5
- 6
5.1 Basic Model QCPU
5.1.2 Program memory
5
MEMORIES AND FILES HANDLED BY CPU MODULE
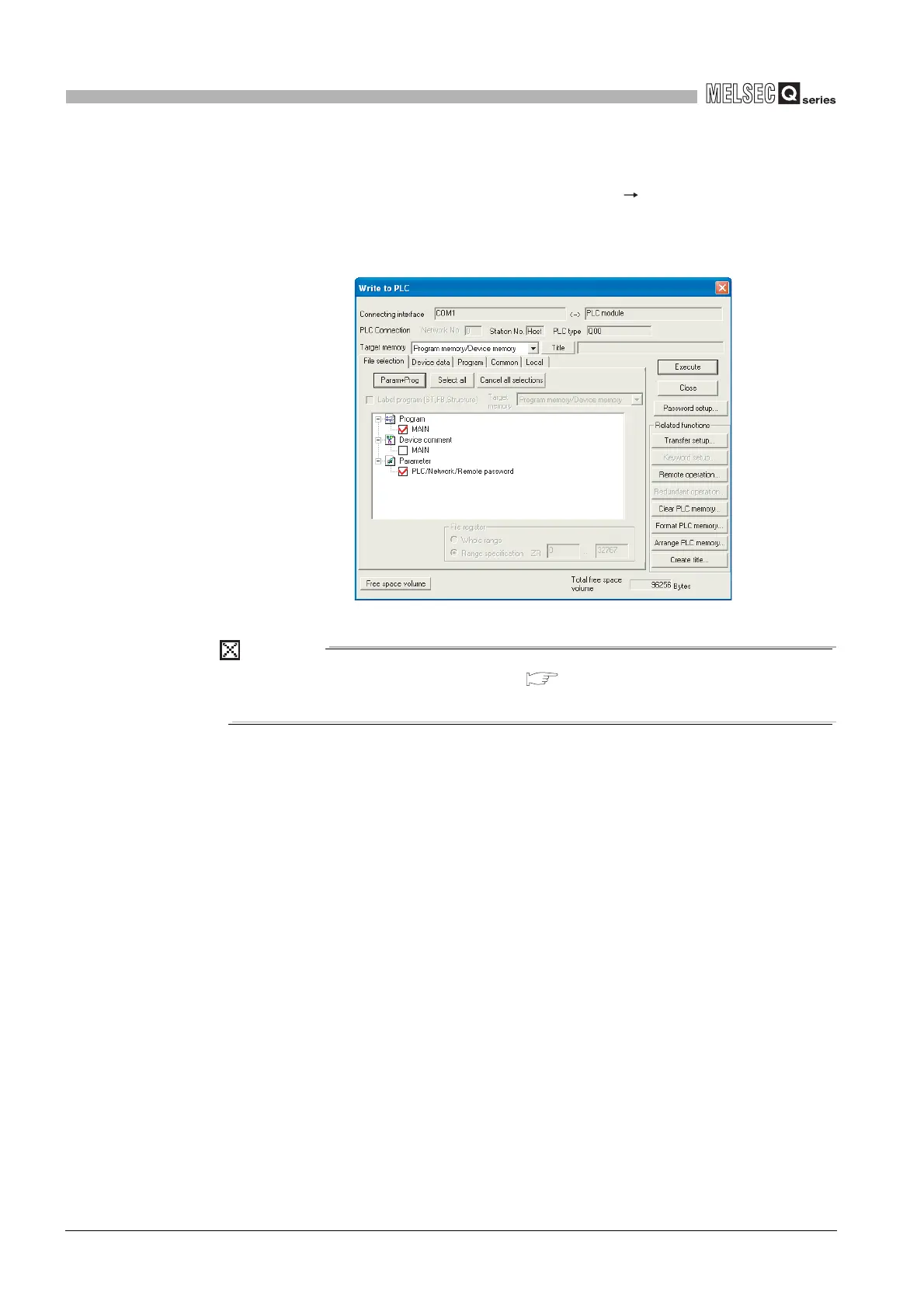
(4) Write to program memory
To write data to the program memory, choose [Online] [Write to PLC] on GX
Developer.
Select "Program memory/Device memory" as the target memory on the Write to PLC
screen and write data to the PLC.
POINT
The file size has the minimum unit. ( Section 5.4.4)
The occupied memory capacity may be greater than the actual file size.
Diagram 5.4 Write to PLC screen

 Loading...
Loading...











