122 IBM z13s Technical Guide
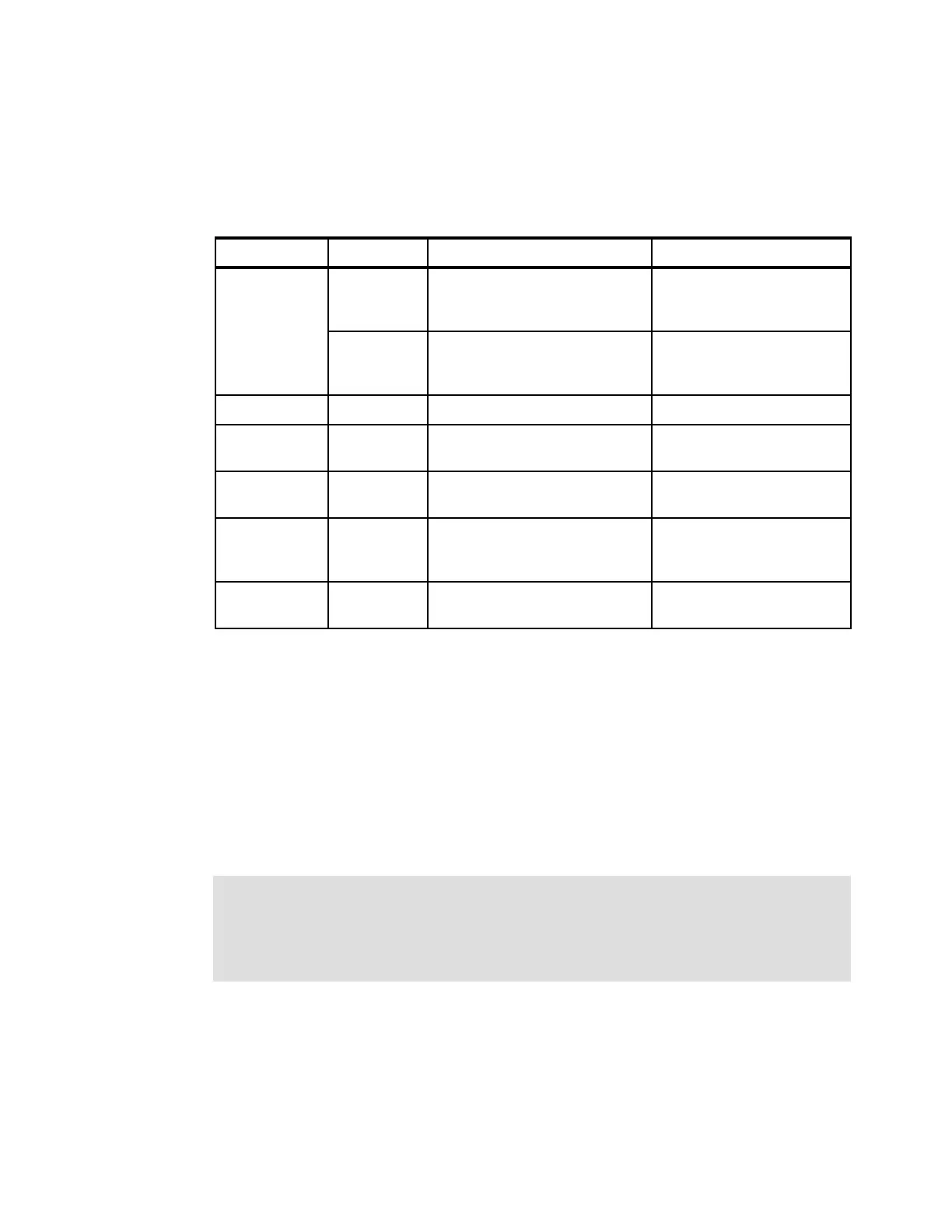
Table 3-5 shows all LPAR modes, required characterized PUs, operating systems, and the PU
characterizations that can be configured to an LPAR image. The available combinations of
dedicated (DED) and shared (SHR) processors are also shown. For all combinations, an
LPAR also can have reserved processors that are defined, allowing nondisruptive LPAR
upgrades.
Table 3-5 LPAR mode and PU usage
Dynamically adding or deleting a logical partition name
Dynamically adding or deleting an LPAR name is the ability to add or delete LPARs and their
associated I/O resources to or from the configuration without a POR.
The extra channel subsystem and multiple image facility (MIF) image ID pairs (CSSID/MIFID)
can be later assigned to an LPAR for use (or later removed). This process can be done
through dynamic I/O commands by using HCD. At the same time, required channels must be
defined for the new LPAR.
Adding logical processors to a logical partition
Logical processors can be concurrently added to an LPAR by defining them as reserved in
the image profile and later configuring them online to the operating system by using the
appropriate console commands. Logical processors can also be concurrently added to a
logical partition dynamically by using the Support Element “Logical Processor Add” function
under the “CPC Operational Customization” task. This SE function allows the initial and
reserved processor values to be dynamically changed. The operating system must support
LPAR mode PU type Operating systems PUs usage
ESA/390 CPs z/Architecture operating systems
ESA/390 operating systems
Linux on z Systems
CPs DED or CPs SHR
CPs
and
zIIPs
z/OS
z/VM (V6R2 and later for guest
exploitation)
CPs DED and (or) zIIPs DED
or
CPs SHR and (or) zIIPs SHR
ESA/390 TPF CPs z/TPF CPs DED or CPs SHR
Coupling
facility
ICFs or
CPs
CFCC ICFs DED or ICFs SHR, or
CPs DED or CPs SHR
Linux only IFLs
or CPs Linux on z Systems
z/VM
IFLs DED or IFLs SHR, or
CPs DED or CPs SHR
z/VM CPs, IFLs,
zIIPs, or
ICFs
z/VM (V6R2 and later) All PUs must be SHR or DED
zACI
a
a. z Appliance Container Infrastructure
IFLs, or CPs IBM zAware
b
IBM z/VSE Network Appliance
c
b. Encapsulated as a firmware appliance.
c. Planned
IFLs DED or IFLs SHR, or
CPs DED or CPs SHR
Partition profile: Cryptographic coprocessors are not tied to partition numbers or MIF IDs.
They are set up with Adjunct Processor (AP) numbers and domain indexes. These are
assigned to a partition profile of a given name. The client assigns these AP numbers and
domains to the partitions and continues to have the responsibility to clear them out when
their profiles change.

 Loading...
Loading...











