5
The command string represented by an alias can include up to nine parameters. Each parameter
starts with the dollar sign ($) and a sequence number in the range of 1 to 9. For example, you can
configure the alias shinc for the command display ip $1 | include $2. Then, to execute the display
ip routing-table | include Static command, you can enter shinc routing-table Static. To execute
the display ip interface | include GigabitEthernet1/0/1 command, you can enter shinc interface
GigabitEthernet1/0/1.
To use a command alias for a command that has parameters, you must specify a value for each
parameter. If you fail to do this, the system informs you that the command is incomplete and displays
the command string represented by the alias.
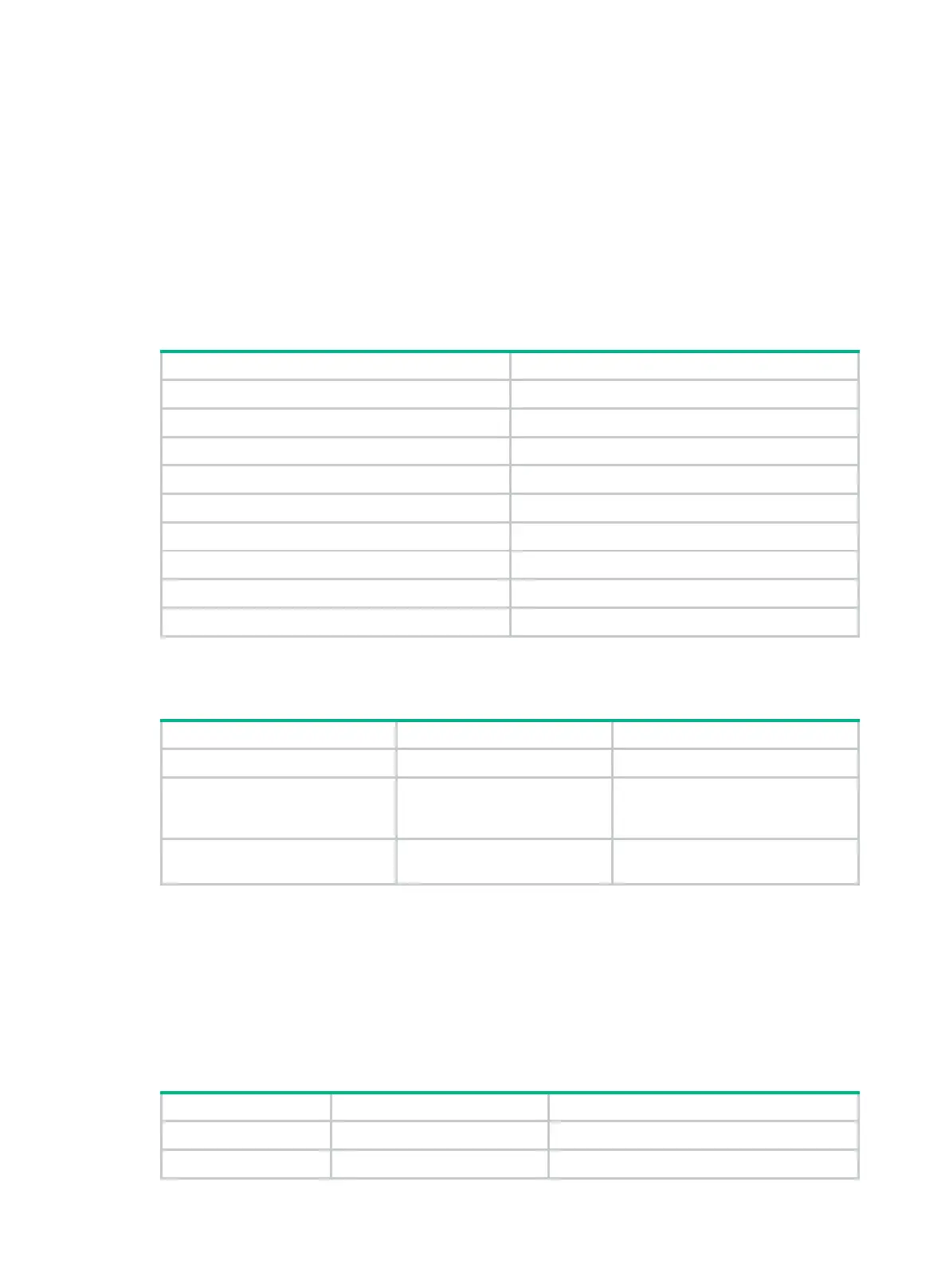
Table 2 lists the system-defined command aliases.
Table 2 System-defined command aliases
access-list acl
end return
erase delete
exit quit
logging info-center
no undo
show display
write save
Configuration procedure
To configure a command alias:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Configure a command alias.
alias
alias command
By default, the device has a set of
system-
as shown in Table 2.
3. (Optional.) Display command
aliases.
display alias
[
alias
]
This command is available in any
view.
Configuring and using command hotkeys
The system defines the hotkeys shown in Table 3 and provides five configurable command hotkeys.
Pressing a command hotkey is the same as entering a command.
If a hotkey is also defined by the terminal software you are using to interact with the device, the
terminal software definition takes effect.
To configure a command hotkey:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Assign a command
hotkey
{
ctrl_g
|
ctrl_l
|
ctrl_o
|
The following are the defaults:

 Loading...
Loading...



















