69
Configuring FTP
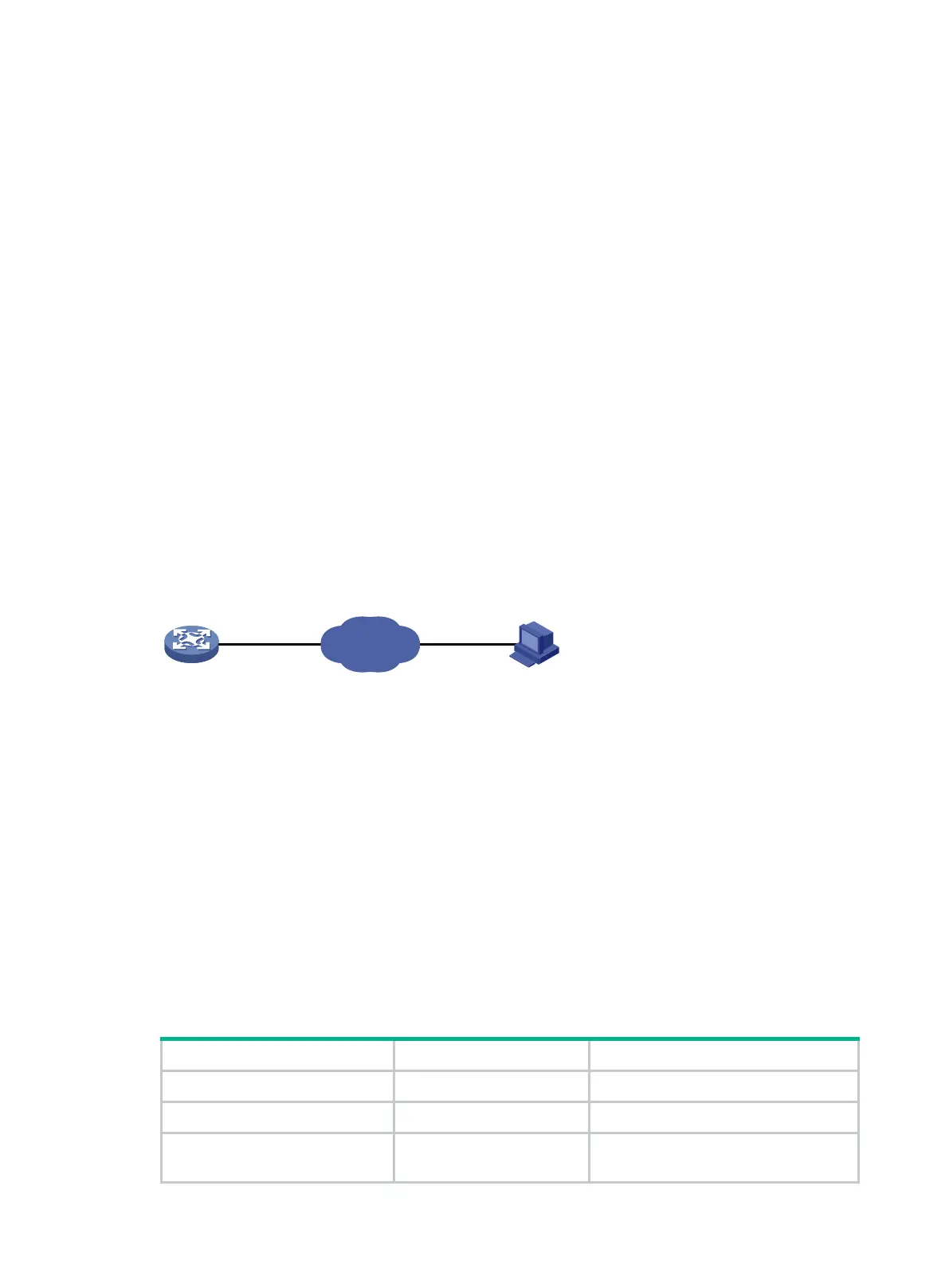
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is an application layer protocol based on the client/server model. It is
used to transfer files from one host to another over an IP network, as shown in Figure 26.
FTP server uses TCP port 20 to transfer data and TCP port 21 to transfer control commands. For
more information about FTP, see RFC 959.
FTP supports the following transfer modes:
Binary mode—Used to transfer image files, such as .app, .bin, and .btm files.
ASCII mode—Used to transfer text files, such as .txt, .bat, and .cfg files.
By default, the transfer mode is binary.
FTP can operate in either of the following modes:
Active mode (PORT)—The FTP server initiates the TCP connection. This mode is not suitable
when the FTP client is behind a firewall, for example, when the FTP client resides in a private
network.
Passive mode (PASV)—The FTP client initiates the TCP connection. This mode is not suitable
when the server does not allow the client to use a random unprivileged port greater than 1024.
The FTP operation mode varies by FTP client program.
The device can act as the FTP server or FTP client. Make sure the FTP server and the FTP client can
reach each other before establishing the FTP connection.
Figure 26 FTP application scenario
FIPS compliance
The device supports the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2 requirements. Support for
features, commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode and non-FIPS mode. For more
information about FIPS mode, see Security Configuration Guide.
FTP is not supported in FIPS mode.
Using the device as an FTP server
To use the device as an FTP server, you must enable the FTP server and configure authentication
and authorization on the device. Other commands are optional.
Configuring basic parameters
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enable the FTP server.
ftp server enable
By default, the FTP server is disabled.
3. (Optional.)
control access to the FTP
ftp server acl
{ acl-number |
ipv6
acl-number6 }
By default, no ACL is used for access
control.

 Loading...
Loading...



















