258
Description A subroutine can be executed by placing SBS(91) in the main program at the
point
where the subroutine is desired. The subroutine number used in SBS(91)
indicates
the desired subroutine. When
SBS(91) is executed (i.e., when the ex
-
ecution condition for it is ON), the instructions between the SBN(92) with the
same
subroutine number and the first RET(93) after it are executed before
ex
-
ecution returns to the instruction following the SBS(91) that made the call.
SBS(91) 00
SBN(92) 00
RET(93)
END(01)
Main program
Subroutine
Main program
SBS(91)
may be used
as many times as desired in the program, i.e., the same
subroutine may be called from different places in the program).
SBS(91)
may also be placed into a subroutine to shift program execution from
one subroutine to another, i.e., subroutines may be nested. When the second
subroutine
has been completed (i.e., RET(93) has been reached), program ex
-
ecution
returns to the original subroutine which is then
completed before return
-
ing
to the main program. Nesting is possible to up to sixteen levels. A subroutine
cannot call itself (e.g., SBS(91) 00 cannot be programmed within
the
subroutine
defined
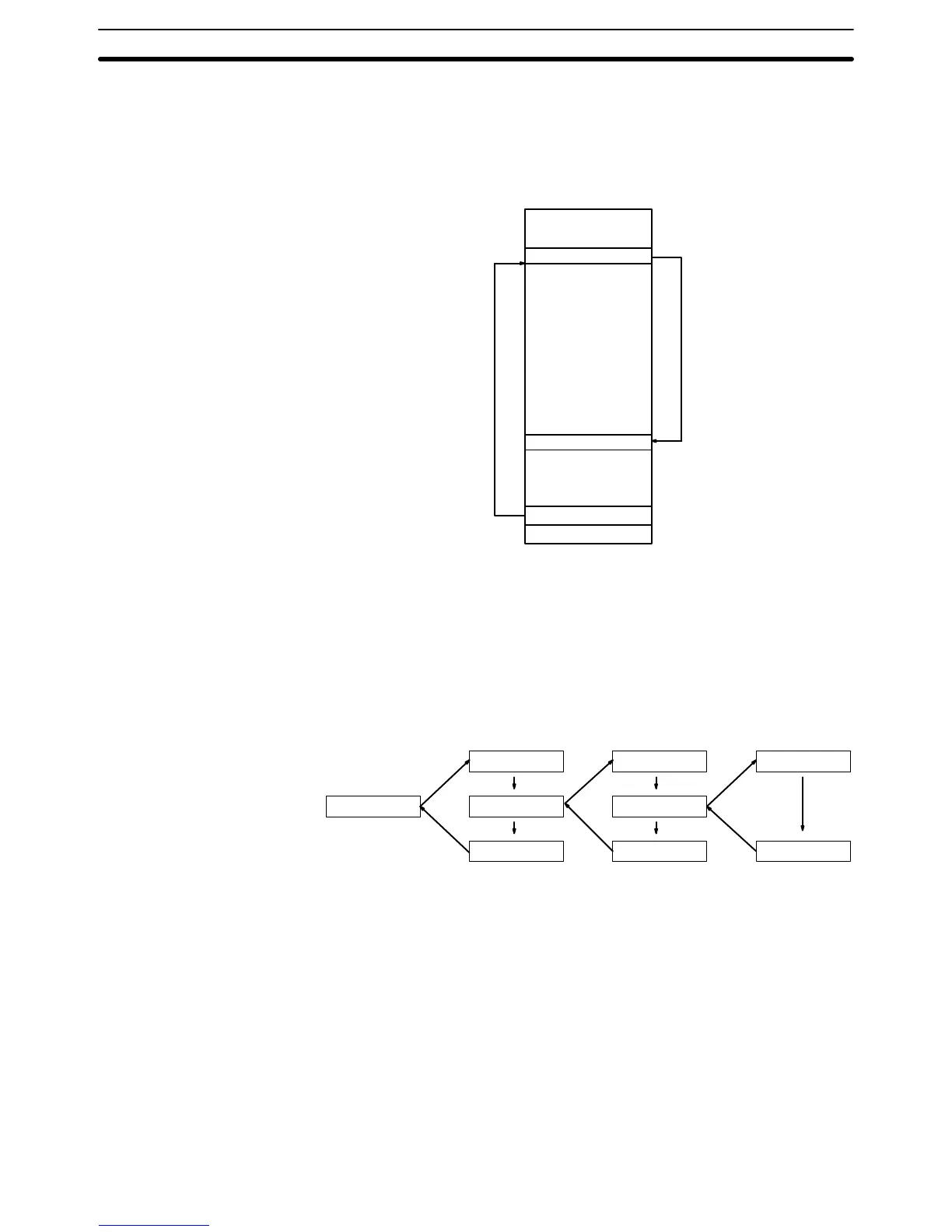
with SBN(92) 00). The following diagram illustrates two levels of nesting.
SBN(92)
10
SBN(92) 1
1
SBN(92) 12
SBS(91) 1
1
RET(93)
SBS(91) 10 SBS(91) 12
RET(93) RET(93)
Subroutines and Interrupt Control Section 5-23
 Loading...
Loading...











