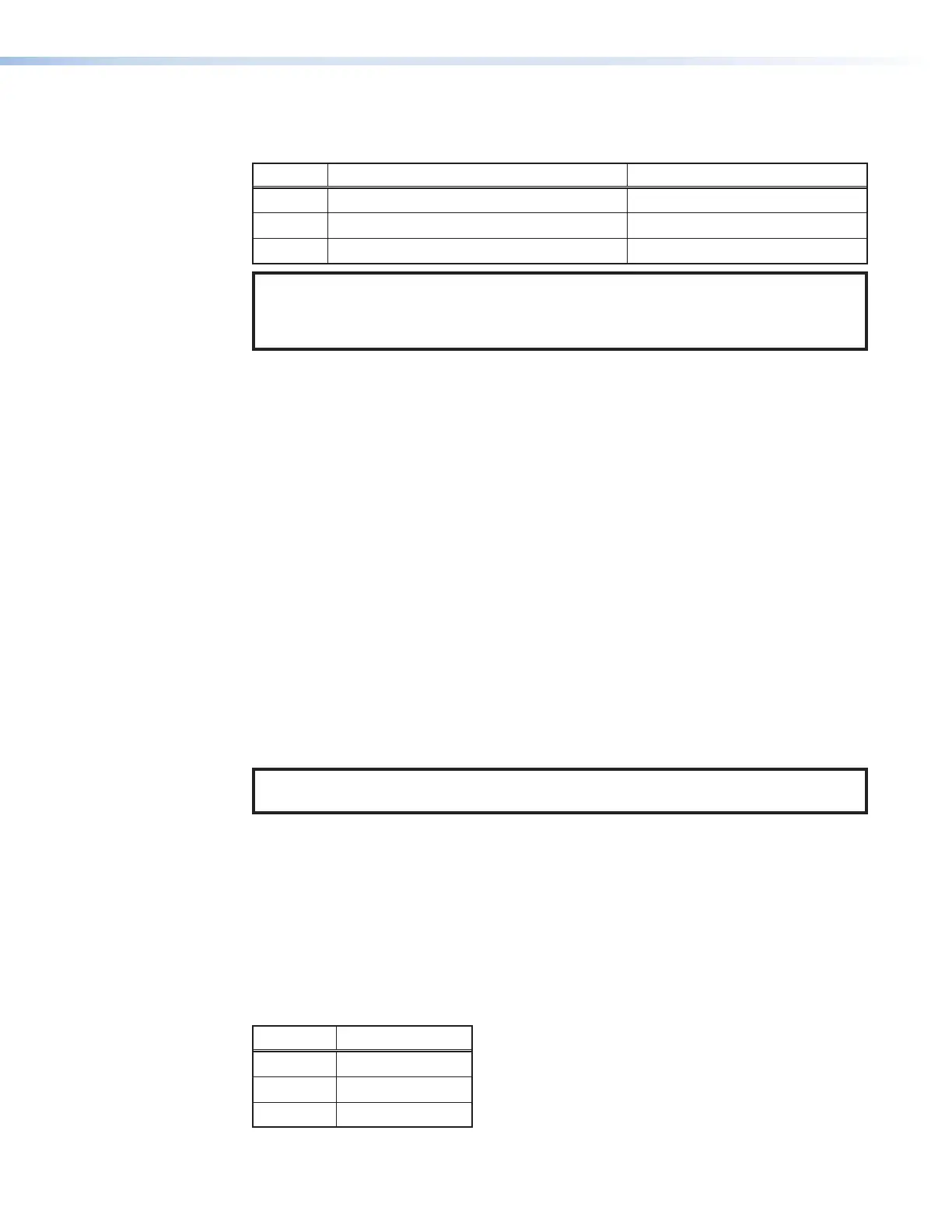
Class Valid Address Range Identifier Arrangement
Class A
0.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.254
NNN.HHH.HHH.HHH
Class B
128.0.0.1 through 191.255.255.254
NNN.NNN.HHH.HHH
Class C
192.0.0.1 through 223.255.255.254
NNN.NNN.NNN.HHH
NOTES:
• NNN = Network identifier
• HHH = Host identifier
Private and Public Address Ranges
Within each of the classes are a range of addresses designated as "private" addresses.
These addresses should only be used on private local networks and intranets and cannot
be accessed directly from the Internet.
• 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
• 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
• 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
• 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
Addresses outside these ranges are considered "public".
Multicast Address Range
A further range of addresses is available for private multicast domain use:
• 239.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
These addresses (also known as class D addresses) are used to allow several devices to be
part of the same multicast group. Each device in the group has the same multicast address
and can effectively send data to all other devices in the same group simultaneously.
NOTE: The SMP uses 239.199.188.138 as the default multicast address for the
archive stream and 239.199.188.142 as the confidence stream default.
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask is a 32‑bit binary number used to "mask" certain bits of the IP address. It
extends the number of network options available for the IP address. The subnet mask does
this by allowing part of the host identifier to be used as a subnetwork identifier.
It is important that the correct value is used for the subnet mask. The value of the subnet
mask is dependent on the IP address class being used. Use the table below and the table
in the What is an IP Address? section on page142 to select the subnet mask class that
matches the IP address class.
Class Subnet Mask
Class A
255.0.0.0
Class B
255.255.0.0
Class C
255.255.255.0

 Loading...
Loading...