5
MEMORIES AND FILES HANDLED BY CPU MODULE
5.2 High Performance Model QCPU, Process CPU and Redundant CPU
5.2.5 Memory card
5
- 29
1
Overview
2
Performance
Specification
3
Sequence Program
Configuration and
Execution Conditions
4
I/O Nunber Assignment
5
Memories and Files
Handled by CPU Module
6
Functions
7
Communication with
Intelligent Function
Module
8
Parameters
5.2.5 Memory card
(1) Memory card
A memory card is used to increase memories in addition to the built-in memory of the
High Performance model QCPU, Process CPU or Redundant CPU.
Available memory cards are the SRAM card, Flash card and ATA card.
(a) SRAM card
Data can be written/read by a sequence program.
The SRAM card is used in the following cases.
• When the number of file register points is greater than the standard RAM
capacity
• When using the sampling trace function ( Section 6.14)
• When saving 17 or more error history data ( Section 6.18)
When the SRAM card is used as file registers, a maximum of 1017k points can be
written/read by a sequence program.
(b) Flash card
Data can be read by a sequence program only.
Write data by GX Developer and read it by a sequence program.
Use the Flash card when data change will not be made.
It can store a maximum of 1018k points of file registers.
(c) ATA card
This is used for PLC user data (general-purpose data).
Using a file access instruction (such as the FWRITE instruction) in a sequence
program, access the PLC user data on the ATA card in CSV format/binary format.
(2) Storable data
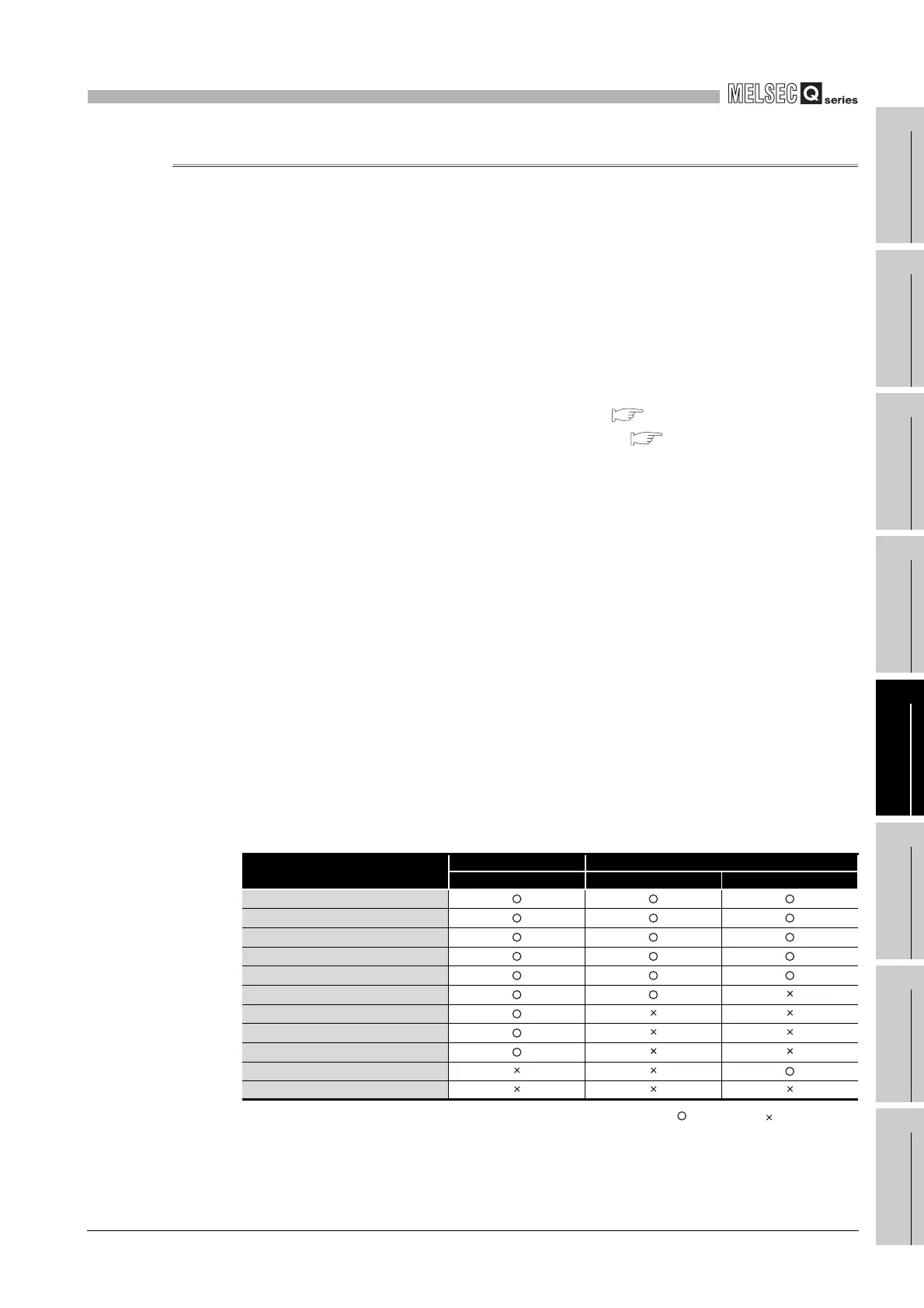
The following data indicated in Table5.7 can be stored into the memory cards.
: Storable data, : Unstorable data
Refer to Section 5.2.1(2) for the list of data that can be stored into each memory.
Table5.7 Data that can be stored into memory cards
Data name
Memory card (RAM) Memory cards (ROM)
SRAM card Flash card ATA card
Parameter
Intelligent function module parameter
Program
Device comment
Device initial value
File register
Local device
Sampling trace file
Failure history data
PLC user data
User setting system area

 Loading...
Loading...











