222
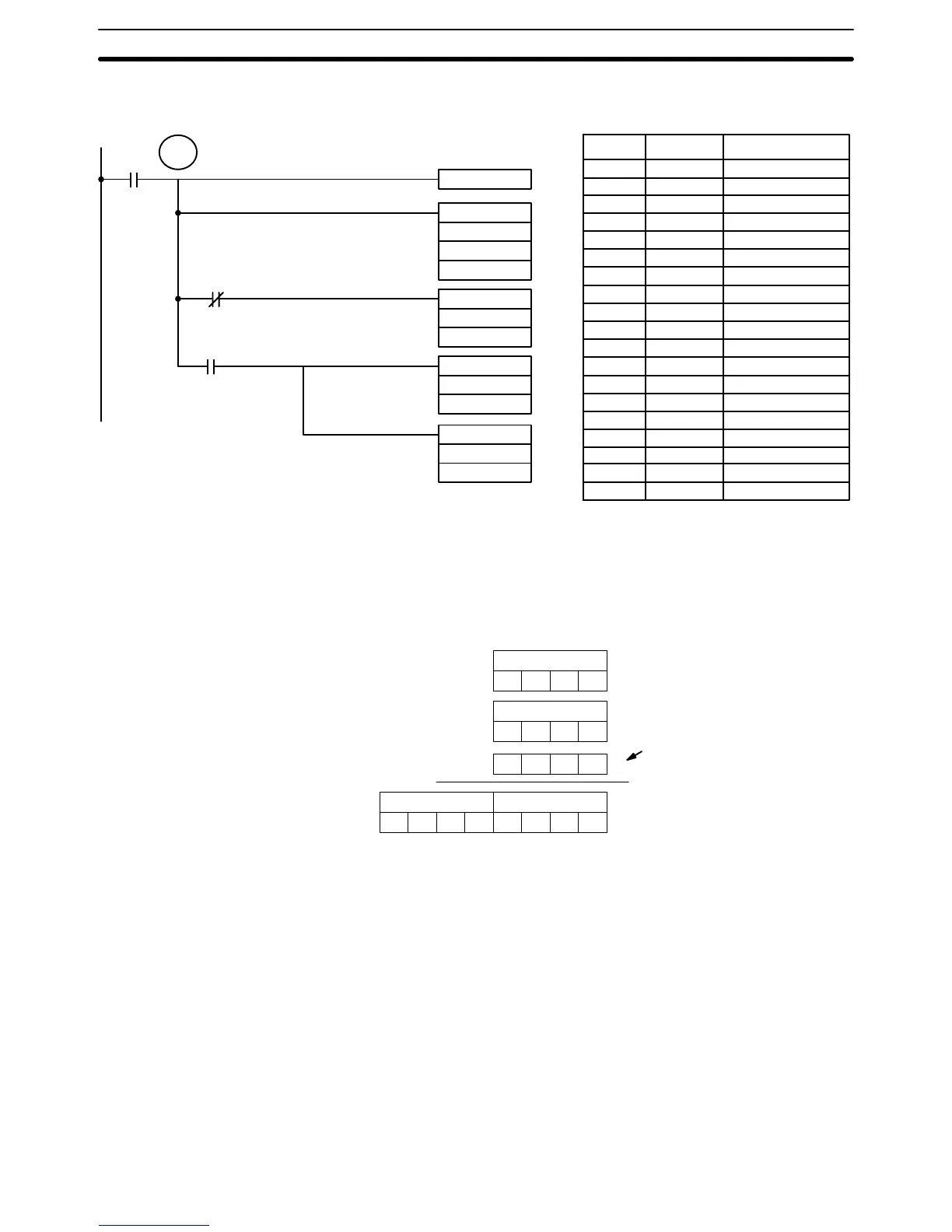
Example 1: Normal Data The
following example shows a four-digit subtraction with CY used to place ei
-
ther #0000 or #0001 into R+1 to ensure that any carry is preserved.
CLC(41)
00001
SBB(51)
001
LR20
HR 21
MOV(21)
#0000
HR 22
MOV(21)
#0001
HR 22
TR 1
25504
25504
= R
= R+1
= R+1
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00001
00001 OUT TR 1
00002 CLC(41)
00003 SBB(51)
001
LR 20
HR 21
00004 AND NOT 25504
00005 MOV(21)
# 0000
HR 22
00006 LD TR 1
00007 AND 25504
00008 MOV(21)
# 0001
HR 22
00009 NEG(––)
HR 21
HR 21
NEG(––)
HR21
HR 21
In the case below, the content of LR 20 (#7A03) and CY are subtracted from
IR 001
(#F8C5). The result is stored in HR 21 and the content of HR 22 (#0000)
indicates that the result is positive.
If the result had been negative, CY would have been set, #0001 would have
been
placed in HR 22, and the result would have been converted to its 2’
s com
-
pliment.
Mi: IR 001
F8C5
Su: LR 20
7A03
–
0000
–
CY = 0
(from CLC(41))
R: HR 21
7EC2
R+1: HR 22
0000
Note The
status of the UF and
OF flags can be ignored since they are relevant only in
the subtraction of signed binary data.
Binary Calculations Section 5-20
 Loading...
Loading...











