Filter
FILTER lets you set the filter response to stabilize noisy measurements. The Model 2000 uses
a digital filter, which is based on reading conversions. The displayed, stored, or transmitted read-
ing is simply an average of a number of reading conversions (from 1 to 100).
To select a filter:
1. Press FILTER once if the FILT annunciator is off; press twice if FILT is on.
2. Enter the number of readings.
3. Select the type of filter you want (moving average or repeating), then press ENTER.
The FILT annunciator turns on. When a filter is enabled, the selected filter configuration for
that measurement function is in effect.
Pressing FILTER once disables the filter.
NOTE
The filter can be set for any measurement function except frequency, period, continu-
ity, and diode test.
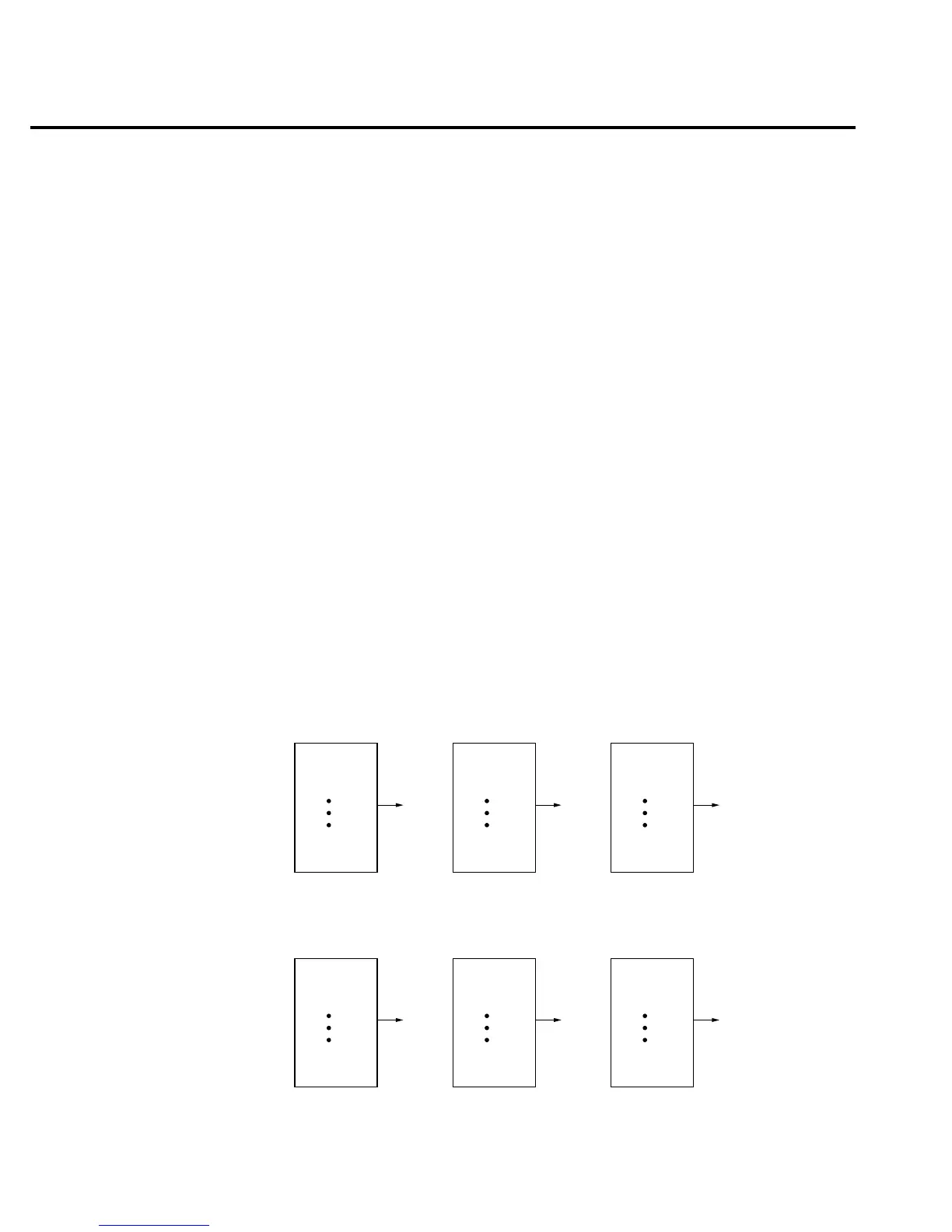
Filter types
The moving average filter uses a first-in, first-out stack. When the stack becomes full, the
measurement conversions are averaged, yielding a reading. For each subsequent conversion
placed into the stack, the oldest conversion is discarded, and the stack is re-averaged, yielding a
new reading.
For the repeating filter, the stack is filled and the conversions are averaged to yield a reading.
The stack is then cleared and the process starts over. Choose this filter for scanning so readings
from other channels are not averaged with the present channel.
Conversion #10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
Conversion #1
Reading
#1
A. Type - Moving Average, Readings = 10
Conversion #11
#10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
Conversion #2
Reading
#2
Conversion #12
#11
#10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
Conversion #3
Reading
#3
Conversion #10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
Conversion #1
Reading
#1
B. Type - Repeating, Readings = 10
Conversion #20
#19
#18
#17
#16
#15
#14
#13
#12
Conversion #11
Reading
#2
Conversion #30
#29
#28
#27
#26
#25
#24
#23
#22
Conversion #21
Reading
#3
3-4 Measurement Options
Figure 3-1
Moving average
and repeating fil-
ters
 Loading...
Loading...



